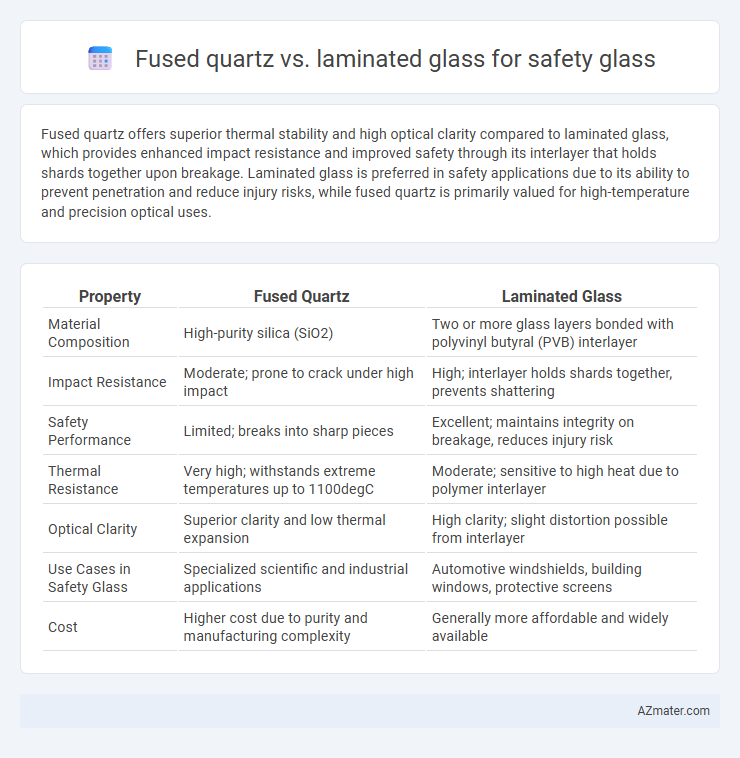
Fused quartz offers superior thermal stability and high optical clarity compared to laminated glass, which provides enhanced impact resistance and improved safety through its interlayer that holds shards together upon breakage. Laminated glass is preferred in safety applications due to its ability to prevent penetration and reduce injury risks, while fused quartz is primarily valued for high-temperature and precision optical uses.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fused Quartz | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | High-purity silica (SiO2) | Two or more glass layers bonded with polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate; prone to crack under high impact | High; interlayer holds shards together, prevents shattering |
| Safety Performance | Limited; breaks into sharp pieces | Excellent; maintains integrity on breakage, reduces injury risk |
| Thermal Resistance | Very high; withstands extreme temperatures up to 1100degC | Moderate; sensitive to high heat due to polymer interlayer |
| Optical Clarity | Superior clarity and low thermal expansion | High clarity; slight distortion possible from interlayer |
| Use Cases in Safety Glass | Specialized scientific and industrial applications | Automotive windshields, building windows, protective screens |
| Cost | Higher cost due to purity and manufacturing complexity | Generally more affordable and widely available |
Introduction to Safety Glass: Fused Quartz vs Laminated Glass
Fused quartz offers exceptional thermal stability and high resistance to impact, making it ideal for specialized safety glass applications requiring high temperature endurance and clarity. Laminated glass consists of multiple glass layers bonded with an interlayer, providing enhanced shatter resistance and improved safety by preventing shards from dispersing upon impact. Both materials serve critical roles in safety glass, with fused quartz favored for extreme conditions and laminated glass widely used in automotive and architectural safety due to its durability and energy absorption properties.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Fused quartz, composed primarily of high-purity silicon dioxide, is manufactured through melting and rapid quenching processes, resulting in a homogenous, non-crystalline structure with exceptional thermal and chemical resistance. Laminated glass consists of multiple glass layers bonded with polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) interlayers, produced by heat and pressure lamination to enhance impact resistance and retain structural integrity upon breakage. The distinct composition and manufacturing techniques of fused quartz offer superior thermal stability, whereas laminated glass prioritizes safety through controlled fragmentation and energy absorption.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Fused quartz offers exceptional mechanical strength and thermal stability due to its high purity and low thermal expansion, making it highly resistant to cracking under mechanical stress and temperature fluctuations. Laminated glass combines layers of glass with interlayer polymers, enhancing impact resistance and preventing shattering, which improves overall durability and safety performance in applications prone to high impact. While fused quartz excels in mechanical strength and temperature resilience, laminated glass provides superior safety by maintaining structural integrity upon breakage.
Impact Resistance: A Comparative Analysis
Fused quartz offers exceptional impact resistance due to its high strength and thermal stability, making it ideal for applications requiring durability under extreme conditions. Laminated glass, composed of multiple layers bonded with a plastic interlayer, provides enhanced safety by preventing shattering and maintaining structural integrity upon impact. Compared to fused quartz, laminated glass offers better energy absorption and minimizes injury risk by holding broken fragments together, while fused quartz excels in resisting high-velocity impacts without creating debris.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
Fused quartz offers superior optical clarity and near-perfect light transmission of approximately 92%, making it ideal for applications requiring minimal distortion and maximum visibility. Laminated glass, while providing enhanced safety through its layered structure, typically transmits around 85-90% of light but may introduce slight haze or minor optical distortions due to interlayers. For safety glass applications where optimal visual performance and high light transmission are critical, fused quartz is the preferred material over laminated glass.
Thermal Properties and Heat Resistance
Fused quartz exhibits exceptional thermal stability with a melting point around 1,650degC and a low coefficient of thermal expansion (0.5 x 10^-6 /degC), making it highly resistant to thermal shock and ideal for applications involving rapid temperature changes. Laminated glass, composed of multiple glass layers bonded with polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayers, has moderate heat resistance limited by the glass type and interlayer's thermal tolerance, generally performing well up to approximately 150-200degC before delamination risks arise. Fused quartz's superior heat resistance outperforms laminated glass in high-temperature environments, while laminated glass prioritizes impact safety and post-breakage cohesion over extreme thermal endurance.
Chemical and UV Resistance
Fused quartz exhibits superior chemical resistance and almost complete UV transparency, making it ideal for extreme environments where prolonged exposure to harsh chemicals and ultraviolet radiation occurs. Laminated glass offers moderate UV protection by incorporating UV-filtering interlayers, but its chemical resistance is generally lower due to vulnerability of the polymer interlayer to solvents and acids. For safety glass applications requiring durable UV and chemical resistance, fused quartz outperforms laminated glass in longevity and clarity under aggressive exposure conditions.
Safety Performance in Real-World Applications
Fused quartz exhibits superior thermal stability and high resistance to shattering under extreme temperature variations, making it ideal for safety glass in high-heat environments. Laminated glass outperforms in impact resistance and post-breakage integrity due to its interlayer, which prevents shards from scattering, enhancing occupant protection during collisions or blasts. Real-world applications favor laminated glass in automotive and architectural safety glass, while fused quartz is preferred in specialized industrial settings requiring enhanced thermal shock resistance and optical clarity.
Cost, Availability, and Installation Considerations
Fused quartz offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance but comes at a significantly higher cost and limited availability compared to laminated glass, which is widely produced and more economical for safety glass applications. Laminated glass provides effective impact resistance and UV protection, with simpler installation processes compatible with standard framing systems, whereas fused quartz requires specialized handling and tools due to its brittle nature and manufacturing complexity. For most safety glass projects, laminated glass remains the practical choice given its balance of performance, affordability, and ease of installation across diverse commercial and residential settings.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Safety Glass
Fused quartz offers exceptional thermal resistance and optical clarity, making it ideal for high-temperature and precision applications in safety glass. Laminated glass, composed of multiple layers with interlayers like PVB or SGP, provides superior impact resistance and shatterproof qualities essential for automotive, architectural, and security purposes. Selecting the right material depends on specific safety requirements, environmental conditions, and desired mechanical properties, with fused quartz favored for thermal durability and laminated glass preferred for impact protection and safety in everyday use.
Infographic: Fused quartz vs Laminated glass for Safety glass
 azmater.com
azmater.com