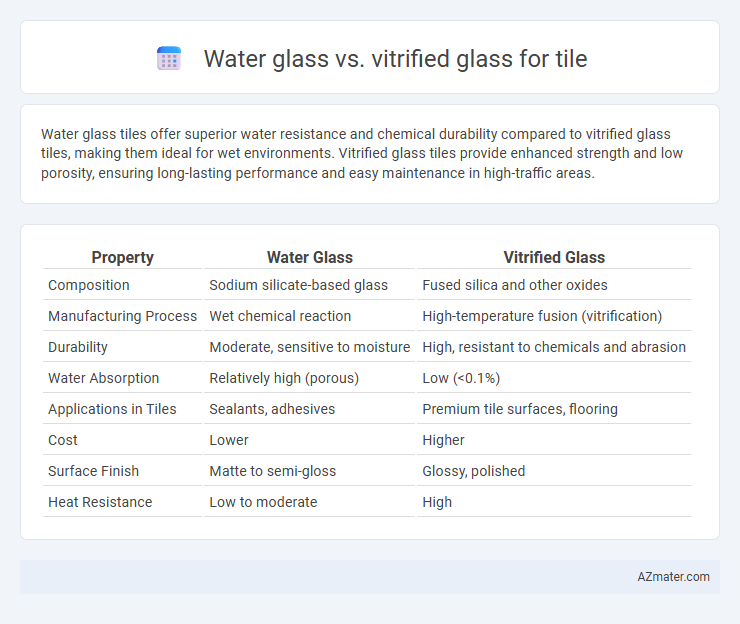
Water glass tiles offer superior water resistance and chemical durability compared to vitrified glass tiles, making them ideal for wet environments. Vitrified glass tiles provide enhanced strength and low porosity, ensuring long-lasting performance and easy maintenance in high-traffic areas.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Water Glass | Vitrified Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Sodium silicate-based glass | Fused silica and other oxides |
| Manufacturing Process | Wet chemical reaction | High-temperature fusion (vitrification) |
| Durability | Moderate, sensitive to moisture | High, resistant to chemicals and abrasion |
| Water Absorption | Relatively high (porous) | Low (<0.1%) |
| Applications in Tiles | Sealants, adhesives | Premium tile surfaces, flooring |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Surface Finish | Matte to semi-gloss | Glossy, polished |
| Heat Resistance | Low to moderate | High |
Introduction to Water Glass and Vitrified Glass
Water glass, also known as sodium silicate, is a liquid compound used in tile manufacturing to enhance adhesion and moisture resistance. Vitrified glass tiles are produced through a process that fuses silica and clay at high temperatures, creating a dense, non-porous surface with superior strength and durability. Comparing water glass treatments and vitrified glass tiles highlights differences in composition, manufacturing methods, and performance characteristics critical for construction and design applications.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Water glass tiles incorporate sodium silicate as a key component, formed through a chemical reaction between silica and sodium carbonate, resulting in a translucent and slightly porous material. Vitrified glass tiles combine clay, silica, feldspar, and quartz, subjected to high-temperature vitrification that fuses particles into a dense, non-porous structure with enhanced strength. The manufacturing process for vitrified tiles involves pressing and firing at temperatures exceeding 1200degC, while water glass tiles are produced using a sol-gel process followed by controlled drying and curing.
Physical Properties Comparison
Water glass tiles exhibit moderate hardness and porosity, providing decent resistance to water absorption but lower mechanical strength compared to vitrified glass tiles. Vitrified glass tiles are characterized by a dense, non-porous surface with high hardness (Mohs scale 7-8), offering exceptional resistance to scratches, stains, and water penetration. The superior physical properties of vitrified tiles result in enhanced durability and suitability for high-traffic areas versus the more absorbent and less robust water glass alternatives.
Durability and Strength Differences
Water glass tiles exhibit moderate durability but are more prone to scratches and chipping compared to vitrified glass tiles, which undergo higher temperature processes resulting in superior strength and resistance. Vitrified glass tiles feature low porosity and higher density, making them ideal for heavy-traffic areas due to their enhanced toughness and long-lasting performance. The vitrification process imparts greater hardness, stain resistance, and minimal water absorption, significantly outperforming traditional water glass tiles in durability.
Water Absorption and Porosity Levels
Water glass tiles exhibit higher water absorption rates, typically around 12-15%, due to their porous structure, which impacts durability and stain resistance. Vitrified glass tiles boast significantly lower water absorption, often below 0.5%, attributed to their dense, non-porous composition that enhances strength and reduces porosity levels. The minimal porosity in vitrified glass tiles makes them ideal for high-moisture environments, outperforming water glass tiles in resisting water penetration and long-term wear.
Aesthetic Variations and Design Flexibility
Water glass tiles offer a translucent, glossy finish that enhances natural light diffusion and creates vibrant, shimmering surfaces ideal for modern, artistic designs. Vitrified glass tiles provide a denser, more durable structure with a matte or semi-gloss finish, supporting minimalist aesthetics and intricate patterns due to their superior strength and lower porosity. The choice between water glass and vitrified glass tiles impacts design flexibility by balancing visual richness with practical usability, making them suitable for different interior styles and functional requirements.
Resistance to Stains and Chemicals
Water glass tiles exhibit moderate resistance to stains and chemicals due to their silica-based composition but can be vulnerable to acidic substances over time. Vitrified glass tiles offer superior resistance to stains and chemicals, as their low porosity and high density prevent absorption and surface damage from harsh agents. This enhanced durability makes vitrified glass tiles ideal for high-traffic and chemically exposed environments.
Installation and Maintenance Concerns
Water glass tiles require careful sealing during installation to prevent water absorption and staining, whereas vitrified glass tiles offer a dense, non-porous surface that simplifies installation by reducing the need for extensive sealing. Maintenance of water glass tiles often involves frequent resealing and gentle cleaning to avoid damage, while vitrified glass tiles provide superior durability and stain resistance, allowing for low-maintenance upkeep with standard cleaning solutions. Choosing vitrified glass tiles can significantly reduce long-term maintenance efforts and installation complexities compared to water glass alternatives.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Water glass tiles generally offer a lower initial cost compared to vitrified glass tiles, making them more budget-friendly for large-scale projects or residential applications. Vitrified glass tiles, known for their superior durability and low water absorption, command a higher price but provide greater long-term value in commercial and high-traffic areas. Market availability favors vitrified glass due to its growing demand in premium construction, while water glass tiles remain widely accessible in standard retail outlets and regional suppliers.
Choosing the Right Glass Type for Tiling Projects
Water glass tiles offer excellent moisture resistance ideal for damp environments, while vitrified glass tiles provide superior strength and low porosity, perfect for high-traffic areas. Selecting the right glass type depends on project requirements such as durability, water absorption rate, and aesthetic preferences. Vitrified tiles are preferable for long-lasting, maintenance-free installations, whereas water glass tiles suit spaces like bathrooms where water exposure is a major concern.
Infographic: Water glass vs Vitrified glass for Tile
 azmater.com
azmater.com