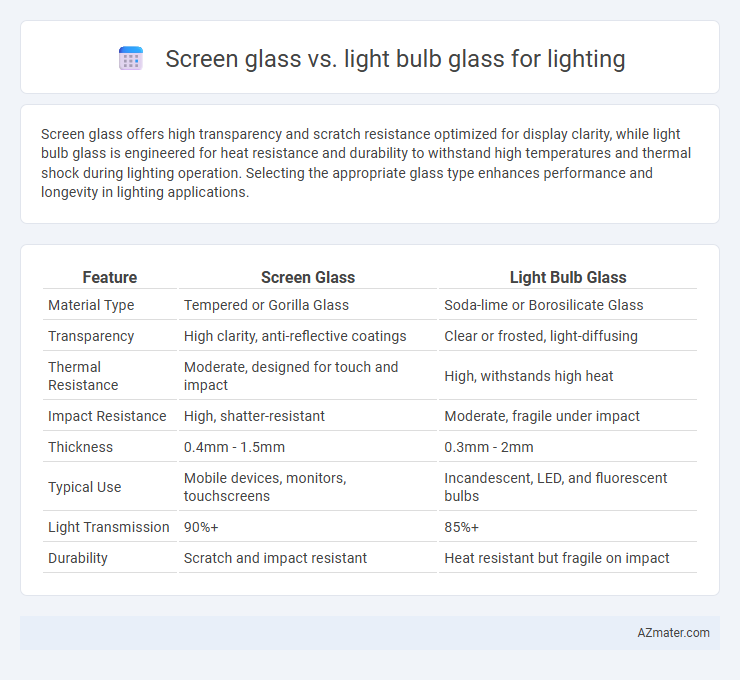
Screen glass offers high transparency and scratch resistance optimized for display clarity, while light bulb glass is engineered for heat resistance and durability to withstand high temperatures and thermal shock during lighting operation. Selecting the appropriate glass type enhances performance and longevity in lighting applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Screen Glass | Light Bulb Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Tempered or Gorilla Glass | Soda-lime or Borosilicate Glass |
| Transparency | High clarity, anti-reflective coatings | Clear or frosted, light-diffusing |
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate, designed for touch and impact | High, withstands high heat |
| Impact Resistance | High, shatter-resistant | Moderate, fragile under impact |
| Thickness | 0.4mm - 1.5mm | 0.3mm - 2mm |
| Typical Use | Mobile devices, monitors, touchscreens | Incandescent, LED, and fluorescent bulbs |
| Light Transmission | 90%+ | 85%+ |
| Durability | Scratch and impact resistant | Heat resistant but fragile on impact |
Introduction to Lighting Glass Types
Screen glass and light bulb glass serve distinct purposes in lighting applications, with screen glass designed for durability and clarity in protection and light diffusion, while light bulb glass focuses on heat resistance and light transmission efficiency. Screen glass often features specialized coatings to reduce glare and enhance visibility, making it essential for devices like smartphones and monitors. Light bulb glass varies in thickness and composition, optimized to withstand high temperatures and maintain brightness in different lighting environments.
What is Screen Glass?
Screen glass is a specialized type of glass used primarily in lighting fixtures to diffuse light evenly, reducing glare and enhancing visual comfort. Unlike light bulb glass, which is designed to contain and protect the filament or LED components while withstanding high temperatures, screen glass often features a textured or frosted surface that scatters light for softer illumination. This makes screen glass ideal for applications requiring ambient lighting and aesthetic appeal, such as lamp covers, panel lights, and architectural fixtures.
What is Light Bulb Glass?
Light bulb glass is a specially designed material that encases the filament or LED components, providing protection and ensuring light diffusion while withstanding high temperatures. Unlike screen glass, which emphasizes clarity and touch sensitivity for displays, light bulb glass prioritizes heat resistance, durability, and optical qualities to optimize illumination. This glass type often includes coatings or treatments to enhance brightness and energy efficiency in various lighting applications.
Key Material Differences
Screen glass for lighting applications is engineered with high transparency and durability, often incorporating anti-reflective coatings and tempered properties to withstand impact and heat. Light bulb glass, typically made from soda-lime glass or borosilicate glass, is designed to endure extreme thermal stress and prevent breakage under rapid temperature changes. The key material difference lies in the thermal resistance and mechanical strength, where light bulb glass offers superior heat tolerance, while screen glass prioritizes optical clarity and surface hardness.
Light Transmission Properties
Screen glass typically offers higher light transmission than light bulb glass, allowing more natural and artificial light to pass through with minimal diffusion. Light bulb glass is engineered to diffuse light evenly, reducing glare and creating a softer illumination by scattering light through its frosted or coated surface. The choice between screen glass and light bulb glass hinges on the desired balance between maximum light transmission and controlled light diffusion for specific lighting applications.
Durability and Heat Resistance
Screen glass used in lighting fixtures typically offers higher durability and superior heat resistance compared to standard light bulb glass, making it ideal for environments with frequent temperature fluctuations. Screen glass is often treated or laminated to withstand impacts and thermal stress, whereas traditional light bulb glass is thinner and more prone to cracking under heat exposure. The enhanced durability and heat resistance of screen glass extend the lifespan of lighting units and improve safety in applications requiring robust thermal management.
Optical Performance in Lighting Applications
Screen glass in lighting applications offers superior optical clarity and minimal light diffusion, enhancing the precision of light distribution. Light bulb glass, typically designed for durability and heat resistance, often exhibits higher light scattering, which softens illumination but reduces optical efficiency. Optimizing lighting systems depends on selecting glass types that balance transmission, diffusion, and durability to achieve desired luminous performance.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Screen glass for lighting applications typically costs more than standard light bulb glass due to its specialized coatings and durability features designed to diffuse or filter light effectively. Light bulb glass is widely available and produced in large quantities, making it more affordable and accessible for mass production and replacement needs. The cost difference is influenced by manufacturing complexity and market demand, with screen glass being less common and often sourced from niche suppliers, impacting availability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Screen glass used in lighting fixtures offers a more sustainable option due to its higher recyclability and lower energy consumption during manufacture compared to traditional light bulb glass. Light bulb glass often contains additives like borosilicate or lead, which complicate recycling processes and contribute to environmental pollution if not properly disposed of. Choosing screen glass helps reduce carbon footprints by enabling longer product lifespans and easier integration into circular economy models.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Lighting Needs
Screen glass offers enhanced durability and scratch resistance, making it ideal for lighting fixtures exposed to outdoor elements or frequent handling. Light bulb glass, typically made from heat-resistant borosilicate or soda-lime glass, provides optimal clarity and thermal stability essential for efficient light diffusion and heat dissipation. Selecting the right glass depends on factors like environmental exposure, desired light quality, and heat tolerance to ensure longevity and performance in your lighting setup.
Infographic: Screen glass vs Light bulb glass for Lighting
 azmater.com
azmater.com