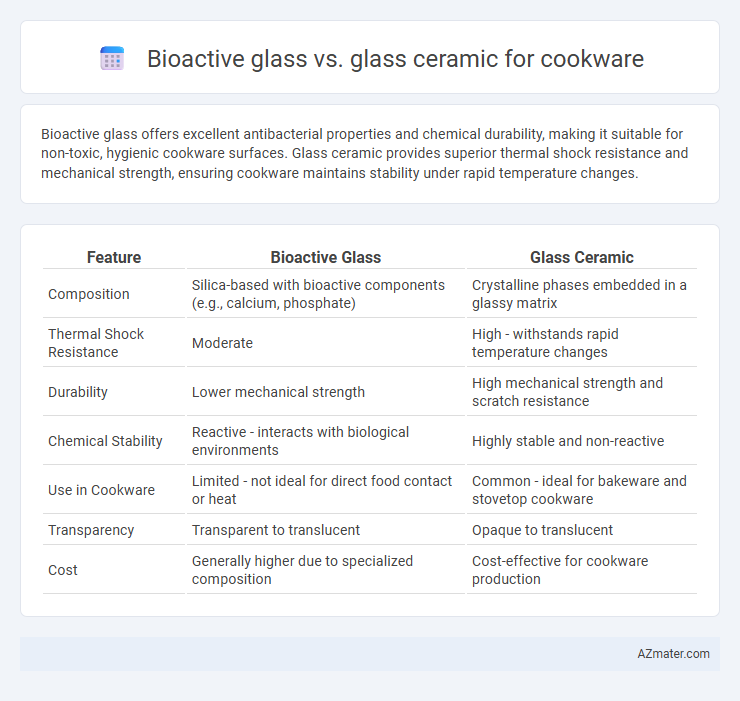
Bioactive glass offers excellent antibacterial properties and chemical durability, making it suitable for non-toxic, hygienic cookware surfaces. Glass ceramic provides superior thermal shock resistance and mechanical strength, ensuring cookware maintains stability under rapid temperature changes.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bioactive Glass | Glass Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Silica-based with bioactive components (e.g., calcium, phosphate) | Crystalline phases embedded in a glassy matrix |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate | High - withstands rapid temperature changes |
| Durability | Lower mechanical strength | High mechanical strength and scratch resistance |
| Chemical Stability | Reactive - interacts with biological environments | Highly stable and non-reactive |
| Use in Cookware | Limited - not ideal for direct food contact or heat | Common - ideal for bakeware and stovetop cookware |
| Transparency | Transparent to translucent | Opaque to translucent |
| Cost | Generally higher due to specialized composition | Cost-effective for cookware production |
Introduction to Bioactive Glass and Glass Ceramic
Bioactive glass exhibits unique biocompatibility and chemical durability, making it suitable for advanced applications beyond traditional cookware, such as medical implants. Glass ceramics, formed through controlled crystallization of glass, combine the mechanical strength of ceramics with the versatility of glass, offering superior thermal shock resistance ideal for cookware. The distinct structural and compositional differences between bioactive glass and glass ceramic influence their thermal properties and durability in cooking environments.
Chemical Composition Differences
Bioactive glass primarily consists of silica (SiO2), calcium oxide (CaO), and phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5), designed to interact biologically by forming hydroxycarbonate apatite layers. Glass ceramics, however, combine a glassy phase with crystalline phases, typically involving compositions like lithium aluminosilicate or mica, enhancing thermal and mechanical properties. The distinct chemical makeup influences bioactivity in bioactive glass and structural durability in glass ceramics, making them suited for different cookware applications.
Manufacturing Processes
Bioactive glass manufacturing involves controlled melting and rapid quenching to achieve its unique composition that promotes bioactivity, often requiring precise temperature management to incorporate therapeutic ions. Glass ceramic production utilizes a two-step process of initial glass melting followed by controlled crystallization through heat treatment, resulting in a material with enhanced thermal stability and mechanical strength. The distinct thermal processing in glass ceramics allows for tailored microstructures, while bioactive glass prioritizes chemical composition to support biological interactions, making manufacturing techniques crucial for their final cookware properties.
Thermal Resistance and Heat Distribution
Bioactive glass cookware offers moderate thermal resistance but lacks the high heat tolerance found in glass ceramics, which can withstand temperatures up to 1400degC without deformation. Glass ceramics provide superior heat distribution due to their crystalline structure, ensuring even cooking and reduced hot spots compared to bioactive glass. The enhanced thermal shock resistance of glass ceramics makes them more durable and reliable for frequent temperature changes in cooking environments.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Bioactive glass offers moderate mechanical strength but is more prone to fracture under thermal stress compared to glass ceramic, which exhibits superior toughness and resistance to cracking. Glass ceramic cookware demonstrates enhanced durability due to its crystalline microstructure, providing better resistance to abrasion and thermal shock. The improved mechanical properties of glass ceramic make it the preferred choice for long-lasting, robust cookware applications.
Non-Toxicity and Food Safety
Bioactive glass and glass ceramic differ significantly in non-toxicity and food safety for cookware applications. Bioactive glass is known for its biocompatibility and releases beneficial ions while maintaining chemical stability, ensuring no harmful substances leach into food. Glass ceramic, often composed of crystalline phases within a glass matrix, offers excellent thermal resistance and inertness, providing a non-toxic, safe surface that does not interact chemically with food during cooking.
Scratch and Stain Resistance
Bioactive glass cookware exhibits moderate scratch resistance but may be more susceptible to surface stains due to its porous structure, whereas glass ceramic offers superior scratch and stain resistance owing to its dense, non-porous composition. The crystalline matrix in glass ceramic enhances durability and maintains aesthetic appeal under frequent kitchen use. Choosing glass ceramic for cookware ensures prolonged resistance to everyday wear and discoloration, making it a practical option for stain- and scratch-prone cooking environments.
Design Versatility and Aesthetics
Bioactive glass offers superior design versatility in cookware due to its ability to be molded into intricate shapes and incorporate vibrant, translucent colors that enhance aesthetic appeal. Glass ceramic cookware provides a sleek, uniform surface with excellent thermal resistance, allowing for minimalist designs favored in modern kitchens. Both materials enable aesthetic customization, but bioactive glass stands out for its unique textures and hues, appealing to consumers seeking distinctive cookware styles.
Price Comparison and Market Availability
Bioactive glass cookware typically commands a premium price due to its advanced material properties and health benefits, while glass ceramic options are more widely available and generally more affordable for everyday use. Market availability favors glass ceramic cookware with a broader range of brands and models accessible in retail and online stores globally. Price comparison reveals that although bioactive glass offers innovative features, glass ceramic remains the cost-effective choice for budget-conscious consumers seeking durability and heat resistance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bioactive glass cookware typically features a non-toxic, eco-friendly composition that reduces harmful chemical leaching and supports recyclability, making it a sustainable choice for environmentally conscious consumers. Glass ceramic cookware is durable and energy-efficient, often boasting a long lifespan that minimizes waste and resource consumption, but its manufacturing process can involve higher energy use and emissions compared to bioactive glass. Both materials offer benefits for reducing environmental impact, yet bioactive glass generally scores better on sustainability metrics due to biodegradability and lower production carbon footprint.
Infographic: Bioactive glass vs Glass ceramic for Cookware
 azmater.com
azmater.com