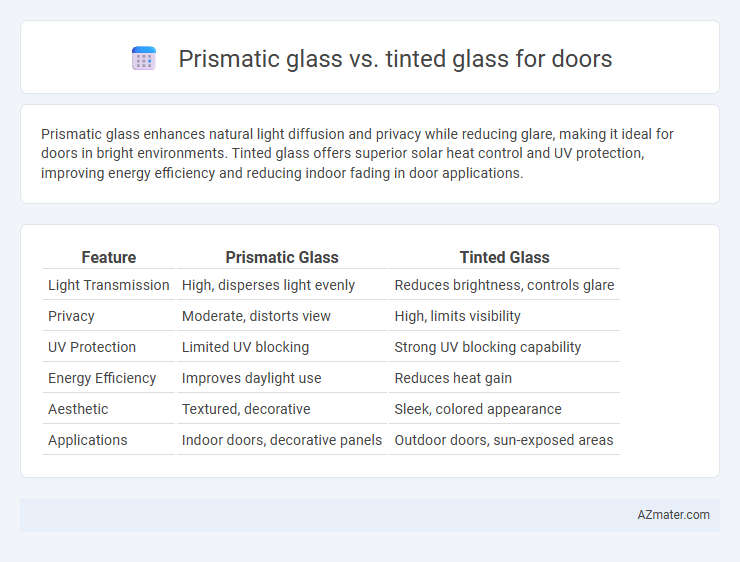
Prismatic glass enhances natural light diffusion and privacy while reducing glare, making it ideal for doors in bright environments. Tinted glass offers superior solar heat control and UV protection, improving energy efficiency and reducing indoor fading in door applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Prismatic Glass | Tinted Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Light Transmission | High, disperses light evenly | Reduces brightness, controls glare |
| Privacy | Moderate, distorts view | High, limits visibility |
| UV Protection | Limited UV blocking | Strong UV blocking capability |
| Energy Efficiency | Improves daylight use | Reduces heat gain |
| Aesthetic | Textured, decorative | Sleek, colored appearance |
| Applications | Indoor doors, decorative panels | Outdoor doors, sun-exposed areas |
Introduction to Prismatic and Tinted Glass for Doors
Prismatic glass enhances door aesthetics and functionality by diffusing light evenly, reducing glare while maintaining privacy through its textured surface. Tinted glass for doors controls solar heat gain and reduces UV exposure by absorbing sunlight, contributing to energy efficiency and glare reduction. Both types offer distinct benefits in light management and privacy, making them ideal choices based on specific architectural and environmental needs.
Definition and Key Features of Prismatic Glass
Prismatic glass is designed with a textured surface that refracts light to enhance brightness and privacy without significantly reducing visibility, making it ideal for doors in both residential and commercial settings. Its key features include light diffusion, glare reduction, and energy efficiency through better natural light distribution, which distinguishes it from tinted glass that primarily reduces light transmission and heat gain by adding color or film. Unlike tinted glass, prismatic glass maintains a clearer view while improving illumination and aesthetic appeal.
Understanding Tinted Glass: Properties and Applications
Tinted glass for doors incorporates metal oxides to reduce solar heat gain and glare, enhancing energy efficiency and occupant comfort in various architectural settings. Its properties include UV protection, reduced visible light transmission, and improved privacy, making it suitable for both residential and commercial entrances. Common applications involve entry doors in hot climates, where controlling light and heat without sacrificing visibility is critical.
Aesthetic Appeal: Visual Differences Between Prismatic and Tinted Glass
Prismatic glass offers a distinctive aesthetic with its faceted surface that refracts light, creating vibrant, kaleidoscopic patterns and enhancing visual interest in door designs. Tinted glass provides a sleek, uniform appearance by reducing glare and adding subtle color tones, complementing modern architectural styles with understated elegance. Both glass types elevate door aesthetics, but prismatic glass emphasizes dynamic light play while tinted glass focuses on consistent, muted shading.
Light Transmission and Privacy: A Comparative Analysis
Prismatic glass enhances light transmission by diffusing natural light evenly, reducing glare while maintaining privacy through its textured surface that obscures clear visibility. Tinted glass lowers light transmission by absorbing and reflecting sunlight, providing better privacy but potentially darkening interior spaces. Choosing between prismatic and tinted glass depends on balancing the need for maximum daylight penetration with the desired level of visual privacy for door applications.
Energy Efficiency and UV Protection in Door Glass Options
Prismatic glass enhances natural light diffusion through doors, reducing reliance on artificial lighting and improving overall energy efficiency by maintaining indoor temperature stability. Tinted glass provides superior UV protection by blocking significant amounts of harmful rays, which helps prevent interior fading and reduces heat buildup. Combining prismatic or tinted options can optimize both energy savings and UV defense, making them ideal for door glass choices in climate-sensitive environments.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Prismatic glass offers enhanced durability due to its textured surface, which resists scratches and minimizes visible smudges, making it ideal for high-traffic door applications. Tinted glass, while providing UV protection and glare reduction, may require more frequent cleaning as smudges and dirt are more noticeable on its smooth surface. Maintenance for prismatic glass involves simple wiping without specialized products, whereas tinted glass maintenance often benefits from specific cleaning agents to preserve tint quality and prevent discoloration.
Cost Comparison: Prismatic vs Tinted Glass for Doors
Prismatic glass typically costs 20-30% more than tinted glass due to its complex manufacturing process and enhanced light diffusion properties. Tinted glass offers a more budget-friendly option, reducing glare and solar heat gain at a lower price point, making it popular for cost-conscious door installations. Choosing between prismatic and tinted glass depends on balancing the higher upfront investment of prismatic glass against the affordability and basic functionality of tinted glass.
Best Use Cases for Prismatic and Tinted Door Glass
Prismatic glass is ideal for doors in commercial and office settings where maximizing natural light while maintaining privacy and reducing glare is essential. Tinted glass suits residential and automotive doors by enhancing privacy, reducing heat gain, and providing UV protection. Choosing prismatic glass benefits spaces requiring diffused light control, while tinted glass excels in environments needing energy efficiency and sun shading.
Choosing the Right Glass: Factors to Consider for Homeowners
Prismatic glass enhances natural light diffusion while maintaining privacy, making it ideal for homeowners seeking bright, glare-free interiors. Tinted glass reduces solar heat gain and UV exposure, which is beneficial in hot climates or for energy efficiency. When choosing the right glass for doors, consider factors such as climate, desired privacy level, energy savings, and aesthetic preferences.
Infographic: Prismatic glass vs Tinted glass for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com