Dichroic glass offers multi-layered optical coatings that selectively reflect and transmit light, enhancing glare reduction and UV protection in windshields. Laminated glass consists of two glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer, providing superior impact resistance and safety by preventing shattering during collisions.
Table of Comparison
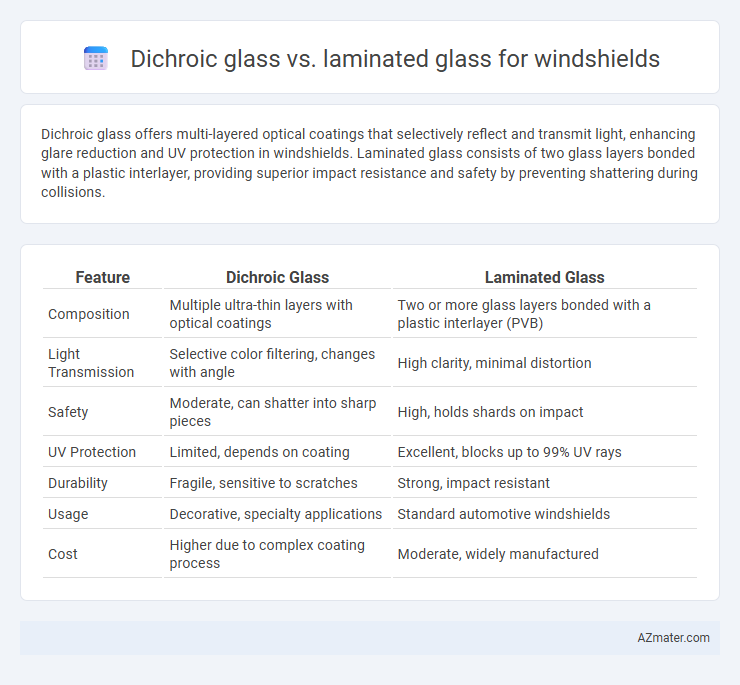
| Feature | Dichroic Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Multiple ultra-thin layers with optical coatings | Two or more glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer (PVB) |
| Light Transmission | Selective color filtering, changes with angle | High clarity, minimal distortion |
| Safety | Moderate, can shatter into sharp pieces | High, holds shards on impact |
| UV Protection | Limited, depends on coating | Excellent, blocks up to 99% UV rays |
| Durability | Fragile, sensitive to scratches | Strong, impact resistant |
| Usage | Decorative, specialty applications | Standard automotive windshields |
| Cost | Higher due to complex coating process | Moderate, widely manufactured |
Introduction to Windshield Glass Technologies
Dichroic glass uses multiple micro-layers to selectively filter light wavelengths, enhancing glare reduction and UV protection in windshields. Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded with an interlayer, providing superior safety by preventing shattering upon impact. Both technologies improve visibility and durability but cater to different functional priorities in automotive windshield design.
What is Dichroic Glass?
Dichroic glass in windshields features a multi-layer coating that selectively reflects and transmits light at different wavelengths, enhancing visibility and reducing glare and heat inside the vehicle. Unlike laminated glass, which consists of layers of glass bonded with a plastic interlayer for impact resistance and shatter prevention, dichroic glass primarily improves optical performance and energy efficiency. This advanced glass technology helps maintain cabin comfort by filtering UV and infrared radiation while preserving natural light transmission.
Understanding Laminated Glass
Laminated glass for windshields consists of two layers of glass bonded by a PVB (polyvinyl butyral) interlayer, offering enhanced safety by preventing shattering upon impact. This construction maintains structural integrity during collisions and reduces the risk of injury from flying glass shards. Compared to dichroic glass, laminated glass prioritizes safety and durability, making it the standard choice for automotive windshields.
Key Differences Between Dichroic and Laminated Glass
Dichroic glass features a multi-layer optical coating that reflects different wavelengths of light, enhancing color and reducing glare, while laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded with an interlayer that improves impact resistance and safety. Dichroic glass is primarily used for its aesthetic and light-filtering properties, whereas laminated glass is designed to provide structural integrity and prevent shattering in windshields. Key differences include dichroic glass's focus on optical effects versus laminated glass's emphasis on safety and durability in automotive applications.
Optical Properties Comparison
Dichroic glass exhibits unique optical properties by selectively filtering light wavelengths, producing vibrant color shifts and enhancing glare reduction, which improves visibility under varying lighting conditions. Laminated glass, composed of multiple layers bonded with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, offers consistent light transmission and reduces UV radiation exposure while maintaining structural integrity and clear vision. The primary optical advantage of dichroic glass lies in its ability to manipulate and enhance light wavelengths, whereas laminated glass prioritizes safety with minimal optical distortion.
Safety and Strength Factors
Dichroic glass offers enhanced safety through its multi-layered coatings that reflect and refract light, reducing glare and improving visibility, which is crucial for windshield performance. Laminated glass, composed of two or more layers of glass with an interlayer of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), provides superior strength and impact resistance, preventing shattering and enhancing occupant protection in collisions. While both improve safety, laminated glass remains the industry standard for windshields due to its ability to maintain structural integrity upon impact.
UV Protection and Light Control
Dichroic glass offers advanced UV protection by reflecting and filtering harmful ultraviolet rays, significantly reducing interior fading and occupant exposure. Laminated glass combines a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer that not only enhances UV blocking but also improves impact resistance and shatter prevention. While dichroic glass excels in controlling visible light transmission and glare through its multi-layer coatings, laminated glass provides consistent light diffusion and UV absorption, making it a reliable choice for comprehensive windshield safety and comfort.
Cost Analysis: Dichroic vs Laminated Glass
Dichroic glass typically incurs higher initial costs compared to laminated glass due to its complex manufacturing process involving multiple layers with special coatings for light filtering and color effects. Laminated glass, commonly used in windshields, offers cost-effective durability by sandwiching polyvinyl butyral (PVB) between two glass layers, providing impact resistance and safety at a lower price point. Over time, laminated glass reduces total ownership cost through easier replacement and proven longevity, while dichroic glass may result in higher maintenance expenses due to its specialized properties.
Suitability for Automotive Windshields
Dichroic glass offers enhanced aesthetic appeal and UV light filtering but lacks the structural integrity and shatter resistance required for automotive windshields. Laminated glass, consisting of two or more layers bonded with a polymer interlayer, provides superior safety by preventing shards from dispersing upon impact, making it the industry standard for windshields. Its durability against impacts, noise reduction properties, and UV protection underscore its suitability for automotive applications over dichroic glass.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Glass for Windshields
Dichroic glass offers superior aesthetic appeal and enhanced light filtering, making it ideal for drivers seeking style and UV protection. Laminated glass ensures maximum safety by providing high impact resistance and preventing shattering, which is crucial for windshield integrity. For optimal windshield performance, laminated glass remains the best choice due to its safety features and compliance with automotive standards.
Infographic: Dichroic glass vs Laminated glass for Windshield
 azmater.com
azmater.com