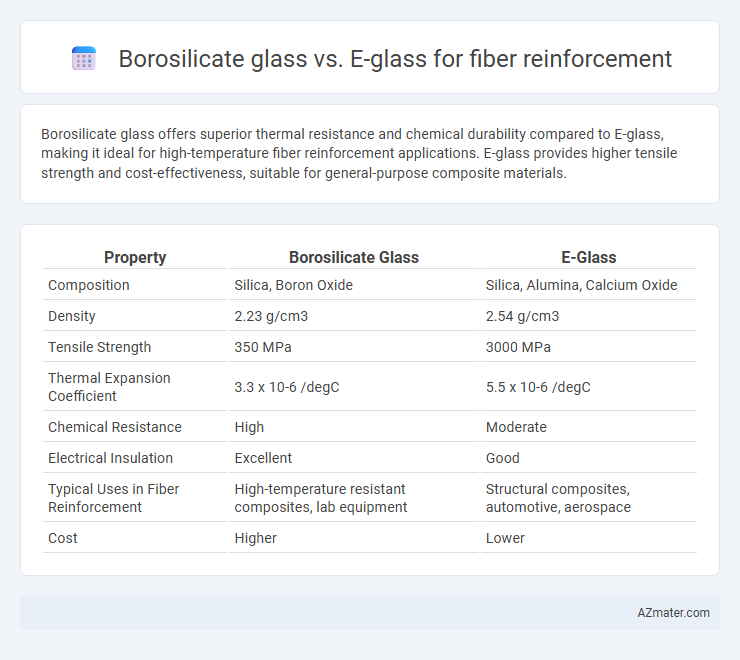
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and chemical durability compared to E-glass, making it ideal for high-temperature fiber reinforcement applications. E-glass provides higher tensile strength and cost-effectiveness, suitable for general-purpose composite materials.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Borosilicate Glass | E-Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Silica, Boron Oxide | Silica, Alumina, Calcium Oxide |
| Density | 2.23 g/cm3 | 2.54 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 350 MPa | 3000 MPa |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | 3.3 x 10-6 /degC | 5.5 x 10-6 /degC |
| Chemical Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent | Good |
| Typical Uses in Fiber Reinforcement | High-temperature resistant composites, lab equipment | Structural composites, automotive, aerospace |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Fiber Reinforced Composites
Fiber reinforced composites utilize fibers like borosilicate glass and E-glass to enhance mechanical properties such as strength, stiffness, and corrosion resistance. Borosilicate glass fibers offer superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, making them ideal for high-temperature and harsh chemical environments. E-glass fibers are more cost-effective and provide excellent electrical insulation and tensile strength, widely applied in structural and marine composites.
Overview of Borosilicate Glass
Borosilicate glass, known for its exceptional thermal resistance and low coefficient of thermal expansion, is widely used in fiber reinforcement applications requiring high durability and chemical stability. Its unique composition, primarily consisting of silica and boron trioxide, imparts superior resistance to thermal shock and corrosion compared to conventional E-glass fibers. These properties make borosilicate glass fibers ideal for advanced composites in aerospace and chemical industries where performance under extreme conditions is critical.
Understanding E-Glass Properties
E-glass offers high tensile strength around 3.45 GPa and excellent corrosion resistance, making it a preferred choice for fiber reinforcement in composites. Its low cost and good electrical insulation properties enhance its application in construction and aerospace industries. Compared to borosilicate glass, E-glass provides superior mechanical durability but lower thermal resistance, highlighting the importance of selecting materials tailored to specific performance needs.
Comparative Chemical Compositions
Borosilicate glass contains approximately 70-80% silica (SiO2) with significant amounts of boron trioxide (B2O3) ranging from 7-13%, which enhances thermal resistance and chemical durability. E-glass, or electrical glass, primarily consists of 52-56% silica, 12-16% alumina (Al2O3), and 16-25% calcium oxide (CaO), providing excellent electrical insulation and mechanical strength. The lower boron content and higher alumina and calcium oxide levels in E-glass contribute to its distinct chemical stability and suitability for electrical applications compared to the more heat-resistant and chemically inert borosilicate glass fibers.
Mechanical Strength: Borosilicate vs E-Glass
Borosilicate glass exhibits higher thermal resistance but lower tensile strength compared to E-glass, which offers superior mechanical strength with tensile strengths typically ranging from 2.4 to 3.5 GPa. E-glass fiber reinforcement is preferred in composite applications requiring higher load-bearing capabilities due to its enhanced elasticity modulus, generally between 72 and 76 GPa. The mechanical performance gap makes E-glass more suitable for structural reinforcements, while borosilicate glass is favored for thermal stability in fiber-reinforced composites.
Thermal Resistance and Stability
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance compared to E-glass, withstanding temperatures up to 821degC due to its low thermal expansion coefficient of approximately 3.3 x 10^-6 /degC, making it ideal for high-temperature fiber reinforcement applications. E-glass, primarily used in composites, has a higher thermal expansion coefficient around 5.5 x 10^-6 /degC and a maximum use temperature near 540degC, which limits its thermal stability under extreme heat. The enhanced thermal stability of borosilicate fibers ensures less structural degradation and better performance in environments requiring prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures.
Application Suitability in Industries
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and chemical durability, making it ideal for high-temperature and corrosive environments in industries such as aerospace and chemical processing. E-glass, renowned for its excellent mechanical strength and cost-effectiveness, is widely used in automotive, marine, and construction sectors where structural reinforcement and impact resistance are critical. Both materials serve distinct industrial applications with borosilicate excelling in specialized high-performance contexts and E-glass dominating general-purpose reinforcement.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Borosilicate glass offers higher thermal and chemical resistance for fiber reinforcement but comes at a significantly higher cost compared to E-glass, which remains the industry standard due to its balance of strength and affordability. E-glass fibers are widely available and produced in large volumes, making them more cost-efficient and accessible for mass-market composite applications. The lower raw material and manufacturing costs of E-glass enable competitive pricing, while borosilicate glass fibers are typically reserved for specialized, high-performance projects where expense is justified.
Environmental and Durability Considerations
Borosilicate glass offers superior chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to E-glass, making it more durable in harsh environmental conditions such as high temperature and acidic or alkaline exposures. E-glass, while cost-effective and widely used, tends to degrade faster under moisture and UV exposure, compromising its long-term environmental performance. The enhanced durability of borosilicate glass fibers results in extended lifespan and reduced maintenance requirements in fiber-reinforced composites exposed to aggressive environments.
Choosing the Right Glass Fiber for Your Project
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and chemical stability, making it ideal for high-temperature and corrosive environments in fiber reinforcement applications. E-glass provides excellent electrical insulation, strength, and cost-effectiveness, widely used in general composite manufacturing. Selecting the right glass fiber depends on project-specific requirements such as thermal performance, mechanical strength, environmental exposure, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Borosilicate glass vs E-glass for Fiber reinforcement
 azmater.com
azmater.com