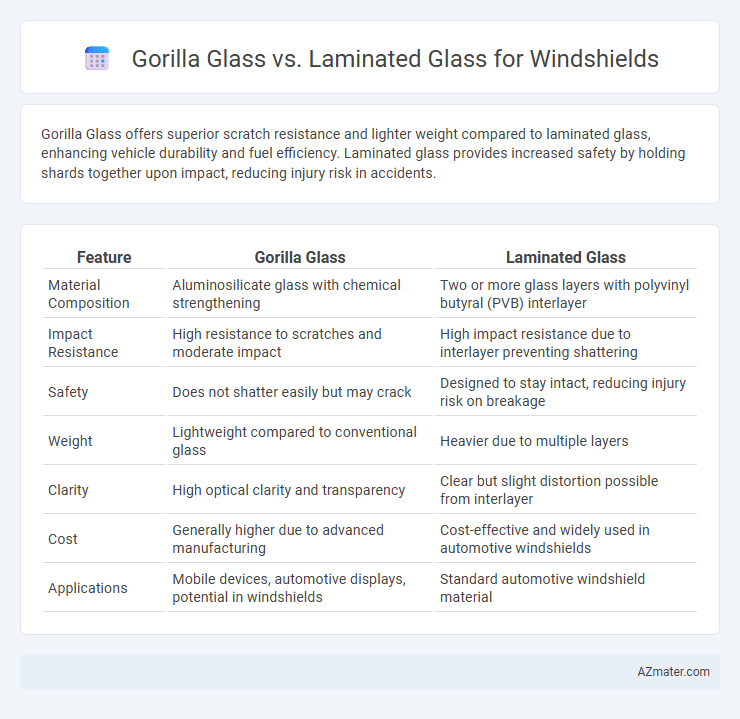
Gorilla Glass offers superior scratch resistance and lighter weight compared to laminated glass, enhancing vehicle durability and fuel efficiency. Laminated glass provides increased safety by holding shards together upon impact, reducing injury risk in accidents.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Gorilla Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Aluminosilicate glass with chemical strengthening | Two or more glass layers with polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer |
| Impact Resistance | High resistance to scratches and moderate impact | High impact resistance due to interlayer preventing shattering |
| Safety | Does not shatter easily but may crack | Designed to stay intact, reducing injury risk on breakage |
| Weight | Lightweight compared to conventional glass | Heavier due to multiple layers |
| Clarity | High optical clarity and transparency | Clear but slight distortion possible from interlayer |
| Cost | Generally higher due to advanced manufacturing | Cost-effective and widely used in automotive windshields |
| Applications | Mobile devices, automotive displays, potential in windshields | Standard automotive windshield material |
Introduction to Gorilla Glass and Laminated Glass
Gorilla Glass is an ultra-thin, chemically strengthened glass developed by Corning, known for its high scratch resistance and durability in electronic devices, now being adapted for automotive windshields. Laminated glass, made by bonding two layers of glass with a plastic interlayer such as polyvinyl butyral (PVB), offers enhanced safety by holding shards together upon impact, reducing the risk of injury. While Gorilla Glass provides superior strength and lighter weight, laminated glass remains the industry standard for windshields due to its proven impact resistance and shatterproof properties.
Material Composition and Structure
Gorilla Glass is an aluminosilicate glass known for its high chemical durability and scratch resistance, achieved through an ion-exchange process that compresses the surface layer. Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded with an interlayer, usually polyvinyl butyral (PVB), providing enhanced impact resistance and preventing shattering. The structured layering in laminated glass offers superior safety for windshields, while Gorilla Glass is prized for its thinness and strength but is less common in automotive applications.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Gorilla Glass offers superior strength due to its chemically strengthened aluminosilicate composition, making it more resistant to scratches and impacts compared to laminated glass. Laminated glass, composed of two glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer, excels in durability by preventing shattering and holding glass fragments together upon impact. In terms of long-term performance, Gorilla Glass provides enhanced resistance to everyday wear and environmental factors, while laminated glass prioritizes occupant safety through impact absorption and retaining structural integrity after collisions.
Impact Resistance and Safety
Gorilla Glass exhibits superior impact resistance compared to laminated glass due to its chemically strengthened composition, making it less prone to shattering upon collision. Laminated glass, composed of two layers of glass with a plastic interlayer, provides enhanced safety by holding shards together when cracked, reducing injury risk during accidents. While Gorilla Glass offers higher durability and scratch resistance, laminated glass remains the industry standard for windshields due to its proven effectiveness in maintaining structural integrity and occupant protection in crashes.
Clarity and Optical Performance
Gorilla Glass offers superior clarity and optical performance due to its thin, chemically strengthened composition, reducing light distortion and providing a clearer view compared to traditional laminated glass. Laminated glass, while effective for safety and impact resistance, often has a multi-layer structure that can slightly diminish optical clarity and increase glare. High-quality Gorilla Glass windshields enhance visibility, making them ideal for advanced driver-assistance systems that rely on precise optical performance.
Weight and Thickness Differences
Gorilla Glass used in windshields is significantly thinner and lighter than traditional laminated glass, reducing overall vehicle weight and improving fuel efficiency. Laminated glass typically measures around 6-8 millimeters in thickness, whereas Gorilla Glass can be as thin as 0.5-1.1 millimeters while maintaining high strength and durability. The reduced thickness and weight of Gorilla Glass contribute to enhanced vehicle performance and increased cargo capacity.
Scratch and Damage Resistance
Gorilla Glass offers superior scratch resistance due to its chemically strengthened aluminosilicate composition, making it highly durable against everyday abrasions. Laminated glass, composed of two glass layers with a plastic interlayer, provides enhanced impact resistance and prevents shattering but is more prone to surface scratches over time. For windshield applications, Gorilla Glass excels in maintaining clarity and structural integrity, while laminated glass prioritizes safety through shatter-resistance despite moderate scratch vulnerability.
Cost and Availability
Gorilla Glass windshields typically cost 20-30% more than laminated glass due to their advanced scratch resistance and durability. Laminated glass remains widely available and is the industry standard for most vehicles, ensuring easier and faster replacement options. The higher price of Gorilla Glass can limit its availability to specific premium or electric car models only.
Installation and Repair Considerations
Gorilla Glass offers a thinner and lighter profile, simplifying installation with reduced frame modifications compared to traditional laminated glass, which is thicker and heavier, often requiring reinforced mounting hardware. Repairing Gorilla Glass can be more challenging due to its chemical composition and strength, often necessitating complete panel replacement, whereas laminated glass allows for localized repairs such as chip filling and crack stabilization. Installation time for Gorilla Glass is typically faster, but repair costs tend to be higher, while laminated glass installations may take longer but offer more cost-effective repair options.
Which Windshield Glass Is Right for You?
Gorilla Glass offers superior scratch resistance, lightweight design, and enhanced durability, making it ideal for drivers seeking a high-tech, long-lasting windshield. Laminated glass provides excellent impact resistance and safety by preventing shattering, which is essential for comprehensive protection and noise reduction. Choosing between Gorilla Glass and laminated glass depends on whether you prioritize cutting-edge strength and weight savings or proven safety and sound insulation for your vehicle.
Infographic: Gorilla glass vs Laminated glass for Windshield
 azmater.com
azmater.com