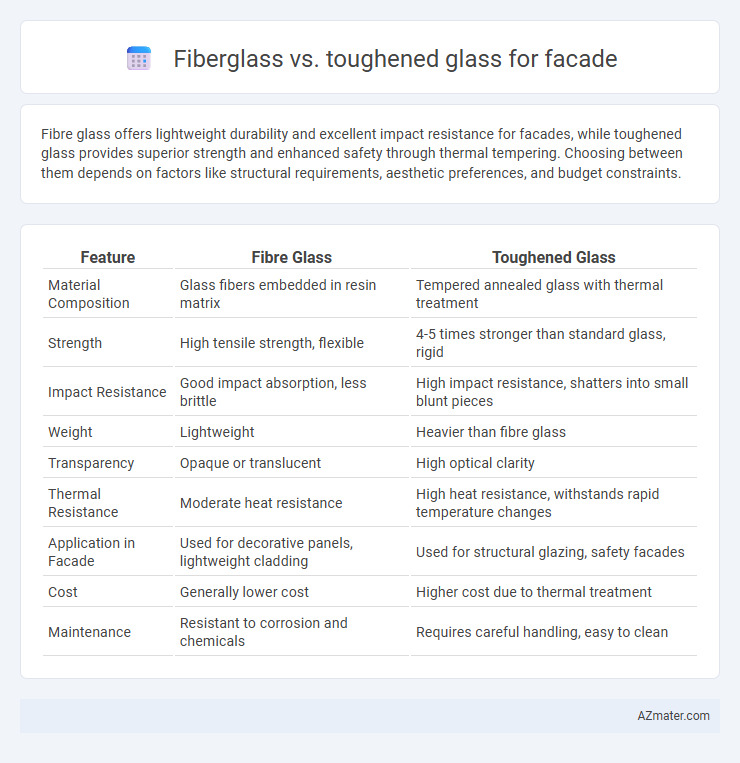
Fibre glass offers lightweight durability and excellent impact resistance for facades, while toughened glass provides superior strength and enhanced safety through thermal tempering. Choosing between them depends on factors like structural requirements, aesthetic preferences, and budget constraints.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fibre Glass | Toughened Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Glass fibers embedded in resin matrix | Tempered annealed glass with thermal treatment |
| Strength | High tensile strength, flexible | 4-5 times stronger than standard glass, rigid |
| Impact Resistance | Good impact absorption, less brittle | High impact resistance, shatters into small blunt pieces |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier than fibre glass |
| Transparency | Opaque or translucent | High optical clarity |
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate heat resistance | High heat resistance, withstands rapid temperature changes |
| Application in Facade | Used for decorative panels, lightweight cladding | Used for structural glazing, safety facades |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to thermal treatment |
| Maintenance | Resistant to corrosion and chemicals | Requires careful handling, easy to clean |
Introduction to Facade Materials: Fibre Glass vs Toughened Glass
Fibre glass offers high tensile strength, lightweight properties, and excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for complex facade shapes and energy-efficient designs. Toughened glass provides superior impact resistance, enhanced safety, and better thermal stability, suitable for modern building facades requiring durability and transparency. Both materials serve distinct roles in facade construction, balancing structural performance with aesthetic considerations.
What is Fibre Glass? Key Properties and Applications
Fibreglass is a composite material made from fine glass fibers woven into a fabric and bonded with a resin, known for its high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance. Key properties include lightweight structure, thermal insulation, flexibility, and durability, making it suitable for complex architectural facades requiring custom shapes and reduced structural load. Common applications in facades involve cladding panels, decorative elements, and lightweight protective barriers that benefit from fibreglass's weather resistance and ease of installation compared to toughened glass.
Understanding Toughened Glass: Features and Uses
Toughened glass, also known as tempered glass, offers exceptional strength and durability, making it ideal for facade applications where safety and impact resistance are critical. Its manufacturing process involves controlled thermal or chemical treatments that increase its strength compared to regular glass, allowing it to withstand high wind loads and resist shattering into sharp shards. Used extensively in architectural designs, toughened glass provides enhanced thermal stability, UV resistance, and can be combined with laminated layers for additional security and noise reduction in building facades.
Comparative Strength and Durability
Fibre glass offers high tensile strength and excellent resistance to impact and weathering, making it a lightweight yet durable choice for facades. Toughened glass provides superior compressive strength and shatter resistance due to its thermal tempering process, enhancing safety and load-bearing capacity. When comparing durability, fibre glass excels in corrosion resistance and flexibility, while toughened glass is more robust against mechanical stress and thermal shocks.
Thermal Performance and Energy Efficiency
Fibreglass offers superior thermal insulation for facades due to its low thermal conductivity, reducing heat transfer and enhancing energy efficiency in buildings. Toughened glass, while stronger and safer under impact, has higher thermal conductivity, which can result in greater heat loss or gain compared to fibreglass. Selecting fibreglass facades can significantly improve building thermal performance, leading to reduced HVAC energy consumption and lower operational costs.
Aesthetic Flexibility and Design Options
Fibre glass offers superior aesthetic flexibility for facades, allowing for custom shapes, textures, and colors due to its moldable nature, making it ideal for intricate architectural designs. In contrast, toughened glass provides a sleek, modern look with high transparency and reflective qualities but is limited to flat or gently curved panels. Designers seeking innovative, bespoke facade solutions often prefer fibre glass, while toughened glass suits projects emphasizing minimalistic elegance and durability.
Safety, Impact Resistance, and Security
Fibre glass offers high impact resistance due to its flexible, tensile strength, making it less likely to shatter upon impact, which enhances safety for building facades. Toughened glass, also known as tempered glass, provides superior security by breaking into small, blunt fragments rather than sharp shards, reducing injury risk and increasing overall safety. Both materials are designed to withstand significant force, but toughened glass excels in maintaining facade integrity under extreme conditions, while fibre glass provides a lightweight yet durable alternative.
Maintenance Demands and Longevity
Fiberglass facades require minimal maintenance due to their resistance to corrosion, moisture, and UV exposure, offering long-lasting performance without frequent repairs or coatings. Toughened glass, while highly durable and impact-resistant, demands regular cleaning and occasional inspections to prevent surface damage and maintain structural integrity. Fiberglass generally outperforms toughened glass in environments with harsh weather conditions, resulting in extended longevity with reduced upkeep costs.
Cost Considerations and Lifecycle Value
Fibre glass facades generally offer lower initial installation costs due to lightweight materials and easier handling compared to toughened glass, which requires precise manufacturing and specialized framing systems. Toughened glass provides superior durability, impact resistance, and longevity, resulting in lower maintenance expenses and enhanced lifecycle value despite higher upfront investment. Evaluating facade projects, owners benefit from balancing fibre glass's cost-effectiveness with toughened glass's long-term asset performance and reduced replacement frequency.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Facade Project
Choosing between fibre glass and toughened glass for your facade project depends on factors like durability, safety, and aesthetic appeal. Toughened glass offers superior strength, impact resistance, and thermal stability, making it ideal for high-traffic or exposed environments. Fibre glass provides lightweight flexibility and excellent insulation properties but lacks the toughness required for heavy-duty facade applications.
Infographic: Fibre glass vs Toughened glass for Facade
 azmater.com
azmater.com