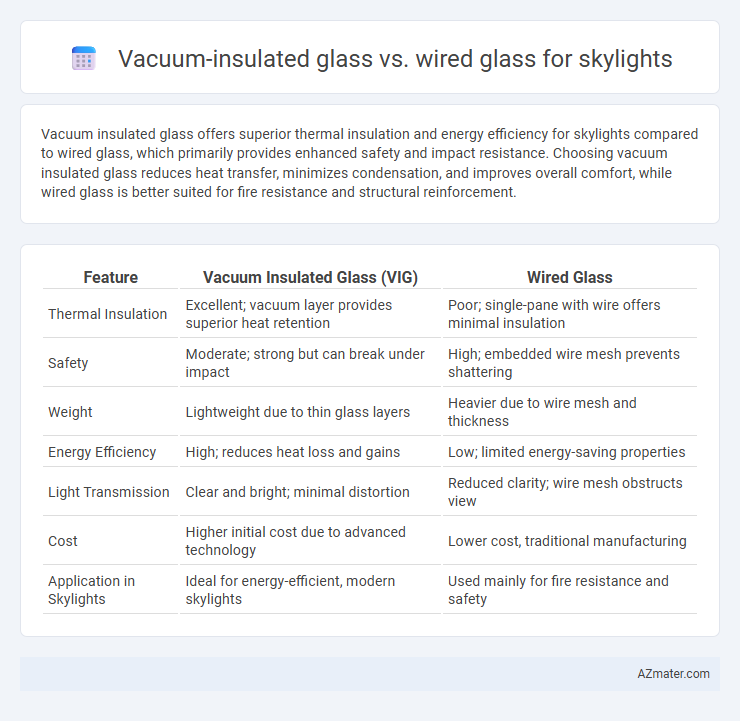
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation and energy efficiency for skylights compared to wired glass, which primarily provides enhanced safety and impact resistance. Choosing vacuum insulated glass reduces heat transfer, minimizes condensation, and improves overall comfort, while wired glass is better suited for fire resistance and structural reinforcement.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vacuum Insulated Glass (VIG) | Wired Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent; vacuum layer provides superior heat retention | Poor; single-pane with wire offers minimal insulation |
| Safety | Moderate; strong but can break under impact | High; embedded wire mesh prevents shattering |
| Weight | Lightweight due to thin glass layers | Heavier due to wire mesh and thickness |
| Energy Efficiency | High; reduces heat loss and gains | Low; limited energy-saving properties |
| Light Transmission | Clear and bright; minimal distortion | Reduced clarity; wire mesh obstructs view |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to advanced technology | Lower cost, traditional manufacturing |
| Application in Skylights | Ideal for energy-efficient, modern skylights | Used mainly for fire resistance and safety |
Understanding Skylight Glazing: Key Considerations
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation and energy efficiency for skylight glazing, reducing heat transfer and condensation compared to wired glass, which is primarily designed for safety and fire resistance. Wired glass incorporates embedded wire mesh that prevents glass shattering but compromises thermal performance and clarity, making it less ideal for skylights seeking optimal daylight and energy savings. Selecting the right glazing involves balancing energy efficiency, safety standards, and visual comfort to meet building codes and occupant needs.
What Is Vacuum Insulated Glass?
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) consists of two glass panes separated by a vacuum space that significantly reduces heat transfer, providing superior thermal insulation for skylights compared to traditional glass types. Unlike wired glass, which incorporates a metal mesh for safety but often compromises clarity and insulation, VIG offers enhanced energy efficiency and clear visibility without added weight. Its vacuum layer minimizes conduction and convection, making it an ideal choice for maintaining indoor temperature and reducing energy consumption in skylight applications.
What Is Wired Glass?
Wired glass is a type of safety glass that incorporates a mesh of thin metal wires embedded within the glass, providing enhanced fire resistance and preventing shattering during extreme heat or impact. Unlike vacuum insulated glass, which prioritizes thermal insulation through a vacuum seal to reduce heat transfer, wired glass primarily focuses on safety and fire protection in skylight applications. The internal wire mesh maintains structural integrity under high temperatures, making wired glass suitable for fire-rated skylights where safety and code compliance are critical.
Thermal Performance: VIG vs. Wired Glass
Vacuum Insulated Glass (VIG) offers superior thermal performance compared to wired glass due to its advanced insulating properties, which significantly reduce heat transfer and improve energy efficiency in skylights. The vacuum layer in VIG minimizes conduction and convection, resulting in a lower U-value and enhanced thermal insulation to maintain indoor comfort. Wired glass, while providing safety benefits, has higher thermal conductivity and lower insulation values, leading to greater heat loss and reduced energy performance in skylight applications.
Safety and Security Comparison
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior safety and security for skylights due to its laminated construction and enhanced impact resistance, reducing the risk of breakage and injury. Wired glass, while fire-resistant and providing some security benefits, is more prone to shattering upon impact, posing potential hazards. The advanced technology in vacuum insulated glass ensures better protection against forced entry and environmental stress, making it a safer choice for modern skylight installations.
Light Transmission and Clarity
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior light transmission compared to wired glass, allowing up to 90% of natural daylight to pass through with minimal distortion, enhancing clarity in skylight applications. Wired glass contains embedded wire mesh that reduces transparency, often transmitting less light and producing a slightly obscured view due to the grid pattern. For skylights prioritizing maximum daylight and visual clarity, vacuum insulated glass is the optimal choice over wired glass.
Energy Efficiency in Skylight Applications
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) offers superior energy efficiency for skylight applications due to its exceptional thermal insulation, reducing heat transfer and maintaining consistent indoor temperatures. Wired glass, while providing enhanced safety and shatter resistance, has higher thermal conductivity, leading to greater heat loss and less effective insulation. Choosing vacuum insulated glass enhances energy savings and comfort by minimizing heat gain and loss through skylights.
Durability and Maintenance
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior durability for skylights due to its robust double-layer construction that resists thermal stress and reduces condensation, extending its lifespan with minimal maintenance. Wired glass, while providing enhanced safety from shattering, is more prone to rusting and requires regular inspections and maintenance to preserve structural integrity. The low-maintenance nature of vacuum insulated glass makes it a preferred choice for long-term skylight installations in harsh weather conditions.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-Term
Vacuum insulated glass offers higher upfront costs compared to wired glass due to advanced technology and superior thermal performance, which reduces energy expenses over time. Wired glass is more affordable initially but lacks the same insulating properties, potentially leading to increased heating and cooling costs in the long term. Investing in vacuum insulated skylight glass can result in substantial savings through enhanced energy efficiency and durability despite a higher initial investment.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Skylight
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation and energy efficiency for skylights, reducing heat transfer and condensation compared to wired glass, which primarily provides fire resistance and safety through its embedded wire mesh. For projects prioritizing energy savings and comfort, vacuum insulated glass enhances natural light while maintaining better temperature control, whereas wired glass is ideal for meeting fire code requirements in commercial or industrial buildings. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing energy performance, safety standards, and the specific building codes applicable to your skylight installation.
Infographic: Vacuum insulated glass vs Wired glass for Skylight
 azmater.com
azmater.com