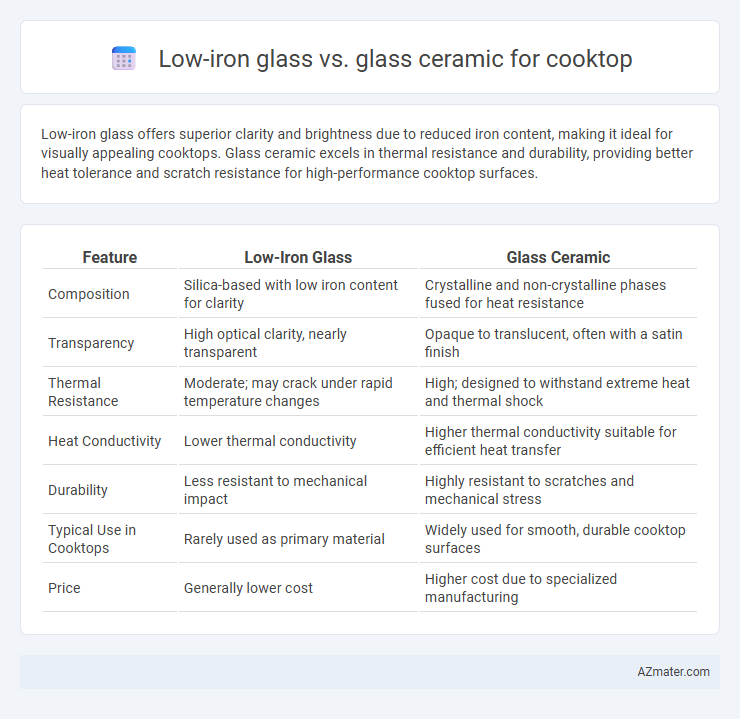
Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and brightness due to reduced iron content, making it ideal for visually appealing cooktops. Glass ceramic excels in thermal resistance and durability, providing better heat tolerance and scratch resistance for high-performance cooktop surfaces.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Low-Iron Glass | Glass Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Silica-based with low iron content for clarity | Crystalline and non-crystalline phases fused for heat resistance |
| Transparency | High optical clarity, nearly transparent | Opaque to translucent, often with a satin finish |
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate; may crack under rapid temperature changes | High; designed to withstand extreme heat and thermal shock |
| Heat Conductivity | Lower thermal conductivity | Higher thermal conductivity suitable for efficient heat transfer |
| Durability | Less resistant to mechanical impact | Highly resistant to scratches and mechanical stress |
| Typical Use in Cooktops | Rarely used as primary material | Widely used for smooth, durable cooktop surfaces |
| Price | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to specialized manufacturing |
Introduction to Cooktop Surface Materials
Low-iron glass and glass ceramic are two popular materials used for cooktop surfaces due to their durability and heat resistance. Low-iron glass offers a clearer, more transparent look, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of modern cooktops, while glass ceramic provides superior thermal shock resistance and can withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking. Choosing between these materials depends on the balance between visual clarity and functional heat tolerance required for the cooktop.
What is Low-Iron Glass?
Low-iron glass is a type of glass that contains reduced iron content, resulting in higher clarity and transparency compared to standard glass. It enhances light transmission, making it ideal for cooktops where visibility and aesthetics are important. In contrast, glass ceramic is a heat-resistant material designed to withstand rapid temperature changes, offering durability but lower clarity than low-iron glass.
What is Glass Ceramic?
Glass ceramic is a durable, heat-resistant material commonly used for cooktops, known for its excellent thermal shock resistance and ability to withstand high temperatures without cracking. Unlike low-iron glass, which offers exceptional clarity and aesthetics, glass ceramic provides superior functionality by evenly distributing heat and enhancing cooking performance. This material combines the strength of glass with the thermal properties of ceramics, making it ideal for stovetop surfaces that require both durability and efficiency.
Visual Clarity and Aesthetics Comparison
Low-iron glass offers superior visual clarity due to its reduced green tint, providing a bright, clear appearance that enhances modern cooktop designs. Glass ceramic, while slightly less transparent, excels in heat resistance and durability but may exhibit subtle cloudiness or color variations under certain lighting conditions. Choosing between low-iron glass and glass ceramic depends on prioritizing aesthetic purity versus functional strength in cooktop surfaces.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Stability
Low-iron glass offers high transparency and moderate heat resistance suitable for cooktop surfaces but can be prone to thermal shock under rapid temperature changes. Glass ceramic cooktops exhibit superior heat resistance and exceptional thermal stability, tolerating temperatures up to 700degC and sudden temperature shifts without cracking. Their crystalline structure minimizes thermal expansion, making glass ceramic the preferred material for durable and safe cooktop applications.
Durability and Scratch Resistance
Low-iron glass is favored for cooktops due to its high transparency and aesthetic appeal but generally offers moderate scratch resistance and durability. Glass ceramic, composed of crystalline and glass phases, excels in thermal shock resistance and superior scratch resistance, making it more durable under everyday kitchen use. Its ability to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking surpasses that of low-iron glass, ensuring enhanced longevity for cooktop surfaces.
Energy Efficiency and Heat Conduction
Low-iron glass offers high transparency and aesthetics but has lower thermal conductivity compared to glass ceramic, which excels in rapid heat conduction and energy efficiency for cooktops. Glass ceramic's crystalline structure enables quick heat transfer and uniform cooking temperatures, reducing energy consumption and enhancing performance. Energy-efficient cooktops benefit from glass ceramic surfaces, which minimize heat loss and support faster heating cycles relative to low-iron glass.
Cleaning and Maintenance Differences
Low-iron glass cooktops have a smooth, non-porous surface that resists stains and is easy to clean with mild detergents and soft cloths. Glass ceramic cooktops, while also relatively easy to maintain, require special cleaning agents to avoid scratching and discoloration caused by residue from burnt-on spills. Both materials demand regular cleaning, but glass ceramic needs more careful handling to preserve its glossy finish and prevent heat damage.
Cost Analysis: Low-Iron Glass vs Glass Ceramic
Low-iron glass cooktops generally have a higher upfront cost due to their enhanced clarity and premium manufacturing process compared to standard glass ceramic surfaces. Glass ceramic cooktops are more cost-effective, offering durability and heat resistance ideal for everyday cooking without the expense associated with low-iron variants. When analyzing long-term value, glass ceramic provides a balance of affordability and performance, whereas low-iron glass caters to aesthetics and premium market segments, influencing the overall cost differential.
Best Applications and User Recommendations
Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and aesthetic appeal, making it ideal for modern cooktop designs where a sleek, transparent surface is desired. Glass ceramic excels in heat resistance and thermal shock tolerance, making it the best choice for cooktops subjected to rapid temperature changes and heavy cooking usage. Users seeking durability and performance for intense cooking tasks prefer glass ceramic, while those prioritizing style and visual appeal often opt for low-iron glass cooktops.
Infographic: Low-iron glass vs Glass ceramic for Cooktop
 azmater.com
azmater.com