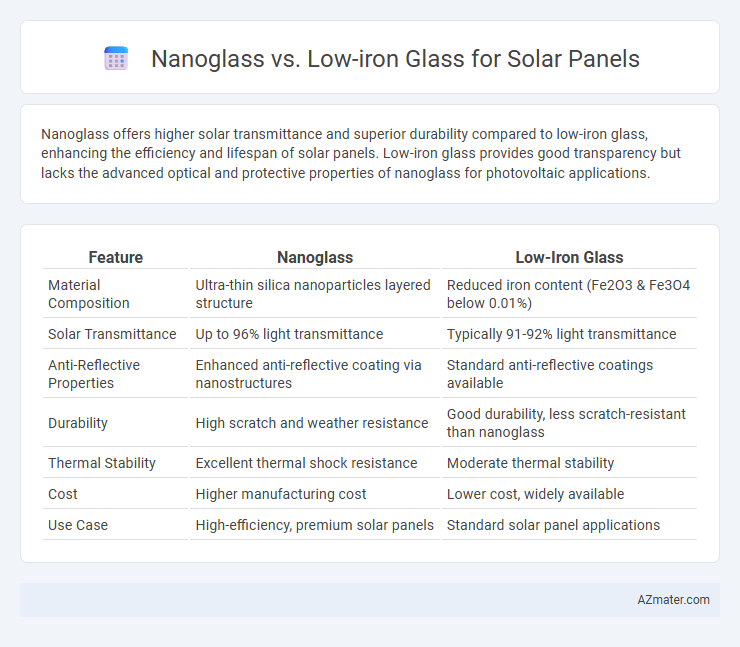
Nanoglass offers higher solar transmittance and superior durability compared to low-iron glass, enhancing the efficiency and lifespan of solar panels. Low-iron glass provides good transparency but lacks the advanced optical and protective properties of nanoglass for photovoltaic applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Nanoglass | Low-Iron Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Ultra-thin silica nanoparticles layered structure | Reduced iron content (Fe2O3 & Fe3O4 below 0.01%) |
| Solar Transmittance | Up to 96% light transmittance | Typically 91-92% light transmittance |
| Anti-Reflective Properties | Enhanced anti-reflective coating via nanostructures | Standard anti-reflective coatings available |
| Durability | High scratch and weather resistance | Good durability, less scratch-resistant than nanoglass |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent thermal shock resistance | Moderate thermal stability |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost | Lower cost, widely available |
| Use Case | High-efficiency, premium solar panels | Standard solar panel applications |
Introduction to Glass Technologies in Solar Panels
Nanoglass and low-iron glass are advanced materials used in solar panel applications to maximize light transmission and energy efficiency. Nanoglass utilizes nanotechnology to create ultra-smooth surfaces that reduce reflection and enhance sunlight absorption, while low-iron glass contains reduced iron oxide content to minimize greenish tint and improve clarity. Both technologies significantly contribute to higher photovoltaic performance by increasing the amount of solar irradiance reaching the solar cells.
What is Nanoglass?
Nanoglass is an advanced glass material engineered with nanostructured coatings to enhance solar panel efficiency by increasing light transmission and reducing reflection. Its nanoscale surface features improve durability and self-cleaning properties, making it ideal for harsh environmental conditions in solar energy systems. Compared to low-iron glass, nanoglass offers superior optical performance and energy yield, optimizing solar panel output even under diffuse light conditions.
What is Low-Iron Glass?
Low-iron glass is a type of glass with reduced iron content, resulting in higher light transmittance and minimal green tint compared to standard glass, making it ideal for solar panels to maximize energy absorption. Nanoglass enhances this by incorporating nanostructures that improve light trapping and durability, whereas low-iron glass primarily focuses on clarity and light passage. The choice between nanoglass and low-iron glass impacts solar panel efficiency, with low-iron glass offering cost-effective transparency and nanoglass providing advanced optical performance.
Optical Clarity Comparison: Nanoglass vs Low-Iron Glass
Nanoglass offers superior optical clarity compared to low-iron glass due to its nanoscale smoothness and reduced light scattering properties, which enhance solar panel efficiency by allowing more light transmission. Low-iron glass improves clarity over standard glass by minimizing iron content that absorbs light, resulting in higher transmittance but still slightly less than nanoglass. The advanced nanocoating on nanoglass further reduces reflectance, maximizing light absorption and boosting overall solar energy yield.
Light Transmission Efficiency in Solar Panels
Nanoglass enhances light transmission efficiency in solar panels by reducing reflection losses and increasing the amount of sunlight reaching the photovoltaic cells, achieving transmittance rates above 92%. Low-iron glass also improves transparency compared to standard glass, with typical light transmission around 90%, but it may allow more impurities that can slightly lower efficiency. The superior purity and anti-reflective properties of Nanoglass contribute to higher overall energy yield in solar energy systems.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Nanoglass exhibits superior durability and weather resistance compared to low-iron glass, thanks to its advanced nanocoating that enhances scratch resistance and protects against UV degradation. Low-iron glass offers excellent clarity but is more prone to surface wear and environmental damage over time. The nanoglass's enhanced hydrophobic properties also reduce dirt accumulation, ensuring longer-lasting performance in harsh weather conditions.
Impact on Solar Panel Performance and Output
Nanoglass enhances solar panel performance by increasing light transmittance up to 96%, reducing reflection, and boosting energy output by up to 5% compared to traditional low-iron glass, which typically offers around 91-92% light transmittance. The superior clarity and anti-reflective properties of nanoglass enable higher efficiency in photovoltaic cells, making it ideal for maximizing power generation in solar panels. Low-iron glass provides good durability and moderate transmittance but falls short in optimizing energy yield compared to nanoglass technologies.
Cost Considerations: Nanoglass vs Low-Iron Glass
Nanoglass typically incurs higher production costs due to advanced manufacturing processes compared to low-iron glass, which is more widely available and less expensive. The energy efficiency gains of nanoglass, with its superior light transmission and self-cleaning properties, may offset the initial investment over the solar panel's lifespan. Low-iron glass offers a cost-effective option with good performance but lacks the enhanced durability and efficiency features inherent in nanoglass technology.
Sustainability and Environmental Benefits
Nanoglass offers enhanced light transmittance and durability compared to low-iron glass, resulting in higher solar panel efficiency and longer lifespan, which reduces resource consumption and waste. Low-iron glass provides good clarity and is widely recyclable, though it has slightly lower efficiency and may require more frequent replacement. Both materials contribute to sustainability by enabling renewable energy generation, but Nanoglass's superior performance supports greater environmental benefits through improved energy yield and reduced material usage.
Choosing the Right Glass for Solar Panel Applications
Nanoglass offers superior light transmittance and self-cleaning properties compared to standard low-iron glass, enhancing solar panel efficiency by maximizing sunlight absorption and reducing maintenance costs. Low-iron glass remains a cost-effective option with higher durability and acceptable transparency, making it suitable for large-scale installations with budget constraints. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing upfront investment, energy yield optimization, and long-term performance requirements in solar panel applications.
Infographic: Nanoglass vs Low-iron glass for Solar panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com