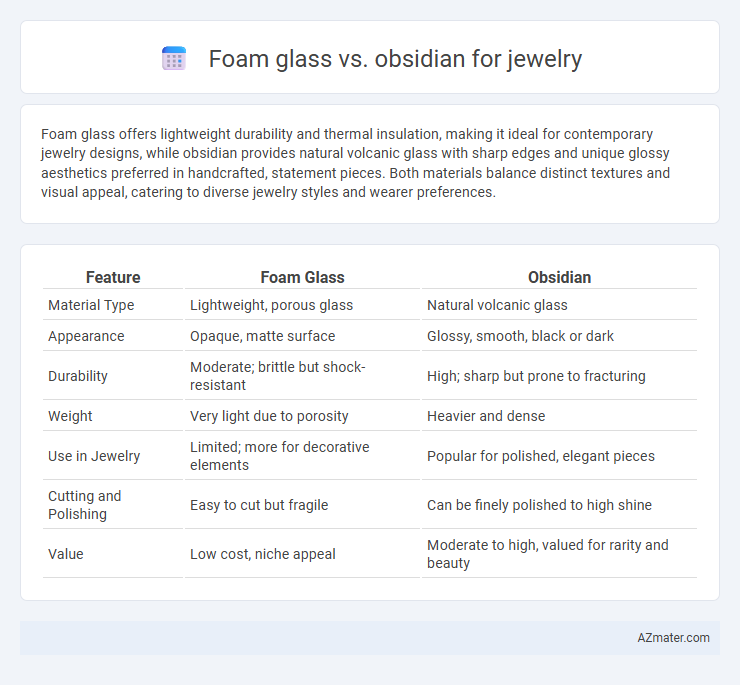
Foam glass offers lightweight durability and thermal insulation, making it ideal for contemporary jewelry designs, while obsidian provides natural volcanic glass with sharp edges and unique glossy aesthetics preferred in handcrafted, statement pieces. Both materials balance distinct textures and visual appeal, catering to diverse jewelry styles and wearer preferences.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Foam Glass | Obsidian |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Lightweight, porous glass | Natural volcanic glass |
| Appearance | Opaque, matte surface | Glossy, smooth, black or dark |
| Durability | Moderate; brittle but shock-resistant | High; sharp but prone to fracturing |
| Weight | Very light due to porosity | Heavier and dense |
| Use in Jewelry | Limited; more for decorative elements | Popular for polished, elegant pieces |
| Cutting and Polishing | Easy to cut but fragile | Can be finely polished to high shine |
| Value | Low cost, niche appeal | Moderate to high, valued for rarity and beauty |
Introduction to Foam Glass and Obsidian
Foam glass is a lightweight, porous material made from recycled glass that offers excellent durability and thermal insulation, making it a unique choice for jewelry with a modern, textured aesthetic. Obsidian, a naturally occurring volcanic glass, is prized for its smooth surface, deep black color, and sharp, reflective properties, often used in jewelry for its striking appearance and historical significance. Both materials provide distinct visual and tactile contrasts, with foam glass emphasizing innovative design and obsidian highlighting natural beauty.
Formation and Origins of Foam Glass
Foam glass is a man-made material created by heating crushed glass with a foaming agent, resulting in a lightweight, porous structure ideal for jewelry with a unique texture and durability. In contrast, obsidian is a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed from rapidly cooled lava, prized for its smooth, sharp edges and deep black sheen. The formation process of foam glass allows for controlled color variations and shapes, making it more versatile in design compared to the naturally limited appearance of obsidian.
Geological Background of Obsidian
Obsidian, a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed from rapidly cooled felsic lava, boasts a rich geological background rooted in igneous activity typically found in areas with rhyolitic lava flows. Unlike engineered foam glass, obsidian's unique vitreous texture and conchoidal fracture result from its high silica content and rapid quenching process during volcanic eruptions, making it prized for jewelry with natural and mystic aesthetic appeal. Its formation typically occurs along the edges of lava domes, volcanic vents, or in rhyolite lava flows, distinguishing it as a gemstone with a direct connection to specific tectonic and volcanic environments.
Physical Properties Comparison
Foam glass, a lightweight, porous material with excellent insulation properties, contrasts sharply with obsidian, a naturally occurring volcanic glass known for its smooth, glassy texture and sharp edges. Foam glass offers durability and resistance to moisture, but lacks the glossy finish and natural luster that make obsidian highly prized in jewelry. Obsidian's high density, fracture toughness, and reflective surface provide a striking aesthetic, while foam glass delivers unique design possibilities through its customizable shape and lightweight nature.
Aesthetic Differences in Jewelry Design
Foam glass in jewelry offers a lightweight, translucent appearance with vibrant color variations and a matte finish, creating an ethereal, modern aesthetic. Obsidian features a deep black, glossy surface with natural sheen and sharp, sleek edges, contributing to a bold, dramatic design style. The contrast between foam glass's frosted texture and obsidian's polished luster influences the choice of jewelry design, catering to minimalist versus statement pieces.
Durability and Wearability in Jewelry
Foam glass, known for its lightweight and porous structure, lacks the density and toughness required for durable jewelry, making it prone to chipping and surface wear. Obsidian, a natural volcanic glass, offers significant hardness and a smooth, glassy finish, enhancing its resistance to scratches and everyday wear. Its strong fracture toughness combined with a polished appearance ensures better long-term wearability in jewelry applications compared to foam glass.
Color Variations and Light Play
Foam glass jewelry displays a limited color palette, often featuring opaque or frosted hues in soft pastels and muted tones, resulting in subtle light diffusion rather than vibrant reflections. Obsidian offers a rich array of natural colors, including deep black, mahogany, and rare multi-hued variations like rainbow or sheen obsidian that exhibit striking iridescence and dynamic light play. The contrast between foam glass's matte finish and obsidian's glossy surface significantly impacts the jewelry's visual appeal, with obsidian providing more pronounced sparkle and color depth under varying lighting conditions.
Popular Uses in Modern Jewelry
Foam glass is rarely used in modern jewelry due to its fragile, porous nature and industrial origins, making it more suitable for decorative art pieces than wearable items. Obsidian, a natural volcanic glass, remains highly popular in jewelry for its smooth texture, deep black color, and ability to be polished into striking cabochons and beads. Modern designers favor obsidian for necklaces, rings, and earrings, appreciating its unique aesthetic and metaphysical properties that appeal to contemporary consumers.
Price and Availability Differences
Foam glass is significantly more affordable than obsidian, making it a popular choice for budget-conscious jewelry designers. Obsidian, being a natural volcanic glass, is rarer and often commands higher prices due to its unique patterns and limited availability in certain regions. While foam glass is mass-produced and widely accessible, obsidian must be sourced from specific volcanic areas, impacting its availability and cost in the jewelry market.
Sustainability and Ethical Considerations
Foam glass and obsidian offer distinct sustainability profiles for jewelry; foam glass is often created from recycled glass, minimizing waste and reducing environmental impact, while obsidian is a natural volcanic glass that requires careful sourcing to avoid ecological disruption. Ethically, foam glass supports circular economy principles by repurposing industrial byproducts, promoting responsible consumption, whereas obsidian mining must consider indigenous rights and habitat preservation. Choosing between the two involves evaluating recycled material benefits against the cultural and environmental implications of natural stone extraction in jewelry design.
Infographic: Foam glass vs Obsidian for Jewelry
 azmater.com
azmater.com