Prismatic glass enhances natural light diffusion and reduces glare in skylights, improving energy efficiency and visual comfort. Wired glass offers increased safety and fire resistance but compromises clarity and light transmission compared to prismatic glass.
Table of Comparison
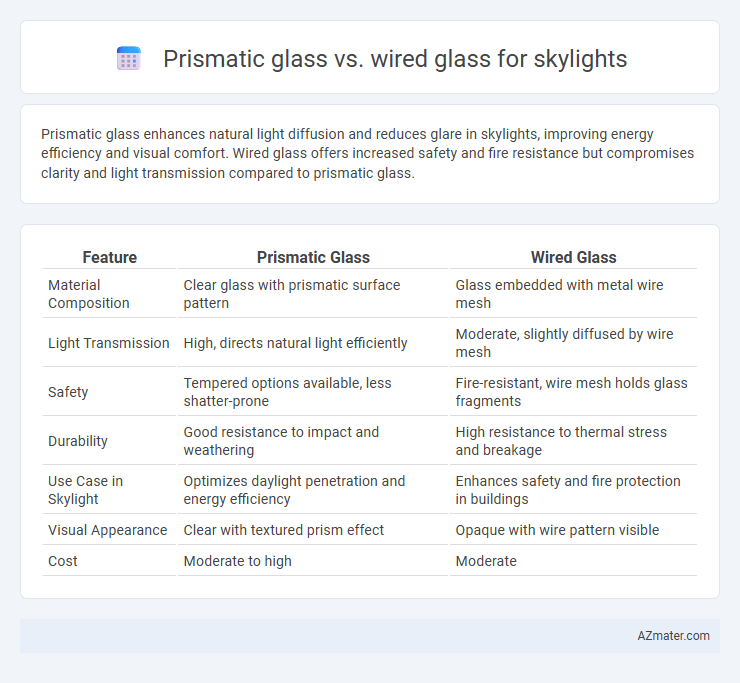
| Feature | Prismatic Glass | Wired Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Clear glass with prismatic surface pattern | Glass embedded with metal wire mesh |
| Light Transmission | High, directs natural light efficiently | Moderate, slightly diffused by wire mesh |
| Safety | Tempered options available, less shatter-prone | Fire-resistant, wire mesh holds glass fragments |
| Durability | Good resistance to impact and weathering | High resistance to thermal stress and breakage |
| Use Case in Skylight | Optimizes daylight penetration and energy efficiency | Enhances safety and fire protection in buildings |
| Visual Appearance | Clear with textured prism effect | Opaque with wire pattern visible |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Moderate |
Introduction to Skylight Glass Options
Prismatic glass and wired glass are two primary options for skylight glazing, each offering distinct advantages in light diffusion and safety. Prismatic glass enhances natural illumination by refracting sunlight, reducing glare and improving energy efficiency within buildings. Wired glass provides added security and fire resistance, making it suitable for skylights in commercial or high-risk environments where safety is a priority.
What is Prismatic Glass?
Prismatic glass is a specialized glazing material designed with built-in optical patterns that efficiently diffuse and redirect natural light within skylights, enhancing daylight distribution while reducing glare. It features micro-structured prisms etched or molded into the glass surface, maximizing light transmission and energy efficiency compared to wired glass, which primarily offers safety and fire resistance. This makes prismatic glass ideal for improving indoor illumination in commercial and residential skylight applications without compromising strength or clarity.
What is Wired Glass?
Wired glass is a type of safety glass that contains a mesh of thin, embedded wire within the glass layers, designed to provide enhanced fire resistance and prevent shattering. It is commonly used in skylight applications where safety and fire code compliance are critical, as the wire mesh holds the glass fragments together during breakage. Unlike prismatic glass, which focuses on light diffusion and optical clarity, wired glass prioritizes structural safety and durability, making it ideal for protecting interior spaces from fire hazards.
Light Transmission: Prismatic vs Wired Glass
Prismatic glass skylights optimize light transmission by diffusing sunlight evenly, reducing glare and enhancing natural illumination within interior spaces. Wired glass, embedded with a wire mesh for safety, tends to diminish light transmission slightly due to its internal wire grid and thicker composition. Prismatic glass offers superior clarity and brightness compared to wired glass, making it ideal for maximizing daylight in skylight applications.
Safety and Security Features
Prismatic glass for skylights enhances safety by diffusing natural light while minimizing glare and reducing the risk of glass breakage through tempered or laminated options. Wired glass provides a robust security feature with its embedded wire mesh that prevents shards from scattering upon impact, making it ideal for areas prone to break-ins or harsh weather. Both types meet stringent building codes, but prismatic glass emphasizes light quality and tempered strength, while wired glass prioritizes containment and fire resistance.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Prismatic glass enhances skylight energy efficiency by diffusing natural light evenly, reducing the need for artificial lighting and minimizing solar heat gain, thereby lowering cooling costs. Wired glass, primarily designed for safety and fire resistance, has lower light transmission and higher thermal conductivity, leading to increased energy consumption for heating and cooling. Choosing prismatic glass over wired glass significantly optimizes daylight utilization and indoor temperature regulation, resulting in better overall energy performance for skylights.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Flexibility
Prismatic glass enhances skylight design by diffusing natural light evenly, creating dynamic shadow patterns and a visually appealing interior ambiance, whereas wired glass offers a more industrial look with limited light diffusion. Prismatic glass provides greater design flexibility through customizable prismatic patterns that can complement modern architectural styles, while wired glass prioritizes safety and structural integrity but with less variation in aesthetic options. Choosing prismatic glass allows architects to maximize natural lighting effects and stylistic creativity, making it ideal for spaces emphasizing visual elegance.
Durability and Maintenance Needs
Prismatic glass offers enhanced durability due to its tempered construction, resisting impacts and harsh weather more effectively than wired glass, which contains embedded wire mesh primarily for safety rather than strength. Maintenance needs for prismatic glass are typically lower because its smooth surface resists dirt accumulation and is easier to clean compared to the textured surface of wired glass that can trap debris and require more frequent upkeep. Choosing prismatic glass for skylights ensures long-lasting performance with reduced maintenance efforts, making it a practical option for both residential and commercial applications.
Cost Analysis: Prismatic vs Wired Glass
Prismatic glass for skylights generally incurs higher initial costs due to its specialized light-diffusing properties and manufacturing complexity compared to wired glass, which is more affordable and commonly used for safety and security purposes. Over time, prismatic glass can offer energy savings by enhancing natural light dispersion, potentially reducing artificial lighting expenses, while wired glass may require additional treatments or replacements to meet insulation standards. Maintenance costs are typically lower for wired glass because of its durability; however, prismatic glass's benefits in daylighting efficiency can offset its upfront investment.
Best Applications and Recommendations
Prismatic glass is ideal for skylights in commercial and residential buildings where maximizing natural light and reducing glare are essential, providing enhanced daylight diffusion and energy efficiency. Wired glass suits industrial or high-safety environments requiring fire resistance and durability, as it maintains structural integrity under heat while offering security benefits. For optimal performance, select prismatic glass in spaces prioritizing daylight quality and visual comfort, and opt for wired glass where safety codes and impact resistance are paramount.
Infographic: Prismatic glass vs Wired glass for Skylight
 azmater.com
azmater.com