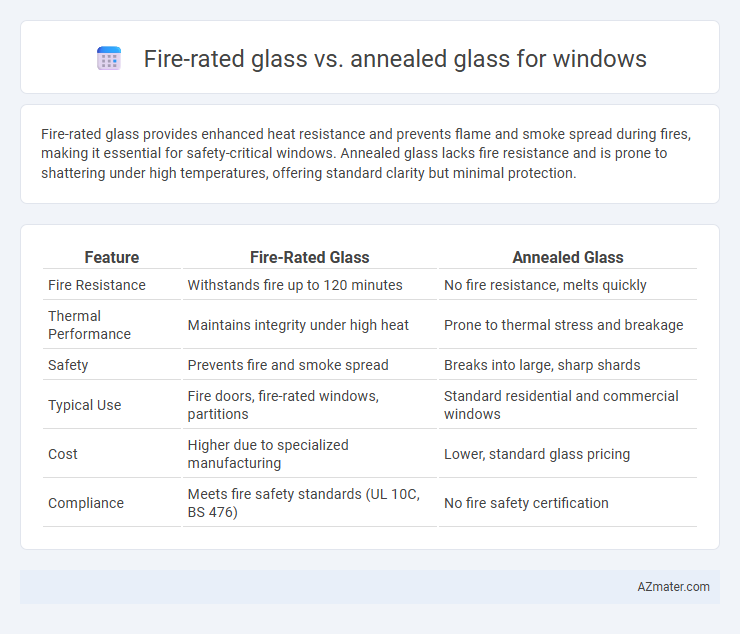
Fire-rated glass provides enhanced heat resistance and prevents flame and smoke spread during fires, making it essential for safety-critical windows. Annealed glass lacks fire resistance and is prone to shattering under high temperatures, offering standard clarity but minimal protection.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fire-Rated Glass | Annealed Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | Withstands fire up to 120 minutes | No fire resistance, melts quickly |
| Thermal Performance | Maintains integrity under high heat | Prone to thermal stress and breakage |
| Safety | Prevents fire and smoke spread | Breaks into large, sharp shards |
| Typical Use | Fire doors, fire-rated windows, partitions | Standard residential and commercial windows |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized manufacturing | Lower, standard glass pricing |
| Compliance | Meets fire safety standards (UL 10C, BS 476) | No fire safety certification |
Introduction to Fire-Rated Glass and Annealed Glass
Fire-rated glass is specifically engineered to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of fire and smoke, making it essential for fire safety in windows of residential and commercial buildings. Annealed glass, on the other hand, is standard float glass cooled slowly to relieve internal stresses but lacks the heat resistance necessary for fire protection. The key difference lies in fire-rated glass's ability to maintain integrity under extreme heat, while annealed glass is prone to shattering when exposed to intense temperatures.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Fire-rated glass is composed of specialized materials like ceramic or tempered glass with intumescent interlayers, designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent heat transfer during fires. Annealed glass is made by slowly cooling molten glass to remove internal stresses, resulting in a standard flat glass sheet without enhanced fire resistance. Manufacturing fire-rated glass requires additional processes such as layering or ceramic coating, whereas annealed glass undergoes a simple controlled cooling phase without these fire-protective enhancements.
Key Safety Features
Fire-rated glass provides enhanced safety by resisting high temperatures and preventing the spread of flames and smoke for specified durations, typically ranging from 20 to 120 minutes. Annealed glass lacks this fire resistance and is prone to breaking under thermal stress, posing higher risks in fire scenarios. Fire-rated glass often incorporates special interlayers or intumescent films to maintain integrity, ensuring critical protection in emergency situations.
Fire Resistance Capabilities Compared
Fire-rated glass offers significantly higher fire resistance capabilities compared to annealed glass, designed to withstand extreme heat and prevent the spread of flames and smoke for up to 120 minutes. Annealed glass, while standard for basic window applications, lacks the thermal insulation and structural integrity under fire conditions, making it susceptible to breaking quickly when exposed to high temperatures. Fire-rated glass incorporates specialized layers or coatings that provide enhanced durability and thermal protection, crucial for maintaining safety in fire-prone environments.
Thermal Performance Analysis
Fire-rated glass offers superior thermal insulation compared to annealed glass, maintaining integrity at high temperatures and preventing heat transfer for extended periods during fire exposure. Annealed glass lacks heat resistance and transfers thermal energy rapidly, increasing the risk of window failure under fire conditions. Thermal performance analysis shows fire-rated glass can withstand temperatures exceeding 800degC, while annealed glass typically fails at around 250degC, making fire-rated glass essential for enhanced safety in fire-prone environments.
Impact Resistance and Durability
Fire-rated glass offers superior impact resistance and enhanced durability compared to annealed glass, as it is designed to withstand high temperatures and physical stress during fire emergencies. Its multi-layer construction includes specialized interlayers that maintain structural integrity under impact, preventing shattering and providing prolonged protection. In contrast, annealed glass lacks these reinforced features, making it more prone to breakage and less effective in maintaining barrier performance under impact or thermal stress.
Application Suitability in Buildings
Fire-rated glass is specifically designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of fire and smoke, making it ideal for use in critical areas such as stairwells, corridors, and fire doors within commercial and residential buildings. Annealed glass, lacking fire-resistant properties, is best suited for non-safety-critical applications like standard windows or decorative features where thermal stress and impact resistance are not paramount. Choosing fire-rated glass enhances building safety codes compliance and occupant protection, whereas annealed glass prioritizes cost-effectiveness and aesthetic versatility without fire protection benefits.
Cost Comparison and Investment Value
Fire-rated glass typically costs 2 to 3 times more than annealed glass due to its specialized manufacturing process and enhanced safety features. Despite the higher initial investment, fire-rated glass can significantly increase a building's fire safety compliance and insurance benefits, adding long-term value. Annealed glass offers a lower upfront cost but lacks the fire resistance and durability that contribute to the overall safety and investment return of fire-rated alternatives.
Building Code and Regulatory Compliance
Fire-rated glass meets stringent building codes and fire safety regulations by providing specified fire resistance ratings, preventing the spread of flames and smoke during a fire event, which annealed glass cannot achieve. Annealed glass lacks the necessary fire protection certifications and does not comply with fire safety standards required in commercial and residential buildings. Using fire-rated glass ensures compliance with regulatory requirements such as ASTM E119 and NFPA 80, essential for legal adherence and occupant safety.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Windows
Fire-rated glass offers enhanced safety by withstanding high temperatures and preventing fire spread, making it ideal for windows in commercial buildings and fire-regulated areas. Annealed glass, while cost-effective and clear, lacks the heat resistance needed for fire protection, making it best suited for standard residential windows without stringent safety requirements. Selecting the right glass depends on regulatory compliance, safety priorities, and specific environmental conditions of the window location.
Infographic: Fire-rated glass vs Annealed glass for Window
 azmater.com
azmater.com