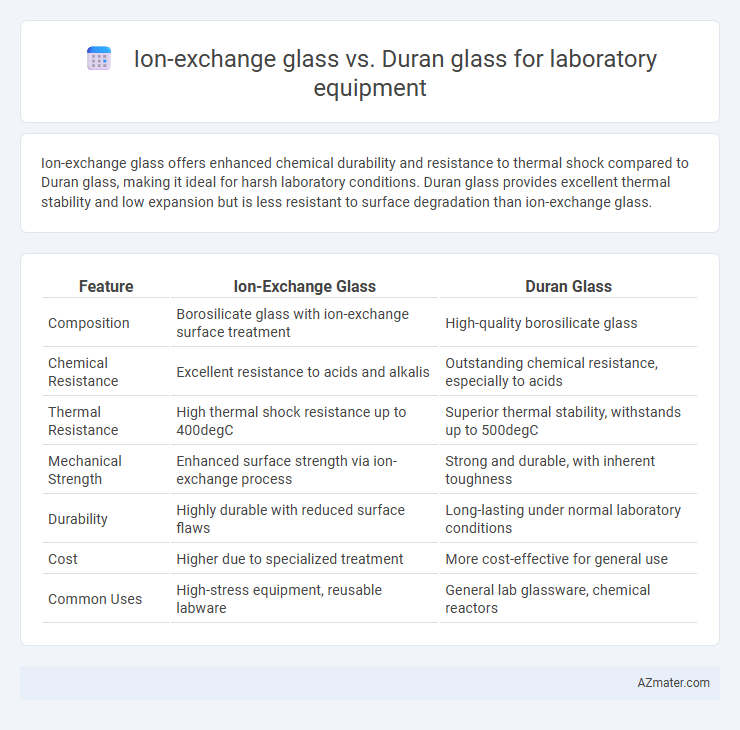
Ion-exchange glass offers enhanced chemical durability and resistance to thermal shock compared to Duran glass, making it ideal for harsh laboratory conditions. Duran glass provides excellent thermal stability and low expansion but is less resistant to surface degradation than ion-exchange glass.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ion-Exchange Glass | Duran Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Borosilicate glass with ion-exchange surface treatment | High-quality borosilicate glass |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to acids and alkalis | Outstanding chemical resistance, especially to acids |
| Thermal Resistance | High thermal shock resistance up to 400degC | Superior thermal stability, withstands up to 500degC |
| Mechanical Strength | Enhanced surface strength via ion-exchange process | Strong and durable, with inherent toughness |
| Durability | Highly durable with reduced surface flaws | Long-lasting under normal laboratory conditions |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized treatment | More cost-effective for general use |
| Common Uses | High-stress equipment, reusable labware | General lab glassware, chemical reactors |
Introduction to Laboratory Glassware Types
Ion-exchange glass offers enhanced chemical resistance and durability compared to Duran glass, making it ideal for handling aggressive reagents in laboratory settings. Duran glass, a borosilicate glass, provides excellent thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock, widely used for general laboratory apparatus like beakers and flasks. Selecting between ion-exchange and Duran glass depends on application-specific needs such as chemical compatibility, mechanical strength, and cost-efficiency for precise laboratory processes.
What is Ion-Exchange Glass?
Ion-exchange glass is a type of laboratory glass treated to improve chemical resistance and mechanical strength by replacing smaller sodium ions with larger potassium ions within its structure. This process enhances durability against thermal shock and chemical attack compared to standard Duran glass, which is a borosilicate glass known for its general chemical resistance and thermal stability. Ion-exchange glass is particularly beneficial for sensitive analytical applications requiring higher resistance to abrasion and stress.
Understanding Duran Glass: Key Properties
Duran glass is a borosilicate glass renowned for its exceptional thermal resistance, chemical durability, and low thermal expansion coefficient around 3.3 x 10-6 K-1, making it ideal for laboratory equipment exposed to rapid temperature changes. Its high resistance to acids, bases, and solvents ensures stability in various chemical processes, outperforming standard soda-lime glass often used in ion-exchange glass. These key properties allow Duran glass to maintain structural integrity and clarity during rigorous laboratory applications.
Chemical Resistance: Ion-Exchange vs Duran Glass
Ion-exchange glass offers superior chemical resistance compared to Duran glass due to its enhanced surface ion exchange process that reduces alkali ion leaching and increases durability against corrosive chemicals. Duran glass, a borosilicate glass, provides excellent resistance to thermal shock and wide chemical compatibility but may be less resistant to aggressive alkaline solutions than ion-exchange glass. Selecting ion-exchange glass improves longevity and performance in highly acidic or basic laboratory environments where chemical resistance is critical.
Thermal Stability and Shock Resistance
Ion-exchange glass offers superior thermal stability compared to Duran glass, maintaining structural integrity at higher temperatures up to 500degC without deformation. Its enhanced shock resistance results from the ion-exchange process, which strengthens the glass surface, making it less prone to cracking during rapid temperature changes or mechanical impact. Duran glass, while durable and chemically resistant, typically withstands temperatures around 450degC and exhibits lower resistance to thermal shock, limiting its use in high-stress laboratory applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Ion-exchange glass exhibits significantly higher mechanical strength than Duran glass due to its chemically toughened surface, which resists scratches and impact, making it ideal for high-stress laboratory applications. This enhanced durability allows ion-exchange glass to withstand thermal shocks and mechanical impacts better than Duran glass, which, while chemically resistant, is more prone to breakage under sudden temperature changes or mechanical stress. Laboratories requiring robust, long-lasting glassware often prefer ion-exchange glass for its superior resistance to physical damage and extended service life compared to Duran glass.
Transparency and Optical Clarity Differences
Ion-exchange glass offers superior optical clarity due to its enhanced surface smoothness and reduced micro-defects, making it ideal for applications requiring high-precision optical measurements. Duran glass, while chemically resistant and durable, exhibits slightly lower transparency and can present minor imperfections that affect optical clarity. The choice between ion-exchange glass and Duran glass depends on prioritizing optical performance over chemical durability in laboratory equipment.
Cost-Efficiency and Availability in Laboratories
Ion-exchange glass offers enhanced chemical resistance and durability compared to Duran glass, resulting in longer equipment lifespan and lower replacement costs, making it cost-efficient for high-usage laboratories. While Duran glass is widely available and more affordable upfront, frequent breakage and chemical wear can increase long-term expenses. Laboratories prioritizing budget-friendly initial investment may prefer Duran glass, but those seeking cost-efficiency through durability and reduced maintenance often opt for ion-exchange glass despite its higher initial price.
Typical Applications in Scientific Research
Ion-exchange glass is commonly used in laboratory equipment requiring high chemical resistance and enhanced mechanical strength, such as microfluidic devices and precision analytical instruments. Duran glass, known for its exceptional thermal resistance and durability, is preferred in applications involving high-temperature reactions, distillation, and storage of corrosive chemicals. Both glasses are vital in scientific research, with ion-exchange glass excelling in microanalysis and Duran glass widely adopted for general-purpose labware including flasks and beakers.
Choosing the Right Glassware for Your Laboratory Needs
Ion-exchange glass offers enhanced chemical resistance and durability, making it ideal for laboratories handling aggressive chemicals and requiring frequent sterilization. Duran glass, a borosilicate glass, is valued for its excellent thermal shock resistance and clarity, suitable for everyday laboratory applications involving heating and cooling cycles. Selecting the right glassware depends on the specific chemical and thermal demands of your experiments, balancing durability with cost-effectiveness.
Infographic: Ion-exchange glass vs Duran glass for Laboratory equipment
 azmater.com
azmater.com