Gorilla Glass offers superior scratch resistance and impact durability, making it ideal for high-performance camera lenses. Borosilicate glass provides excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance but lacks the toughness found in Gorilla Glass.
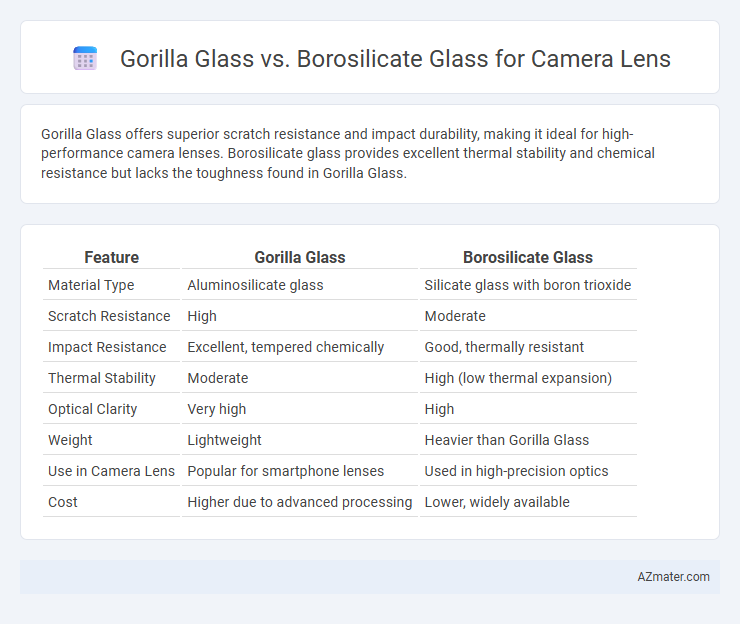
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Gorilla Glass | Borosilicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Aluminosilicate glass | Silicate glass with boron trioxide |
| Scratch Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Impact Resistance | Excellent, tempered chemically | Good, thermally resistant |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate | High (low thermal expansion) |
| Optical Clarity | Very high | High |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier than Gorilla Glass |
| Use in Camera Lens | Popular for smartphone lenses | Used in high-precision optics |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced processing | Lower, widely available |
Introduction to Gorilla Glass and Borosilicate Glass
Gorilla Glass is a chemically strengthened, aluminosilicate glass known for its high scratch resistance and durability, often used in smartphone camera lenses to protect against daily wear and impact. Borosilicate glass, composed of silica and boron trioxide, offers excellent thermal resistance and chemical stability, making it suitable for precision optical components but generally less resistant to scratches compared to Gorilla Glass. The choice between Gorilla Glass and Borosilicate glass for camera lenses depends on the priority between durability and optical clarity under varying environmental conditions.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Gorilla Glass is an alkali-aluminosilicate sheet glass known for its chemical strengthening through an ion-exchange process, which enhances durability and scratch resistance ideal for camera lenses. Borosilicate glass, composed primarily of silica and boron trioxide, is manufactured by melting and then annealing to reduce thermal expansion, providing superior thermal stability but less impact resistance. The ion-exchange in Gorilla Glass results in a compressive surface layer, while borosilicate's structure offers chemical resistance and thermal shock resilience, influencing their suitability for different camera lens applications.
Scratch Resistance Comparison
Gorilla Glass offers superior scratch resistance compared to Borosilicate glass, making it a preferred choice for camera lenses that require durability against everyday abrasion. Chemically strengthened through an ion-exchange process, Gorilla Glass achieves higher surface hardness and better impact resistance, reducing the likelihood of scratches during regular use. In contrast, Borosilicate glass, while thermally stable and resistant to chemical damage, tends to be softer and more prone to surface scratches under similar conditions.
Impact and Drop Durability
Gorilla Glass offers superior impact and drop durability for camera lenses due to its chemically strengthened alkali-aluminosilicate composition, which enhances scratch resistance and reduces shattering risk. Borosilicate glass, while thermally stable and resistant to chemical corrosion, generally exhibits lower impact resistance and is more prone to cracking under drops compared to Gorilla Glass. This makes Gorilla Glass the preferred choice for rugged smartphone camera lenses where durability against physical impact is critical.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
Gorilla Glass offers superior optical clarity and higher light transmission rates of up to 90%, making it ideal for camera lenses that require sharp image quality and minimal light distortion. Borosilicate glass, while highly durable and resistant to thermal shock, generally exhibits lower light transmission around 85%, which can slightly reduce lens clarity and color accuracy. The advanced chemical strengthening in Gorilla Glass also minimizes surface imperfections, enhancing overall transparency and light passage critical for high-performance camera optics.
Weight and Thickness Factors
Gorilla Glass, known for its lightweight and thin profile, typically weighs less and offers superior durability compared to Borosilicate glass, making it ideal for sleek camera lens designs. Borosilicate glass tends to be thicker and heavier due to its thermal resistance properties, which can add bulk and affect the overall weight of camera lenses. Opting for Gorilla Glass enhances portability and impact resistance without compromising optical clarity, crucial for advanced photography equipment.
Thermal Expansion and Temperature Resistance
Gorilla Glass offers a low coefficient of thermal expansion around 8.1 x 10^-6 /degC, providing excellent dimensional stability for camera lenses under temperature fluctuations. Borosilicate glass features an even lower thermal expansion coefficient near 3.3 x 10^-6 /degC, making it highly resistant to thermal shock and temperature-induced stress. Temperature resistance for Gorilla Glass typically ranges up to 500degC, while borosilicate glass can withstand temperatures exceeding 800degC, enhancing durability in extreme environments.
Cost and Availability in Camera Lenses
Gorilla Glass is widely used in camera lenses due to its affordability and high availability, making it a cost-effective choice for mass production in smartphones and consumer cameras. Borosilicate glass, while offering superior thermal and chemical resistance, tends to be more expensive and less commonly available in camera lens manufacturing, limiting its use to specialized or high-end equipment. Manufacturers often prefer Gorilla Glass for balancing durability with budget constraints without sacrificing lens clarity.
Suitability for Different Photography Conditions
Gorilla Glass offers superior scratch resistance and impact durability, making it ideal for rugged outdoor photography and environments prone to physical stress. Borosilicate glass provides excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance, suited for extreme temperature variations and scientific or industrial photography settings. Both materials excel in clarity and light transmission, but Gorilla Glass is better for versatile field use, while Borosilicate glass is preferred for controlled or harsh chemical conditions.
Final Verdict: Which Glass is Better for Camera Lenses?
Gorilla Glass offers superior scratch resistance and durability, making it ideal for protecting camera lenses in rugged environments. Borosilicate glass excels in thermal stability and optical clarity, which benefits high-precision lenses requiring minimal distortion. For most consumer and professional camera applications, Gorilla Glass provides a better balance of toughness and optical performance, while Borosilicate glass suits specialized uses needing enhanced thermal and chemical resistance.
Infographic: Gorilla glass vs Borosilicate glass for Camera lens
 azmater.com
azmater.com