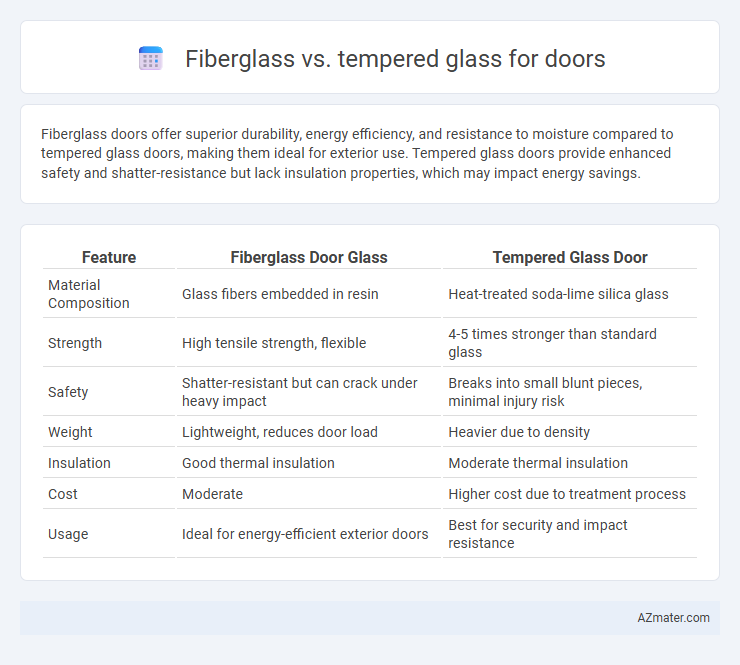
Fiberglass doors offer superior durability, energy efficiency, and resistance to moisture compared to tempered glass doors, making them ideal for exterior use. Tempered glass doors provide enhanced safety and shatter-resistance but lack insulation properties, which may impact energy savings.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fiberglass Door Glass | Tempered Glass Door |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Glass fibers embedded in resin | Heat-treated soda-lime silica glass |
| Strength | High tensile strength, flexible | 4-5 times stronger than standard glass |
| Safety | Shatter-resistant but can crack under heavy impact | Breaks into small blunt pieces, minimal injury risk |
| Weight | Lightweight, reduces door load | Heavier due to density |
| Insulation | Good thermal insulation | Moderate thermal insulation |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher cost due to treatment process |
| Usage | Ideal for energy-efficient exterior doors | Best for security and impact resistance |
Introduction to Door Materials: Fibre Glass vs Tempered Glass
Fiberglass doors offer superior resistance to moisture, dents, and warping, making them ideal for exterior use where durability and energy efficiency are critical. Tempered glass doors provide enhanced safety and strength due to their heat-treated manufacturing process, delivering impact resistance and shatterproof qualities that are essential for security and visibility. Choosing between fiberglass and tempered glass depends on priorities such as insulation, maintenance, safety, and aesthetic appeal in door applications.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Fiberglass doors consist of a composite material made from fine glass fibers embedded in a resin matrix, providing high strength and flexibility, while tempered glass is manufactured by heating standard glass to around 620degC and rapidly cooling it to increase its strength and safety. Fiberglass production involves layering glass fibers and resin, curing under heat or pressure to form a durable, lightweight panel, whereas tempered glass is produced through thermal or chemical treatments to enhance its impact resistance and shatter-proof properties. The differences in material composition and manufacturing processes result in fiberglass doors offering superior insulation and corrosion resistance, compared to tempered glass doors which provide enhanced safety and clarity.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Fiberglass doors offer excellent durability due to their resistance to dents, warping, and moisture damage, making them ideal for harsh weather conditions. Tempered glass, known for its high strength, is four to five times stronger than regular glass, providing superior impact resistance and enhanced safety in door applications. Comparing durability, fiberglass excels in longevity and low maintenance, while tempered glass ensures robust structural integrity and shatter resistance.
Aesthetic Options and Customization
Fiberglass doors offer extensive aesthetic options with customizable finishes that mimic natural wood grains and a wide range of colors, providing versatile design choices for various architectural styles. Tempered glass doors prioritize sleek, modern aesthetics with clear, frosted, or tinted glass panels, allowing for enhanced light transmission and privacy customization through etching or decorative patterns. Both materials enable tailored designs, but fiberglass excels in texture and color variety, while tempered glass focuses on elegant transparency and artistic glass customization.
Energy Efficiency and Insulation Properties
Fiberglass doors offer superior energy efficiency due to their excellent insulation properties, minimizing heat transfer and reducing energy bills. Tempered glass, while providing strength and safety, has lower insulation capabilities compared to fiberglass, potentially leading to higher energy loss. Choosing fiberglass enhances thermal performance and maintains consistent indoor temperatures, making it ideal for energy-conscious homeowners.
Security Features and Safety Performance
Tempered glass offers superior security features for doors due to its high tensile strength and ability to shatter into small, blunt pieces, reducing injury risk during breakage. Fibre glass doors provide enhanced safety performance by being impact-resistant and not shattering, maintaining structural integrity under forced entry attempts. Both materials contribute to security, but tempered glass excels in preventing sharp glass-related injuries, while fibre glass offers robust durability and resistance to sustained force.
Maintenance Requirements and Longevity
Fiberglass doors require minimal maintenance, resisting dents, rust, and corrosion while retaining their appearance over time, making them ideal for long-term durability in various weather conditions. Tempered glass doors provide enhanced strength and safety compared to regular glass, but they demand regular cleaning to prevent scratches and may require replacement if shattered, impacting overall longevity. Choosing fiberglass ensures lower upkeep and extended lifespan, whereas tempered glass balances durability with the need for careful maintenance to preserve its structural integrity.
Cost Factors and Value for Money
Fiberglass doors typically cost between $200 and $500, offering excellent durability and low maintenance compared to tempered glass doors, which range from $300 to $600 and provide superior strength and shatter resistance. Fiberglass doors deliver better energy efficiency and resist dents, making them a cost-effective long-term investment, while tempered glass doors enhance aesthetic appeal and security but may incur higher replacement costs if broken. Choosing fiberglass generally maximizes value for money due to its combination of affordability, durability, and minimal upkeep requirements.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Fibre glass doors have a lower environmental impact due to their energy-efficient manufacturing process and longer lifespan, which reduces waste compared to tempered glass doors. Tempered glass, while recyclable, requires intensive energy consumption during production and contributes to higher carbon emissions. Sustainable building practices favor fibre glass for its durability, lower maintenance, and reduced need for replacements, enhancing overall ecological benefits.
Best Use Cases: Choosing the Right Door Material
Fiberglass doors excel in durability, energy efficiency, and resistance to dents or rust, making them ideal for extreme weather conditions and high-traffic entryways. Tempered glass doors provide enhanced safety and visibility, perfect for modern interiors, patios, or entryways requiring natural light without compromising security. Selecting the right material depends on priorities such as insulation, maintenance, safety, and aesthetic appeal specific to the door's location and functionality.
Infographic: Fibre glass vs Tempered glass for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com