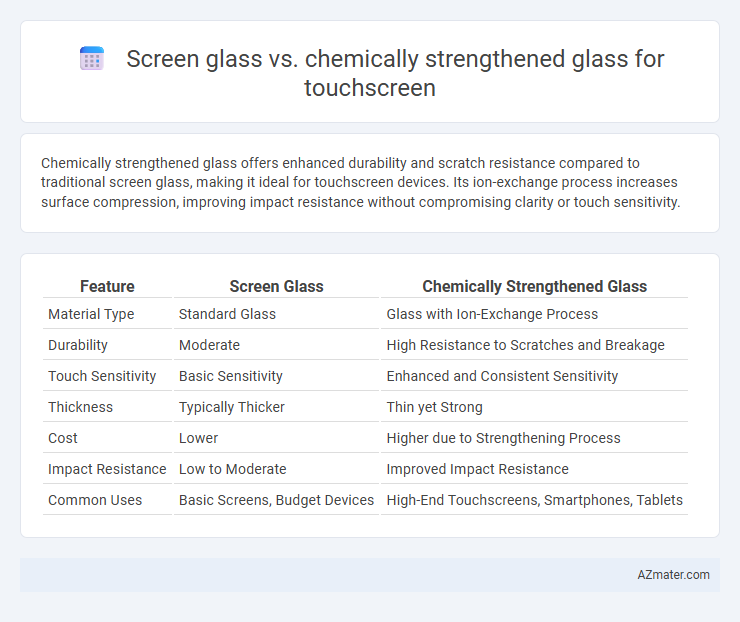
Chemically strengthened glass offers enhanced durability and scratch resistance compared to traditional screen glass, making it ideal for touchscreen devices. Its ion-exchange process increases surface compression, improving impact resistance without compromising clarity or touch sensitivity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Screen Glass | Chemically Strengthened Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Standard Glass | Glass with Ion-Exchange Process |
| Durability | Moderate | High Resistance to Scratches and Breakage |
| Touch Sensitivity | Basic Sensitivity | Enhanced and Consistent Sensitivity |
| Thickness | Typically Thicker | Thin yet Strong |
| Cost | Lower | Higher due to Strengthening Process |
| Impact Resistance | Low to Moderate | Improved Impact Resistance |
| Common Uses | Basic Screens, Budget Devices | High-End Touchscreens, Smartphones, Tablets |
Introduction to Touchscreen Glass Technologies
Touchscreen glass technologies primarily utilize either standard screen glass or chemically strengthened glass, each offering distinct advantages in durability and responsiveness. Chemically strengthened glass, such as aluminosilicate glass, undergoes an ion-exchange process that significantly enhances its resistance to scratches and impact compared to regular screen glass. This advanced strengthening capability makes chemically strengthened glass a preferred choice for modern touchscreen devices requiring high performance and longevity.
What is Standard Screen Glass?
Standard screen glass, commonly used in touchscreens, is typically made from soda-lime or aluminosilicate glass, offering basic protection against scratches and minor impacts. Chemically strengthened glass undergoes an ion-exchange process that enhances its surface compression, significantly boosting scratch resistance and durability compared to standard glass. This treatment makes chemically strengthened glass particularly suitable for high-use devices, providing improved longevity and improved resistance to damage while maintaining transparency and touch sensitivity.
Understanding Chemically Strengthened Glass
Chemically strengthened glass undergoes an ion-exchange process that replaces smaller sodium ions with larger potassium ions, creating a compressive stress layer on the surface that significantly enhances its strength and scratch resistance compared to standard screen glass. This ion-exchange method allows chemically strengthened glass to better withstand impacts and pressure, making it ideal for durable touchscreen applications such as smartphones, tablets, and interactive displays. Unlike tempered glass, chemically strengthened glass maintains high optical clarity and touch sensitivity while providing improved resistance to cracks and shattering in everyday use.
Key Differences: Screen Glass vs Chemically Strengthened Glass
Screen glass typically refers to standard glass used in display devices, offering basic protection and clarity but limited resistance to scratches and impacts. Chemically strengthened glass, such as aluminosilicate glass, undergoes an ion-exchange process that enhances surface compression, resulting in significantly improved durability, scratch resistance, and shatter toughness ideal for touchscreen devices. Key differences include the chemical strengthening process, higher mechanical strength, and superior resistance to damage in chemically strengthened glass compared to regular screen glass.
Durability and Scratch Resistance Comparison
Screen glass and chemically strengthened glass differ significantly in durability and scratch resistance for touchscreen applications. Chemically strengthened glass undergoes ion exchange treatment, enhancing surface compression to resist scratches and impacts better than standard screen glass. This process results in superior mechanical strength, making chemically strengthened glass more durable against daily wear and accidental drops compared to untreated screen glass.
Impact on Touch Sensitivity and Display Clarity
Screen glass used in touchscreens often balances durability with maximum touch sensitivity, ensuring accurate and responsive user interactions by maintaining optimal capacitance levels. Chemically strengthened glass, such as aluminosilicate glass, undergoes ion exchange processes that enhance surface hardness and impact resistance without significantly compromising the glass's transparency or touch responsiveness. This treatment preserves display clarity by minimizing surface distortions and enhances touch sensitivity by maintaining a smooth, uniform surface conducive to precise capacitive detection.
Cost Implications for Manufacturers and Consumers
Screen glass tends to be less expensive to produce compared to chemically strengthened glass, reducing initial manufacturing costs for touchscreen devices. Chemically strengthened glass, such as Gorilla Glass, offers higher durability and scratch resistance, which can lower warranty claims and replacement rates, providing long-term cost savings for manufacturers and consumers. Consumers may pay a premium upfront for devices with chemically strengthened glass but benefit from enhanced durability and longer device lifespan, offsetting the initial cost difference.
Applications in Consumer Electronics
Screen glass commonly used in consumer electronics relies on tempered glass to provide durability and scratch resistance for touchscreens in smartphones, tablets, and laptops. Chemically strengthened glass, such as Gorilla Glass, offers superior hardness and enhanced resistance to cracks and impacts, making it a preferred choice for high-end devices and wearables. Advances in chemical strengthening processes enable thinner, lighter glass panels without compromising touchscreen sensitivity or optical clarity, improving overall user experience.
Selecting the Right Glass for Your Device
Selecting the right glass for your touchscreen involves understanding the durability and responsiveness differences between screen glass and chemically strengthened glass. Chemically strengthened glass offers enhanced scratch resistance and higher impact tolerance due to ion-exchange processes, making it ideal for devices exposed to frequent use and harsh environments. Screen glass, while generally less robust, provides sufficient clarity and touch sensitivity for everyday applications, balancing cost and performance effectively.
Future Trends in Touchscreen Glass Technology
Chemically strengthened glass, such as Gorilla Glass, dominates the touchscreen market due to its enhanced scratch resistance and impact durability compared to traditional screen glass. Future trends in touchscreen glass technology emphasize the integration of ultra-thin, flexible, and self-healing materials that improve user experience while maintaining touch sensitivity and clarity. Advances in nanotechnology and ion-exchange processes will drive the development of next-generation chemically strengthened glass that supports foldable and rollable displays with superior durability.
Infographic: Screen glass vs Chemically strengthened glass for Touchscreen
 azmater.com
azmater.com