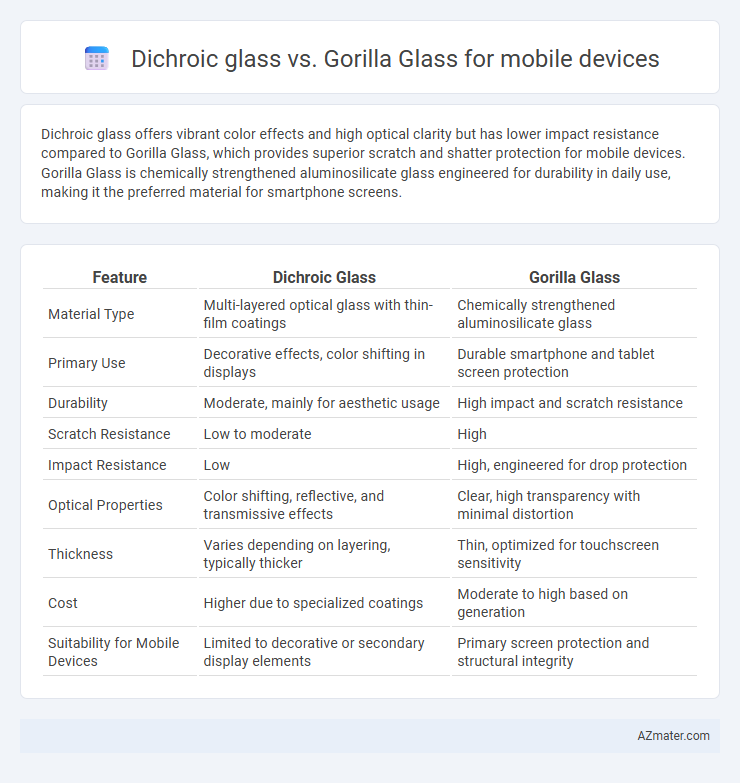
Dichroic glass offers vibrant color effects and high optical clarity but has lower impact resistance compared to Gorilla Glass, which provides superior scratch and shatter protection for mobile devices. Gorilla Glass is chemically strengthened aluminosilicate glass engineered for durability in daily use, making it the preferred material for smartphone screens.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Dichroic Glass | Gorilla Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Multi-layered optical glass with thin-film coatings | Chemically strengthened aluminosilicate glass |
| Primary Use | Decorative effects, color shifting in displays | Durable smartphone and tablet screen protection |
| Durability | Moderate, mainly for aesthetic usage | High impact and scratch resistance |
| Scratch Resistance | Low to moderate | High |
| Impact Resistance | Low | High, engineered for drop protection |
| Optical Properties | Color shifting, reflective, and transmissive effects | Clear, high transparency with minimal distortion |
| Thickness | Varies depending on layering, typically thicker | Thin, optimized for touchscreen sensitivity |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized coatings | Moderate to high based on generation |
| Suitability for Mobile Devices | Limited to decorative or secondary display elements | Primary screen protection and structural integrity |
Introduction to Dichroic Glass and Gorilla Glass
Dichroic glass features multiple micro-layers of metal oxides that create a unique, color-shifting effect by selectively reflecting and transmitting light, making it ideal for decorative and artistic applications. Gorilla Glass is an alkali-aluminosilicate sheet designed by Corning to provide strong, scratch-resistant, and durable protection for mobile device screens. While Gorilla Glass prioritizes toughness and clarity for practical use, dichroic glass emphasizes aesthetic appeal through vibrant and dynamic visual effects.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Dichroic glass for mobile devices is composed of multiple ultra-thin layers of metal oxides deposited onto glass substrates using vacuum deposition techniques, resulting in distinctive color-shifting properties due to interference effects. Gorilla Glass, developed by Corning, is chemically strengthened alkali-aluminosilicate glass created through an ion-exchange process where smaller sodium ions are replaced by larger potassium ions to enhance durability and scratch resistance. The manufacturing of dichroic glass emphasizes precise thin-film layering for optical effects, whereas Gorilla Glass production focuses on thermal and chemical treatments to optimize toughness for everyday mobile device use.
Optical Properties and Aesthetics
Dichroic glass offers vibrant color-shifting effects due to its multiple ultra-thin metal oxide layers, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of mobile devices with dynamic optical properties. Gorilla Glass, engineered for durability and scratch resistance, prioritizes clarity and robustness without altering color perception, ensuring a pristine viewing experience under various lighting conditions. While Dichroic glass excels in decorative visual impact, Gorilla Glass is optimized for functional protection and optical transparency in mobile screens.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Dichroic glass, known for its unique optical properties, offers moderate strength and is primarily used for aesthetic enhancement rather than impact resistance. Gorilla Glass, engineered by Corning, is specifically designed for mobile devices, providing superior scratch resistance and drop durability due to its chemically strengthened composition. In durability comparison, Gorilla Glass outperforms Dichroic glass by delivering enhanced toughness and longevity under typical smartphone usage conditions.
Scratch and Impact Resistance
Dichroic glass offers unique optical properties with moderate scratch resistance but lacks the toughness required for high-impact protection in mobile devices. Gorilla Glass is engineered with aluminosilicate components, providing superior scratch resistance due to its chemically strengthened surface and enhanced impact resistance through ion-exchange processes. Mobile devices equipped with Gorilla Glass benefit from significantly improved durability against daily wear and accidental drops compared to those using dichroic glass.
Weight and Thickness Considerations
Dichroic glass, known for its lightweight and thin profile, offers enhanced aesthetic appeal but lacks the durability needed for mobile devices, whereas Gorilla Glass provides superior strength with minimal added thickness and weight. Gorilla Glass balances robustness and slimness, typically ranging from 0.4 to 0.6 mm in thickness, ensuring device protection without significantly increasing overall weight. In comparison, dichroic glass is heavier and thicker, which can negatively impact mobile device ergonomics and portability.
Cost and Availability
Dichroic glass, known for its unique optical properties and color-shifting effects, is generally more expensive and less readily available than Gorilla Glass, which is widely produced by Corning and specifically engineered for mobile device durability. Gorilla Glass dominates the market due to its cost-effective manufacturing and extensive distribution channels, making it the preferred choice for most smartphones and tablets. Cost differences stem from dichroic glass's complex layering process, while Gorilla Glass benefits from economies of scale, ensuring easier procurement and repair availability.
Applications in Mobile Devices
Dichroic glass in mobile devices is primarily used for decorative and aesthetic purposes, offering vibrant color shifts and light reflection effects that enhance device design and user customization options. Gorilla Glass, engineered by Corning, provides robust protection through its chemically strengthened properties, significantly increasing scratch resistance and durability in touchscreens and device displays. While Dichroic glass focuses on visual appeal in mobile applications, Gorilla Glass is essential for functional durability and screen longevity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Dichroic glass, known for its unique color-shifting properties, often requires complex manufacturing processes involving multiple metal oxide layers, contributing to higher energy consumption and resource use compared to Gorilla Glass. Gorilla Glass, engineered with aluminosilicate, emphasizes durability and scratch resistance, extending device lifespan and reducing electronic waste through improved screen longevity. From an environmental perspective, Gorilla Glass supports sustainability by minimizing repair frequency and promoting recyclability, while dichroic glass's intricate production may present greater ecological challenges due to higher emissions and material intensity.
Future Trends in Mobile Glass Technology
Dichroic glass offers vibrant color-shifting properties and unique aesthetic appeal, making it a potential choice for future mobile device displays that emphasize design innovation. Gorilla Glass continues to lead in durability and scratch resistance, with advancements toward thinner, more flexible, and ultra-strong formulations enhancing device protection and user experience. Emerging trends suggest a hybrid approach combining dichroic visual effects with Gorilla Glass's toughness could define next-generation mobile glass technology.
Infographic: Dichroic glass vs Gorilla glass for Mobile device
 azmater.com
azmater.com