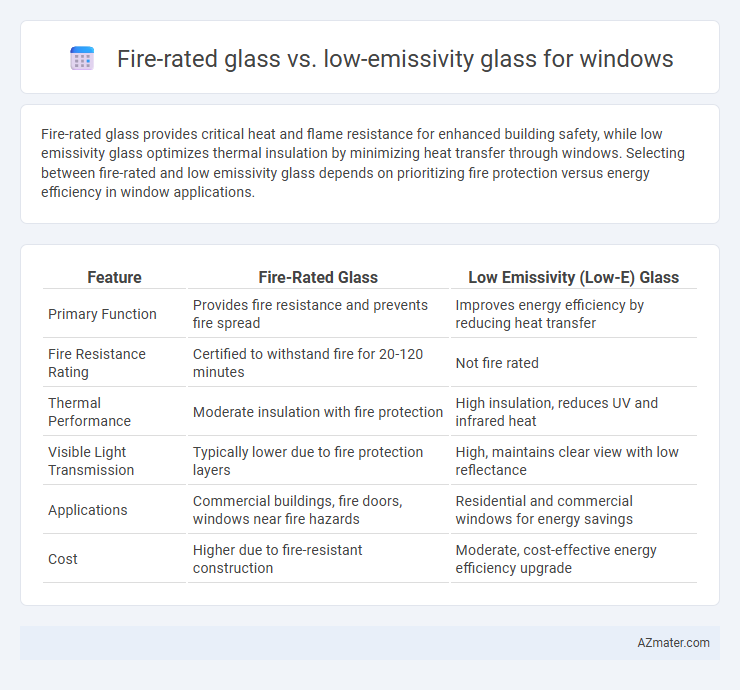
Fire-rated glass provides critical heat and flame resistance for enhanced building safety, while low emissivity glass optimizes thermal insulation by minimizing heat transfer through windows. Selecting between fire-rated and low emissivity glass depends on prioritizing fire protection versus energy efficiency in window applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fire-Rated Glass | Low Emissivity (Low-E) Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Provides fire resistance and prevents fire spread | Improves energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer |
| Fire Resistance Rating | Certified to withstand fire for 20-120 minutes | Not fire rated |
| Thermal Performance | Moderate insulation with fire protection | High insulation, reduces UV and infrared heat |
| Visible Light Transmission | Typically lower due to fire protection layers | High, maintains clear view with low reflectance |
| Applications | Commercial buildings, fire doors, windows near fire hazards | Residential and commercial windows for energy savings |
| Cost | Higher due to fire-resistant construction | Moderate, cost-effective energy efficiency upgrade |
Introduction to Fire-Rated Glass and Low Emissivity Glass
Fire-rated glass is engineered to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of fire and smoke, meeting strict safety standards for use in fire-rated doors and windows. Low emissivity (Low-E) glass features a microscopically thin coating designed to reduce heat transfer, enhancing energy efficiency by reflecting infrared and ultraviolet light while allowing natural daylight. Both types of glass serve distinct purposes: fire-rated glass prioritizes safety and containment, whereas Low-E glass focuses on thermal performance and energy savings.
Key Properties of Fire-Rated Glass
Fire-rated glass is specifically designed to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of flames and smoke during a fire, making it essential for safety in commercial and residential buildings. Its key properties include thermal resistance, structural integrity under extreme heat, and compliance with fire safety standards such as ASTM E119 or BS 476. Unlike low emissivity glass, which focuses on energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer, fire-rated glass prioritizes fire containment and visibility while maintaining durability under fire exposure.
Core Features of Low Emissivity (Low-E) Glass
Low Emissivity (Low-E) glass features a microscopically thin metallic coating that minimizes infrared and ultraviolet light penetration while maximizing visible light transmission, significantly improving energy efficiency. Its core function reduces heat transfer through windows, maintaining indoor temperature stability and lowering heating and cooling costs. Unlike fire-rated glass, Low-E glass is primarily designed for thermal insulation and solar control, not for fire resistance or safety.
Safety and Fire Protection: How Fire-Rated Glass Performs
Fire-rated glass is specifically engineered to withstand high temperatures and prevent the spread of flames and smoke, making it essential for fire safety in windows, while low emissivity (Low-E) glass primarily enhances energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer. Fire-rated glass incorporates multiple layers and intumescent materials that expand under heat, maintaining structural integrity and protecting occupants during a fire event. In contrast, Low-E glass lacks fire protection capabilities and should be combined with fire-rated glazing systems for comprehensive safety and energy performance.
Energy Efficiency Benefits of Low-E Glass
Low emissivity (Low-E) glass significantly improves window energy efficiency by minimizing heat transfer through its microscopically thin, transparent coatings that reflect infrared energy while allowing visible light to pass. Unlike fire-rated glass, which prioritizes safety and heat resistance, Low-E glass reduces heating and cooling costs by maintaining indoor temperature stability and decreasing reliance on HVAC systems. Its superior thermal insulation properties contribute to reduced energy consumption and enhanced comfort in both residential and commercial buildings.
Cost Differences: Fire-Rated vs Low-E Glass
Fire-rated glass typically costs significantly more than low emissivity (Low-E) glass due to its specialized construction and ability to withstand high temperatures and prevent fire spread. Low-E glass is primarily designed to improve energy efficiency by reflecting infrared light, resulting in lower manufacturing costs compared to the complex layers and materials used in fire-rated glass. Budget considerations for window installations often weigh the higher upfront investment in fire-rated glass against the potential energy savings and environmental benefits offered by Low-E glass.
Applications in Residential and Commercial Buildings
Fire-rated glass provides critical fire protection by withstanding high temperatures and preventing the spread of flames, making it ideal for use in stairwells, corridors, and exit doors of commercial buildings and multi-family residential complexes. Low emissivity (Low-E) glass enhances energy efficiency by reflecting infrared heat while allowing visible light, suitable for residential homes and commercial offices aiming to reduce heating and cooling costs. Selecting fire-rated glass is essential for meeting building safety codes, whereas Low-E glass supports sustainability goals and occupant comfort through improved thermal performance.
Aesthetic Considerations for Fire-Rated and Low-E Glass
Fire-rated glass offers robust safety features with a clear or lightly tinted appearance, maintaining visual clarity while meeting stringent building codes, but it may have a slightly thicker profile that affects sleek design aesthetics. Low emissivity (Low-E) glass enhances energy efficiency through a microscopically thin coating that reflects infrared heat, providing a subtle tint that can slightly alter the window's color and reflectivity, contributing to a modern, polished look. Both options balance functional performance with design appeal, but Low-E glass generally offers more versatility in aesthetics for contemporary architectural styles.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Fire-rated glass requires precise installation with fire-resistant frames and intumescent seals to maintain its integrity under high temperatures, demanding professional expertise and compliance with strict building codes. Low emissivity (Low-E) glass installation focuses on ensuring airtight seals within standard frames to maximize energy efficiency, with fewer specialized requirements compared to fire-rated glass. Maintenance for fire-rated glass involves regular inspections for cracks or seal deterioration affecting fire performance, whereas Low-E glass primarily needs routine cleaning to preserve its thermal insulation properties.
Choosing the Right Glass: Factors to Consider
When choosing between fire-rated glass and low emissivity (Low-E) glass for windows, consider fire safety standards, thermal insulation, and energy efficiency needs. Fire-rated glass offers critical protection against heat and flames, suitable for building codes requiring fire resistance, while Low-E glass significantly reduces heat transfer, lowering energy costs by reflecting infrared rays without compromising natural light. Assess building location, safety requirements, climate, and energy savings goals to select the glass that best balances fire protection and thermal performance.
Infographic: Fire-rated glass vs Low emissivity glass for Window
 azmater.com
azmater.com