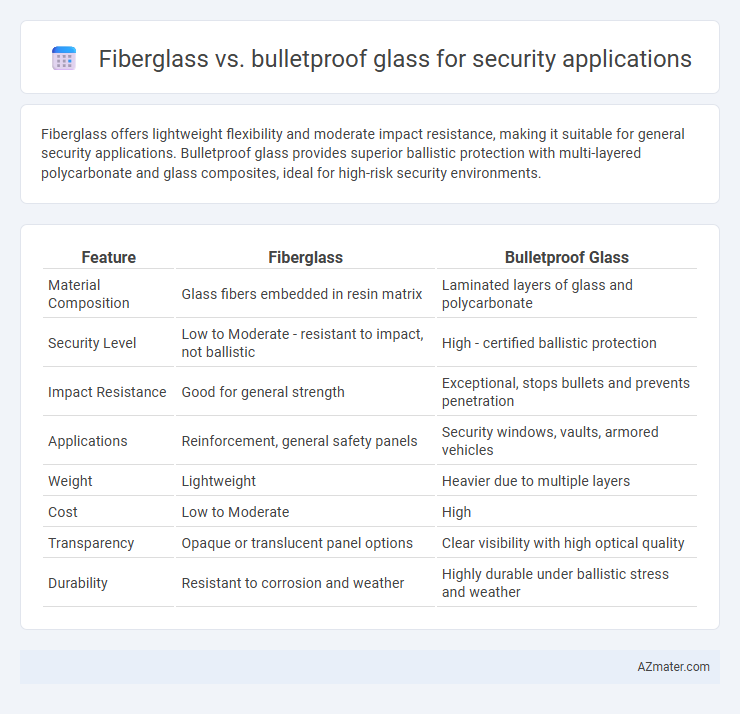
Fiberglass offers lightweight flexibility and moderate impact resistance, making it suitable for general security applications. Bulletproof glass provides superior ballistic protection with multi-layered polycarbonate and glass composites, ideal for high-risk security environments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fiberglass | Bulletproof Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Glass fibers embedded in resin matrix | Laminated layers of glass and polycarbonate |
| Security Level | Low to Moderate - resistant to impact, not ballistic | High - certified ballistic protection |
| Impact Resistance | Good for general strength | Exceptional, stops bullets and prevents penetration |
| Applications | Reinforcement, general safety panels | Security windows, vaults, armored vehicles |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier due to multiple layers |
| Cost | Low to Moderate | High |
| Transparency | Opaque or translucent panel options | Clear visibility with high optical quality |
| Durability | Resistant to corrosion and weather | Highly durable under ballistic stress and weather |
Introduction to Security Glass Solutions
Security glass solutions offer varying levels of protection depending on material composition, with fiberglass and bulletproof glass being prominent options. Fiberglass is a composite material known for its lightweight and flexible properties, providing moderate resistance against impacts and forced entry attempts. Bulletproof glass, typically composed of laminated layers of polycarbonate or glass and resin, delivers higher ballistic resistance and is designed to withstand firearm projectiles, making it ideal for critical security environments.
Understanding Fibre Glass in Security Applications
Fibre glass in security applications offers high tensile strength and flexibility, making it suitable for impact resistance and shatterproof barriers. Its composite structure enhances durability while maintaining lightweight properties, ideal for preventing forced entry and vandalism. Unlike bulletproof glass, fibre glass provides cost-effective protection against moderate physical threats but lacks the multi-layer ballistic resistance necessary for high-caliber ammunition.
What is Bulletproof Glass?
Bulletproof glass, also known as ballistic glass, is a layered composite material made from multiple layers of glass and polycarbonate designed to resist high-velocity projectiles and prevent penetration. It offers superior impact resistance and transparency, making it ideal for security applications such as bank windows, armored vehicles, and safes. In contrast to fiberglass, bulletproof glass provides a higher level of protection against ballistic threats while maintaining optical clarity.
Material Composition: Fibre Glass vs Bulletproof Glass
Fibre glass consists primarily of fine glass fibers woven into a fabric and embedded in a resin matrix, offering lightweight strength and flexibility ideal for general security uses. Bulletproof glass, also known as ballistic glass, is a laminated composite made of multiple layers of glass and polycarbonate or other plastics, engineered to absorb and disperse bullet energy, providing high-impact resistance. The layered structure and material density of bulletproof glass create superior protection compared to the relatively lower tensile strength and energy absorption capacity of fibre glass.
Impact Resistance Comparison
Bulletproof glass, typically composed of layers of polycarbonate and laminated glass, offers significantly higher impact resistance than fiberglass, effectively stopping high-velocity projectiles and reducing penetration risks in security applications. Fiberglass, while strong and lightweight, lacks the multi-layered structure needed to absorb and disperse ballistic energy, making it less suitable for scenarios requiring protection against firearms. The superior energy absorption and toughness of bulletproof glass make it the preferred choice for security installations needing proven resistance to forced entry and ballistic threats.
Cost Effectiveness and Affordability
Fiberglass offers a cost-effective solution for security applications due to its low material and manufacturing expenses compared to bulletproof glass. While bulletproof glass provides superior protection through multi-layered polycarbonate and glass composites, its higher production costs result in less affordability for large-scale projects. For budget-conscious security installations, fiberglass balances durability and budget constraints without compromising basic impact resistance.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Fiberglass offers lightweight installation advantages and requires minimal maintenance due to its corrosion resistance, making it suitable for flexible security applications. Bulletproof glass demands precise fitting protocols and relies on professional installation to ensure optimal ballistic performance, while maintenance involves careful cleaning to avoid surface damage and preserve clarity. Both materials necessitate regular inspections, but bulletproof glass typically involves higher upkeep costs related to damage repair and certification compliance.
Transparency and Aesthetic Versatility
Bulletproof glass offers superior transparency with minimal distortion, ensuring clear visibility while maintaining high impact resistance, making it ideal for security applications requiring both protection and aesthetic appeal. Fiberglass, though durable and strong, typically exhibits less optical clarity and can create a hazy appearance, limiting its use where transparency is critical. The aesthetic versatility of bulletproof glass allows seamless integration into architectural designs, unlike fiberglass, which often requires additional finishing to meet visual standards.
Typical Use Cases for Each Glass Type
Fibre glass is commonly used in security applications such as sports equipment, boat hulls, and protective panels where lightweight and impact resistance are essential but ballistic protection is not required. Bulletproof glass, composed of laminated layers of polycarbonate and glass, is designed for high-security environments including bank teller windows, armored vehicles, and government buildings to provide robust protection against firearm projectiles. For scenarios demanding enhanced safety against explosive blasts or armed assault, bulletproof glass offers superior ballistic resistance compared to fibre glass.
Choosing the Optimal Glass Solution for Security Needs
Fibre glass offers lightweight, cost-effective protection ideal for low-risk security applications, while bulletproof glass provides superior ballistic resistance essential for high-threat environments. Choosing the optimal glass solution depends on factors such as the level of threat, budget constraints, and installation requirements, with bulletproof glass often incorporating multiple layers of laminated polycarbonate and glass for maximum durability. Understanding the specific security needs ensures the selection of the appropriate material, balancing protection performance with structural and financial considerations.
Infographic: Fibre glass vs Bulletproof glass for Security application
 azmater.com
azmater.com