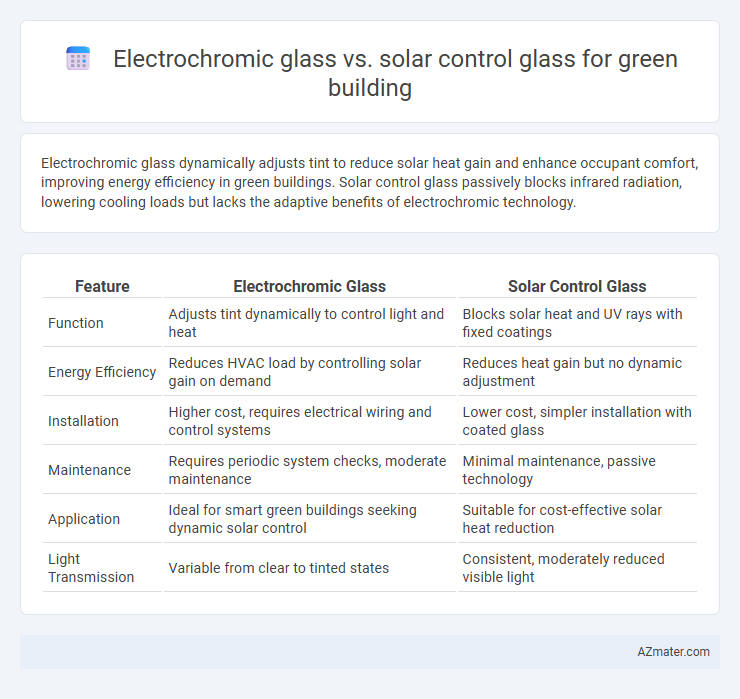
Electrochromic glass dynamically adjusts tint to reduce solar heat gain and enhance occupant comfort, improving energy efficiency in green buildings. Solar control glass passively blocks infrared radiation, lowering cooling loads but lacks the adaptive benefits of electrochromic technology.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Electrochromic Glass | Solar Control Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Adjusts tint dynamically to control light and heat | Blocks solar heat and UV rays with fixed coatings |
| Energy Efficiency | Reduces HVAC load by controlling solar gain on demand | Reduces heat gain but no dynamic adjustment |
| Installation | Higher cost, requires electrical wiring and control systems | Lower cost, simpler installation with coated glass |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic system checks, moderate maintenance | Minimal maintenance, passive technology |
| Application | Ideal for smart green buildings seeking dynamic solar control | Suitable for cost-effective solar heat reduction |
| Light Transmission | Variable from clear to tinted states | Consistent, moderately reduced visible light |
Understanding Electrochromic Glass Technology
Electrochromic glass technology incorporates electrically controlled materials that adjust light transmission to regulate solar heat gain and glare dynamically, enhancing energy efficiency in green buildings. This smart glazing reduces reliance on HVAC systems by modulating indoor temperatures through tint changes, unlike solar control glass that passively filters specific wavelengths to block heat. Understanding the electrochromic process involves recognizing its multilayer structure, including transparent conductors, electrochromic layers, and ion conductors, enabling reversible color changes with low voltage application for responsive daylight management.
What Is Solar Control Glass?
Solar control glass is designed to reduce heat gain and glare in buildings by selectively reflecting and absorbing solar radiation, enhancing energy efficiency in green building applications. It typically features coatings that block infrared and ultraviolet rays while allowing visible light to pass through, thus minimizing cooling loads. Compared to electrochromic glass, solar control glass offers a passive solution without the need for electrical control, making it a cost-effective choice for sustainable architecture.
Energy Efficiency: Electrochromic vs Solar Control Glass
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic energy efficiency by adjusting tint based on sunlight, reducing cooling loads and optimizing natural light in green buildings. Solar control glass provides static solar heat gain reduction through coatings that reflect infrared radiation, lowering air conditioning demand without altering visible transparency. Combining these technologies can maximize energy savings by balancing heat control and daylight management throughout the day.
Light Control and Comfort Benefits
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic light control by electronically tinting the glass, reducing glare and heat gain while maintaining natural daylight, enhancing occupant comfort throughout the day. Solar control glass provides static protection by reflecting and absorbing solar radiation, effectively lowering cooling loads but lacking adaptive light modulation. Combining both technologies can optimize indoor comfort and energy efficiency in green buildings by balancing daylight access and solar heat management.
Cost Comparison and Lifecycle Analysis
Electrochromic glass typically has higher upfront costs due to advanced smart tinting technology, whereas solar control glass offers a more affordable initial investment with passive solar heat reduction features. Lifecycle analysis shows electrochromic glass improves energy efficiency by dynamically regulating solar heat gain, resulting in significant long-term savings on HVAC energy consumption. Solar control glass, while less adaptive, provides durability and low maintenance costs, making it a cost-effective choice for projects with budget constraints.
Smart Building Integration Capabilities
Electrochromic glass offers advanced smart building integration through its ability to dynamically adjust tint levels based on real-time environmental data, optimizing natural light and reducing HVAC loads efficiently. Solar control glass primarily provides passive solar heat gain reduction but lacks automated responsiveness or integration with intelligent building management systems. Electrochromic technology enhances energy savings and occupant comfort by synchronizing with smart sensors and IoT devices, essential for next-generation green buildings.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Electrochromic glass dynamically adjusts tint to reduce solar heat gain, lowering energy use for cooling and decreasing carbon emissions in green buildings. Solar control glass passively blocks infrared rays, improving thermal comfort and reducing HVAC energy consumption but lacks real-time adaptability. Both technologies contribute to sustainability by enhancing energy efficiency, yet electrochromic glass offers superior performance through smart control, optimizing daylight use and minimizing artificial lighting needs.
Maintenance and Longevity Considerations
Electrochromic glass offers low maintenance due to its solid-state technology with no moving parts, ensuring minimal degradation over time and a lifespan typically exceeding 20 years. Solar control glass requires periodic cleaning and occasional replacement of coatings to maintain its reflective efficiency, with durability usually around 10 to 15 years depending on environmental exposure. Choosing electrochromic glass significantly reduces maintenance costs and enhances longevity, making it a superior option for sustainable green building design.
Architectural Applications and Aesthetics
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic tinting capabilities, allowing architects to control solar heat gain and natural light levels in real-time, enhancing occupant comfort while maintaining sleek, modern aesthetics in green buildings. Solar control glass provides a static solution by filtering ultraviolet and infrared rays, reducing energy loads through high-performance coatings designed for specific climatic conditions. Both materials contribute to sustainable building design, with electrochromic glass enabling adaptive facades and solar control glass ensuring optimal thermal performance and glare reduction in architectural applications.
Choosing the Right Glass for Green Building Projects
Electrochromic glass offers dynamic tinting capabilities that adjust to sunlight intensity, significantly reducing glare and HVAC energy consumption in green building projects. Solar control glass provides passive heat rejection through coatings that reflect infrared radiation, enhancing thermal comfort and lowering cooling loads without the need for power input. Selecting the right glass depends on factors such as building orientation, climate conditions, and energy efficiency targets, with electrochromic glass favored for adaptive shading and solar control glass preferred for cost-effective, static solar heat management.
Infographic: Electrochromic glass vs Solar control glass for Green building
 azmater.com
azmater.com