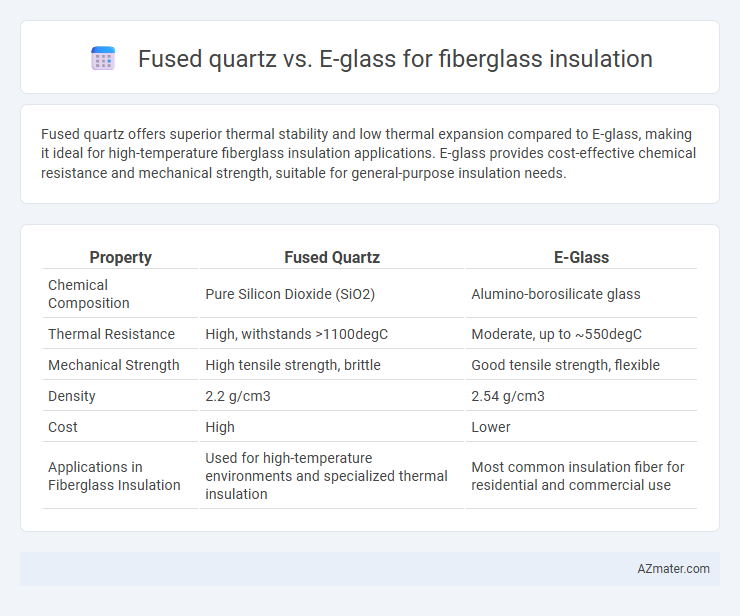
Fused quartz offers superior thermal stability and low thermal expansion compared to E-glass, making it ideal for high-temperature fiberglass insulation applications. E-glass provides cost-effective chemical resistance and mechanical strength, suitable for general-purpose insulation needs.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fused Quartz | E-Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Pure Silicon Dioxide (SiO2) | Alumino-borosilicate glass |
| Thermal Resistance | High, withstands >1100degC | Moderate, up to ~550degC |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength, brittle | Good tensile strength, flexible |
| Density | 2.2 g/cm3 | 2.54 g/cm3 |
| Cost | High | Lower |
| Applications in Fiberglass Insulation | Used for high-temperature environments and specialized thermal insulation | Most common insulation fiber for residential and commercial use |
Introduction to Fiberglass Insulation Materials
Fiberglass insulation primarily uses E-glass fibers, known for their high tensile strength and cost-effectiveness in thermal and acoustic insulation applications. Fused quartz fibers offer superior thermal stability and lower thermal expansion, making them ideal for high-temperature environments but at a higher cost. The choice between fused quartz and E-glass depends on specific insulation requirements, including operating temperature, mechanical stress, and budget constraints.
What is Fused Quartz?
Fused quartz is a high-purity, non-crystalline silica glass made by melting natural quartz crystals at extremely high temperatures, resulting in exceptional thermal stability and low thermal expansion. In contrast to E-glass, which is an alumino-borosilicate glass optimized for electrical insulation and cost efficiency, fused quartz offers superior resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion. These properties make fused quartz ideal for specialized fiberglass insulation applications requiring extreme heat resistance and durability.
What is E-Glass?
E-glass, or electrical-grade glass, is a type of fiberglass known for its high tensile strength and excellent electrical insulation properties, making it a common choice in fiberglass insulation. Compared to fused quartz, E-glass offers greater flexibility and cost-effectiveness, though it has a lower melting point and less resistance to thermal shock. Its composition primarily includes silica, alumina, and boron oxide, optimizing it for durability and performance in insulation applications.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Fused quartz and E-glass differ significantly in manufacturing processes for fiberglass insulation. Fused quartz is produced through melting high-purity silica at temperatures exceeding 1700degC, resulting in ultra-pure glass with superior thermal and chemical resistance. E-glass manufacturing involves melting a mixture of silica, alumina, calcium oxide, and boron oxide around 1400-1600degC, optimizing cost and mechanical properties for electrical insulation and structural applications.
Thermal Properties: Fused Quartz vs E-Glass
Fused quartz exhibits superior thermal stability with a melting point around 1,710degC and extremely low thermal expansion (~0.5 x 10^-6 /degC), making it ideal for insulation in high-temperature environments. E-glass fibers have a melting point near 1,200degC and higher thermal expansion (~5.4 x 10^-6 /degC), resulting in moderate performance in thermal insulation applications. The low thermal conductivity of fused quartz (about 1.4 W/m*K) surpasses that of E-glass (approximately 1.1-1.4 W/m*K), offering enhanced resistance to heat transfer and improved insulation efficiency.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Fused quartz offers superior mechanical strength and exceptional thermal stability compared to E-glass, making it highly resistant to deformation and thermal shock in fiberglass insulation applications. E-glass, while providing adequate strength and good chemical resistance, tends to have lower tensile strength and is more prone to degradation under prolonged heat exposure. The enhanced durability of fused quartz fibers ensures longer lifespan and improved performance in demanding insulation environments.
Chemical Resistance and Stability
Fused quartz exhibits superior chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to E-glass, making it ideal for environments with aggressive chemicals and high temperatures. E-glass, while cost-effective and mechanically strong, is more susceptible to alkali attack and chemical degradation over time. The high purity and crystalline structure of fused quartz contribute to its enhanced durability and long-term stability in corrosive applications.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Fused quartz offers superior thermal resistance and durability but comes at a significantly higher price point compared to E-glass, impacting overall project budgets for fiberglass insulation. E-glass is widely available and mass-produced, resulting in lower costs and easier procurement for large-scale insulation applications. Cost analysis favors E-glass for budget-conscious projects, while fused quartz is reserved for specialized environments requiring enhanced performance.
Practical Applications in Insulation
Fused quartz offers superior thermal stability and resistance to high temperatures, making it ideal for industrial and high-temperature insulation applications where durability and minimal thermal expansion are critical. E-glass, widely used in residential and commercial fiberglass insulation, provides excellent tensile strength, moisture resistance, and cost-effectiveness for general thermal and acoustic insulation purposes. The choice between fused quartz and E-glass hinges on application requirements, with fused quartz preferred for extreme conditions and E-glass favored for everyday insulation needs.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Project
Fused quartz offers superior thermal stability and low thermal expansion, making it ideal for high-temperature insulation applications, whereas E-glass excels in cost-effectiveness and mechanical strength suitable for general-purpose fiberglass insulation. Consider fused quartz for projects requiring enhanced heat resistance and durability, while E-glass is preferable for standard insulation needs due to its balance of performance and affordability. Evaluating environmental conditions, temperature ranges, and budget constraints is essential for selecting between fused quartz and E-glass materials.
Infographic: Fused quartz vs E-glass for Fiberglass insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com