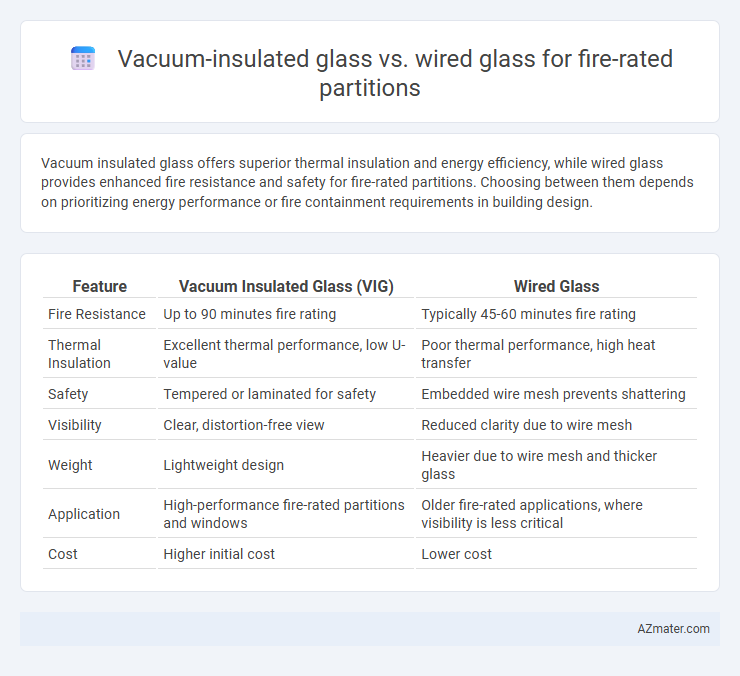
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation and energy efficiency, while wired glass provides enhanced fire resistance and safety for fire-rated partitions. Choosing between them depends on prioritizing energy performance or fire containment requirements in building design.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vacuum Insulated Glass (VIG) | Wired Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | Up to 90 minutes fire rating | Typically 45-60 minutes fire rating |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent thermal performance, low U-value | Poor thermal performance, high heat transfer |
| Safety | Tempered or laminated for safety | Embedded wire mesh prevents shattering |
| Visibility | Clear, distortion-free view | Reduced clarity due to wire mesh |
| Weight | Lightweight design | Heavier due to wire mesh and thicker glass |
| Application | High-performance fire-rated partitions and windows | Older fire-rated applications, where visibility is less critical |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost |
Understanding Fire-Rated Partitions
Fire-rated partitions use specialized glass like vacuum insulated glass (VIG) and wired glass to maintain safety and thermal performance during fires. Vacuum insulated glass offers superior insulation and clarity but requires precise engineering to meet fire-resistance standards, while wired glass provides enhanced heat resistance and structural integrity by embedding wire mesh to prevent breakage and fire spread. Selecting the appropriate fire-rated glass depends on balancing thermal insulation, visibility, and compliance with fire safety codes for partitions in buildings.
What is Vacuum Insulated Glass (VIG)?
Vacuum Insulated Glass (VIG) consists of two glass panes separated by a vacuum space, significantly reducing heat transfer through conduction and convection, which enhances its thermal insulation performance in fire-rated partitions. Unlike Wired Glass, which contains embedded wire mesh to maintain integrity during fire exposure, VIG provides superior clarity and energy efficiency while maintaining fire resistance due to its vacuum gap that limits heat flow. VIG panels are increasingly used in modern fire-rated systems for their combination of thermal insulation, fire protection, and aesthetic appeal.
Overview of Wired Glass Construction
Wired glass consists of a single glass pane embedded with a metal wire mesh that enhances its integrity during high-temperature exposure, preventing shattering and maintaining a fire barrier. This mesh acts as a reinforcement, allowing the glass to withstand fire for specified durations, typically 45 to 90 minutes, making it suitable for fire-rated partitions in commercial and industrial buildings. Its construction prioritizes safety and visibility, balancing fire resistance with the need for see-through partitions in fire-rated assemblies.
Fire Resistance: VIG vs Wired Glass
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) offers superior thermal insulation but generally lacks the high fire resistance properties of wired glass, which is specifically designed to withstand intense heat and prevent fire spread in fire-rated partitions. Wired glass contains embedded metal mesh that maintains structural integrity under fire conditions, providing effective fire resistance and safety. VIG is better suited for energy efficiency applications, while wired glass remains the preferred choice for fire-rated partitions requiring stringent fire performance standards.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal performance compared to wired glass in fire-rated partitions due to its low thermal conductivity and minimal heat transfer properties. The vacuum gap between glass panes significantly reduces heat transmission, enhancing insulation and maintaining structural integrity under fire conditions. Conversely, wired glass has higher thermal conductivity, leading to greater heat passage and less effective thermal resistance in fire scenarios.
Safety Considerations in Fire-Rated Applications
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation and maintains structural integrity under high temperatures, reducing heat transfer and enhancing fire safety in fire-rated partitions. Wired glass, embedded with metal mesh, prevents glass shattering by holding fragments in place during fire exposure, providing a reliable barrier against flames and smoke. Prioritizing safety in fire-rated applications requires assessing both thermal performance and impact resistance to comply with fire code regulations and protect occupants effectively.
Acoustic Insulation Differences
Vacuum insulated glass provides superior acoustic insulation compared to wired glass, thanks to its hermetically sealed air gap that effectively reduces sound transmission. Wired glass, commonly used for fire-rated partitions, typically lacks the soundproofing benefits due to its single-pane construction and embedded wire mesh, which can allow more noise to pass through. Therefore, vacuum insulated glass is preferred in environments where both fire safety and high acoustic performance are critical.
Aesthetic and Design Flexibility
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) offers superior aesthetic appeal for fire-rated partitions due to its sleek, frameless design and high transparency, allowing maximum light transmission and unobstructed views. Wired glass, while traditionally favored for fire safety, compromises on design flexibility with its embedded metal mesh, which can appear visually intrusive and reduce clarity. The slim profile and customization options of vacuum insulated glass enable architects to achieve modern, minimalist interiors without sacrificing fire protection standards.
Cost and Installation Factors
Vacuum insulated glass typically incurs higher upfront costs compared to wired glass due to advanced manufacturing processes and materials, but offers superior thermal insulation and soundproofing for fire-rated partitions. Wired glass is generally more cost-effective and easier to install, with established compatibility for fire safety codes, making it a preferred choice in budget-sensitive projects. Installation of vacuum insulated glass requires specialized handling and skilled labor to maintain the vacuum seal integrity, whereas wired glass benefits from simpler glazing methods and faster on-site installation times.
Choosing the Right Glass for Fire-Rated Partitions
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation and clarity but lacks the fire-resistant properties required for fire-rated partitions, making wired glass the preferred choice due to its embedded metal mesh that maintains glass integrity under high temperatures. Wired glass complies with many fire safety codes, providing a barrier that prevents flame and smoke spread during fires, whereas vacuum insulated glass primarily focuses on energy efficiency rather than fire performance. Selecting wired glass ensures compliance with fire-rated partition standards while maintaining safety and visibility in critical building areas.
Infographic: Vacuum insulated glass vs Wired glass for Fire-rated partition
 azmater.com
azmater.com