Smart glass for eyewear dynamically tints in response to electrical signals, providing instant light adjustment and UV protection. Photochromic glass darkens gradually when exposed to UV rays, offering passive sun protection but slower transition times.
Table of Comparison
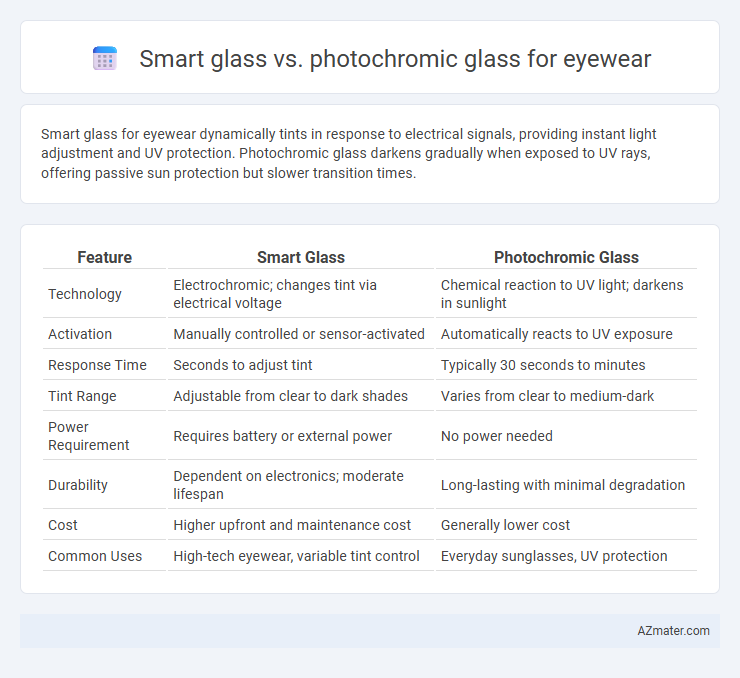
| Feature | Smart Glass | Photochromic Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Electrochromic; changes tint via electrical voltage | Chemical reaction to UV light; darkens in sunlight |
| Activation | Manually controlled or sensor-activated | Automatically reacts to UV exposure |
| Response Time | Seconds to adjust tint | Typically 30 seconds to minutes |
| Tint Range | Adjustable from clear to dark shades | Varies from clear to medium-dark |
| Power Requirement | Requires battery or external power | No power needed |
| Durability | Dependent on electronics; moderate lifespan | Long-lasting with minimal degradation |
| Cost | Higher upfront and maintenance cost | Generally lower cost |
| Common Uses | High-tech eyewear, variable tint control | Everyday sunglasses, UV protection |
Introduction to Smart Glass and Photochromic Glass
Smart glass for eyewear utilizes advanced technologies like electrochromic or liquid crystal systems to adjust tint levels instantly when activated by electrical signals, offering customizable light control and reducing glare. Photochromic glass contains molecules that chemically react to ultraviolet (UV) light, darkening automatically outdoors and reverting indoors without electrical input, providing seamless transition between lighting conditions. Both types enhance visual comfort and UV protection but differ in activation mechanisms, response speed, and energy requirements.
How Smart Glass Works in Eyewear
Smart glass in eyewear uses electrochromic technology to change tint when an electrical current is applied, allowing users to control light transmission actively. This adaptive feature provides instant darkening or lightening based on user input or environmental conditions, enhancing visual comfort and energy efficiency. Unlike photochromic glass, which relies on UV light to trigger color changes gradually, smart glass offers precise, on-demand modulation of lens opacity.
How Photochromic Glass Functions in Eyewear
Photochromic glass functions in eyewear by undergoing a chemical reaction when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light, causing the lenses to darken automatically while brightening in low-light conditions. This adaptive change is due to molecules embedded in the glass that alter their structure in response to UV radiation, providing seamless protection from glare and UV rays. Unlike smart glass, which relies on electronic controls to adjust opacity, photochromic lenses offer a passive, energy-free transition ideal for everyday outdoor wear.
Key Differences Between Smart Glass and Photochromic Glass
Smart glass for eyewear uses electronic tinting technology, allowing users to control light transmission through a connected device or automatic sensors, providing instant adaptability to changing light conditions. Photochromic glass relies on chemical compounds embedded in the lenses that react to ultraviolet (UV) light, darkening outdoors and returning to clear indoors without electronic input. Key differences include response time, with smart glass offering near-instant transitions, and power dependency, as smart glass requires a power source while photochromic glass operates passively on UV exposure.
Advantages of Smart Glass Eyewear
Smart glass eyewear offers superior adaptability by electronically adjusting tint levels instantly to varying light conditions, providing enhanced visual comfort and protection against glare and UV rays. Unlike photochromic glass, which relies on chemical reactions triggered by UV exposure and may be slower to change, smart glass delivers precise control via user settings or sensors. This technology extends battery life in wearable devices, improves style versatility, and supports integration with augmented reality features.
Benefits of Photochromic Glass Eyewear
Photochromic glass eyewear offers automatic light adjustment, darkening on exposure to UV rays and thus enhancing visual comfort and reducing eye strain. These lenses provide convenience by eliminating the need to switch between regular glasses and sunglasses, making them ideal for varied lighting conditions. Their UV protection also helps guard against harmful solar radiation, promoting long-term eye health.
Limitations of Smart Glass for Eyewear
Smart glass for eyewear often faces limitations such as higher power consumption and reliance on electrical components, which can lead to bulkier designs and reduced battery life. The complexity of integrating smart technology into lightweight, comfortable frames remains a challenge, impacting user experience. In contrast, photochromic glass naturally adjusts to lighting conditions without power, offering a more seamless and maintenance-free solution.
Drawbacks of Photochromic Glass Lenses
Photochromic glass lenses often struggle with slow reaction times, especially in changing light conditions, leading to inconsistent tinting that can impair vision. They typically underperform in hot weather, as high temperatures can prevent full darkening, reducing their effectiveness outdoors. Additionally, photochromic lenses may not darken adequately inside vehicles due to UV-blocking windshields, limiting their convenience for drivers.
Ideal Use Cases: Choosing the Right Glass for Your Needs
Smart glass is ideal for dynamic environments where instant light modulation and privacy control are needed, such as office settings and smart homes, offering on-demand tint adjustment via electronic control. Photochromic glass suits outdoor and everyday wear, automatically darkening in response to UV light, making it perfect for transitioning between indoor and outdoor use without manual intervention. Selecting between these technologies depends on lifestyle demands: choose smart glass for customizable, rapid changes and photochromic glass for seamless, automatic adaptation to sunlight.
Future Trends in Eyewear Technology
Smart glass and photochromic glass represent two groundbreaking technologies advancing the future of eyewear, with smart glass offering dynamic tint adjustment controlled electronically for instant adaptation to changing light conditions, while photochromic glass relies on chemical reactions to UV exposure for gradual darkening and lightening. Emerging trends in smart glass integrate AI and IoT connectivity, enabling personalized vision experiences and seamless compatibility with other smart devices, whereas innovations in photochromic technology focus on faster response times and enhanced UV protection. Both technologies are converging toward hybrid eyewear solutions that combine real-time adaptability and energy efficiency, promising unprecedented comfort and functionality for users in diverse environments.
Infographic: Smart glass vs Photochromic glass for Eyewear
 azmater.com
azmater.com