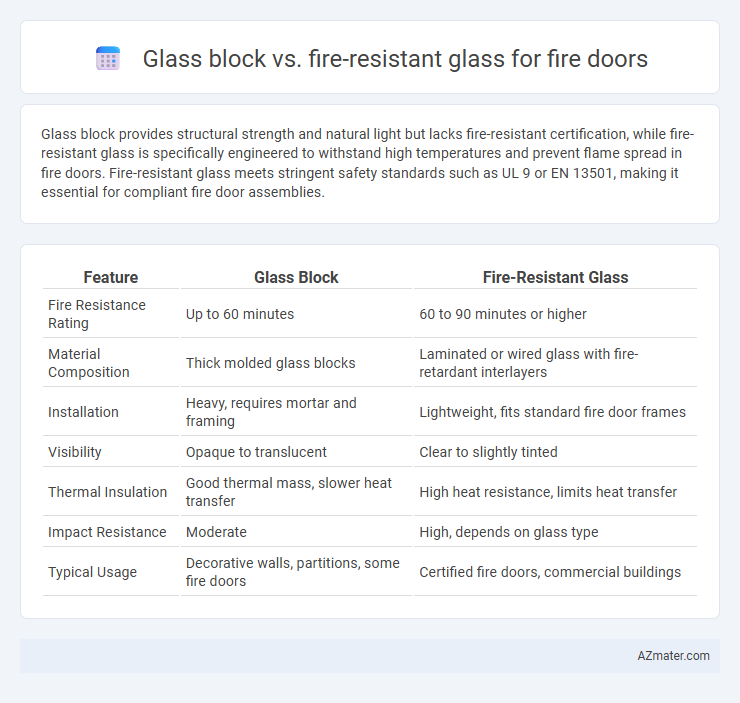
Glass block provides structural strength and natural light but lacks fire-resistant certification, while fire-resistant glass is specifically engineered to withstand high temperatures and prevent flame spread in fire doors. Fire-resistant glass meets stringent safety standards such as UL 9 or EN 13501, making it essential for compliant fire door assemblies.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Glass Block | Fire-Resistant Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance Rating | Up to 60 minutes | 60 to 90 minutes or higher |
| Material Composition | Thick molded glass blocks | Laminated or wired glass with fire-retardant interlayers |
| Installation | Heavy, requires mortar and framing | Lightweight, fits standard fire door frames |
| Visibility | Opaque to translucent | Clear to slightly tinted |
| Thermal Insulation | Good thermal mass, slower heat transfer | High heat resistance, limits heat transfer |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | High, depends on glass type |
| Typical Usage | Decorative walls, partitions, some fire doors | Certified fire doors, commercial buildings |
Understanding Glass Block and Fire-Resistant Glass
Glass block offers excellent insulation and aesthetic appeal with its thick, translucent structure but typically lacks certified fire resistance for fire doors. Fire-resistant glass is engineered with specialized layers or treatments to withstand high temperatures and prevent flame spread, meeting stringent building codes for fire doors. Understanding both materials highlights that fire-resistant glass ensures safety compliance, while glass block primarily enhances design and natural light without guaranteed fire protection.
Key Differences in Fire Performance
Glass block offers limited fire resistance, typically rated up to 20-45 minutes, relying on its thickness and mortar joints to inhibit flames, while fire-resistant glass is engineered with special interlayers or coatings to maintain integrity and temperature control for 60-120 minutes or more. Fire-resistant glass withstands direct exposure to high temperatures and prevents heat transfer, crucial for maintaining safe evacuation routes in fire doors, whereas glass blocks primarily serve as a barrier without advanced heat insulation properties. The certified fire ratings and ASTM or UL standards distinguish fire-resistant glass as the preferred choice for compliance with stringent building codes and safety regulations in fire door applications.
Structural Strength and Durability Comparison
Glass blocks offer high compressive strength and excellent durability due to their thick, solid construction, making them resilient under pressure and less prone to impact damage in fire door applications. Fire-resistant glass, typically composed of multiple laminated layers designed to withstand extreme heat, provides superior thermal insulation and prevents fire spread, but may have lower structural strength compared to solid glass blocks. The choice between glass block and fire-resistant glass hinges on balancing the need for structural robustness and fire performance requirements, with fire-resistant glass excelling in fire containment and glass blocks offering enhanced mechanical endurance.
Installation Requirements and Methods
Glass blocks in fire doors require precise mortar setting within steel or aluminum frames, ensuring tight seals and alignment to maintain fire resistance according to ASTM E119 standards. Fire-resistant glass installations demand certified framing systems that accommodate specific thicknesses, with tempered or laminated glass fitted using fire-rated glazing gaskets and sealants to prevent smoke and heat penetration. Both systems must comply with NFPA 80 and NFPA 101 regulations, emphasizing proper anchoring, clearances, and inspection protocols to guarantee effective fire barrier performance.
Aesthetic Options and Design Flexibility
Glass block offers a distinctive, textured aesthetic that diffuses light while providing privacy, making it ideal for decorative fire doors with a classic or retro look. Fire-resistant glass delivers sleek, transparent surfaces that maintain visibility and modern design appeal, granting greater flexibility for contemporary architectural styles. Both materials meet safety standards, but fire-resistant glass allows extensive customization in size and shape, enhancing design versatility for fire doors.
Sound Insulation Capabilities
Fire-resistant glass used in fire doors typically offers superior sound insulation capabilities compared to standard glass blocks due to its laminated and multi-layered construction that absorbs and dampens sound waves effectively. Glass blocks, while providing good natural light and basic sound reduction, generally lack the specialized acoustic properties and thickness that fire-resistant glass possesses, resulting in lower overall soundproofing performance. Choosing fire-resistant glass enhances both fire safety and acoustic comfort in environments requiring stringent noise control.
Cost Analysis: Glass Block vs Fire-Resistant Glass
Glass block typically offers a more affordable initial cost compared to fire-resistant glass, making it a budget-friendly option for fire doors. However, fire-resistant glass provides superior safety with rated fire protection, potentially reducing long-term costs related to fire damage and insurance premiums. Evaluating installation expenses and compliance with fire safety codes is crucial in determining the overall cost-effectiveness between glass block and fire-resistant glass for fire doors.
Compliance with Fire Safety Regulations
Fire-resistant glass in fire doors meets strict fire safety regulations by providing specified fire resistance ratings, typically ranging from 20 to 120 minutes, crucial for containing flames and heat during emergencies. Glass blocks generally lack official fire resistance certifications and may not comply with building codes for fire-rated openings, limiting their use in fire door applications. Compliance with standards such as UL 10C, BS 476, or EN 1634 is essential, making fire-resistant glass the preferred choice for regulatory adherence in fire safety designs.
Maintenance and Longevity
Fire-resistant glass used in fire doors requires minimal maintenance due to its durable construction and resistance to heat-induced damage, ensuring long-lasting performance under fire safety standards. Glass blocks, while sturdy and decorative, may demand more frequent inspection and sealing to prevent moisture ingress and cracking over time. Choosing fire-resistant glass enhances longevity and reduces maintenance costs by maintaining structural integrity and clarity in extreme conditions.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Fire Door
Choosing the right glass for your fire door involves weighing the benefits of glass blocks versus fire-resistant glass. Glass blocks provide excellent thermal insulation and aesthetic appeal but may not meet stringent fire-resistance standards required for certain door applications. Fire-resistant glass, specifically designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent fire spread, ensures compliance with safety regulations and maintains visibility while enhancing fire protection.
Infographic: Glass block vs Fire-resistant glass for Fire door
 azmater.com
azmater.com