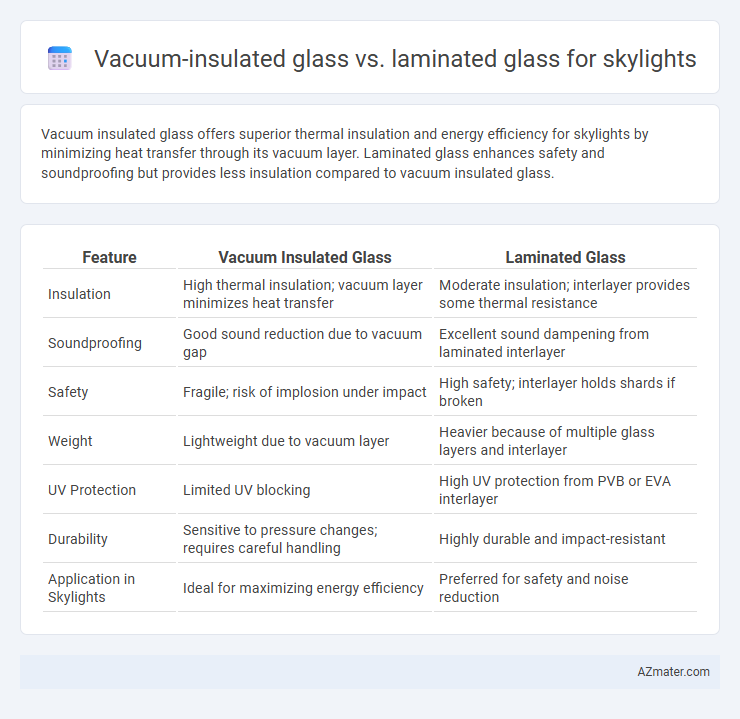
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation and energy efficiency for skylights by minimizing heat transfer through its vacuum layer. Laminated glass enhances safety and soundproofing but provides less insulation compared to vacuum insulated glass.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vacuum Insulated Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Insulation | High thermal insulation; vacuum layer minimizes heat transfer | Moderate insulation; interlayer provides some thermal resistance |
| Soundproofing | Good sound reduction due to vacuum gap | Excellent sound dampening from laminated interlayer |
| Safety | Fragile; risk of implosion under impact | High safety; interlayer holds shards if broken |
| Weight | Lightweight due to vacuum layer | Heavier because of multiple glass layers and interlayer |
| UV Protection | Limited UV blocking | High UV protection from PVB or EVA interlayer |
| Durability | Sensitive to pressure changes; requires careful handling | Highly durable and impact-resistant |
| Application in Skylights | Ideal for maximizing energy efficiency | Preferred for safety and noise reduction |
Introduction to Skylight Glazing Options
Skylight glazing options primarily include vacuum insulated glass and laminated glass, each offering distinct benefits for energy efficiency and safety. Vacuum insulated glass provides superior thermal insulation by eliminating air gaps, reducing heat transfer and enhancing indoor climate control. Laminated glass enhances security and noise reduction due to its layered structure, making it an optimal choice for impact resistance and soundproofing in skylights.
What is Vacuum Insulated Glass (VIG)?
Vacuum Insulated Glass (VIG) consists of two glass panes separated by a vacuum layer that drastically reduces heat transfer, providing superior thermal insulation compared to conventional glazing. This technology minimizes energy loss, controls condensation, and enhances soundproofing, making it highly suitable for skylights in energy-efficient buildings. Unlike laminated glass, which uses interlayers for impact resistance and safety, VIG focuses on thermal performance by eliminating conductive and convective heat flow within the glass cavity.
What is Laminated Glass?
Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together with an interlayer, typically made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), which enhances safety by preventing shattering upon impact. It provides excellent sound insulation, UV protection, and increased security, making it ideal for skylights where durability and occupant safety are critical. Compared to vacuum insulated glass, laminated glass offers superior impact resistance and retains structural integrity even when broken, ensuring continued protection in skylight applications.
Key Performance Differences
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation with a U-value as low as 0.4 W/m2K, significantly reducing heat transfer compared to laminated glass, which typically ranges between 2.0 and 3.0 W/m2K. Laminated glass excels in safety and sound insulation due to its polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, providing enhanced impact resistance and noise reduction, whereas vacuum insulated glass prioritizes energy efficiency with minimal thickness and weight. For skylight applications, vacuum insulated glass maximizes daylight harvesting while minimizing heat loss, whereas laminated glass enhances security and acoustic comfort.
Thermal Insulation Capabilities
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) offers superior thermal insulation for skylights by eliminating conductive heat transfer through the vacuum layer, achieving U-values as low as 0.5 W/m2K, surpassing laminated glass typically rated around 2.8 W/m2K. Laminated glass consists of multiple layers bonded with a plastic interlayer, providing moderate thermal performance but primarily enhancing safety and sound insulation rather than advanced heat retention or loss prevention. For energy-efficient skylights, VIG's advanced thermal properties reduce heating and cooling demands, making it a preferred choice over laminated glass in climates with significant temperature variations.
Soundproofing and Noise Reduction
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) provides superior soundproofing for skylights due to its vacuum layer, which eliminates air particles and significantly reduces sound transmission frequencies compared to laminated glass. Laminated glass incorporates a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer that effectively dampens noise by absorbing sound vibrations, making it a reliable choice for moderate noise reduction. For environments with high external noise, VIG outperforms laminated glass by offering enhanced acoustic insulation while maintaining thermal efficiency.
Safety and Security Features
Vacuum insulated glass (VIG) offers enhanced thermal insulation and reduced condensation, while laminated glass provides superior safety and security through its shatter-resistant interlayer that holds broken pieces together upon impact. Laminated glass is preferred for skylights in high-risk areas due to its ability to prevent glass shards from falling and its resistance to forced entry. Combining VIG with laminated layers can maximize both energy efficiency and occupant protection in skylight applications.
Longevity and Maintenance Needs
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior longevity for skylights due to its durable multi-layer design that resists thermal stress and condensation, significantly reducing maintenance needs over time. Laminated glass, while providing excellent impact resistance and safety benefits, may require more frequent inspections for seal integrity and potential delamination. Both types enhance skylight performance, but vacuum insulated glass ensures lower long-term upkeep and better durability in varied environmental conditions.
Cost Comparison and Value
Vacuum insulated glass typically costs 20-30% more than laminated glass for skylights due to its complex manufacturing process and superior thermal insulation properties, which lead to significant energy savings over time. Laminated glass offers a lower upfront cost and enhanced safety by holding glass fragments together if broken, but it lacks the same level of energy efficiency as vacuum insulated glass. When evaluating long-term value, vacuum insulated glass provides better return on investment through reduced heating and cooling expenses, while laminated glass remains a cost-effective option for those prioritizing budget over maximum insulation performance.
Choosing the Best Glass for Your Skylight
Vacuum insulated glass offers superior thermal insulation and energy efficiency for skylights by eliminating air gaps between panes, reducing heat transfer significantly compared to laminated glass. Laminated glass excels in impact resistance and safety, as it holds shards together upon breakage, making it ideal for areas with high risk of storm damage or falling debris. Choosing the best glass for your skylight depends on prioritizing energy savings through vacuum insulated glass or enhanced safety and security with laminated glass.
Infographic: Vacuum insulated glass vs Laminated glass for Skylight
 azmater.com
azmater.com