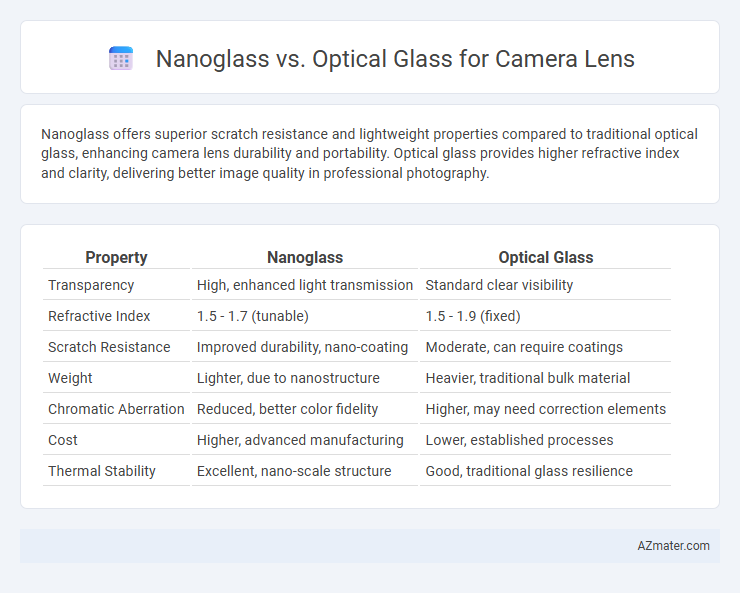
Nanoglass offers superior scratch resistance and lightweight properties compared to traditional optical glass, enhancing camera lens durability and portability. Optical glass provides higher refractive index and clarity, delivering better image quality in professional photography.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nanoglass | Optical Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Transparency | High, enhanced light transmission | Standard clear visibility |
| Refractive Index | 1.5 - 1.7 (tunable) | 1.5 - 1.9 (fixed) |
| Scratch Resistance | Improved durability, nano-coating | Moderate, can require coatings |
| Weight | Lighter, due to nanostructure | Heavier, traditional bulk material |
| Chromatic Aberration | Reduced, better color fidelity | Higher, may need correction elements |
| Cost | Higher, advanced manufacturing | Lower, established processes |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent, nano-scale structure | Good, traditional glass resilience |
Introduction to Nanoglass and Optical Glass
Nanoglass, an advanced material featuring nano-scale structures, offers exceptional light transmission and reduced aberrations for high-performance camera lenses. Optical glass, traditionally used in lenses, provides reliable clarity and durability but may suffer from chromatic aberration and weight limitations. Nanoglass enhances image quality by improving light refraction and reducing distortion compared to conventional optical glass.
What is Nanoglass?
Nanoglass is an advanced optical material composed of nano-sized glass particles engineered to improve light transmission and reduce optical aberrations in camera lenses. Compared to traditional optical glass, nanoglass offers enhanced clarity and durability by minimizing internal scattering and increasing resistance to scratches and environmental damage. Its unique nanostructure enables superior image quality through improved resolution and contrast, making it a preferred choice for high-performance camera systems.
What is Optical Glass?
Optical glass is a high-purity, precision-engineered material specifically designed to manipulate light with minimal distortions, essential for camera lenses to produce sharp and clear images. It offers excellent refractive index control and low dispersion, enabling accurate light transmission and reducing chromatic aberrations. Compared to nanoglass, optical glass provides tried-and-tested durability and clarity, making it a standard choice in high-quality photographic lenses.
Key Material Properties Comparison
Nanoglass offers superior hardness and scratch resistance compared to traditional optical glass, improving lens durability in camera applications. Its enhanced light transmittance and reduced surface reflection result in clearer image quality and better low-light performance. Optical glass, while still effective, typically has lower resistance to abrasion and higher weight, affecting portability and long-term lens maintenance.
Durability and Scratch Resistance
Nanoglass exhibits superior durability and scratch resistance compared to traditional optical glass, thanks to its advanced nanostructured coating that enhances hardness and minimizes abrasion. Optical glass, while offering excellent optical clarity, is more prone to surface scratches and damage over time, reducing lens lifespan and image quality. The enhanced wear resistance of nanoglass makes it a preferred choice for high-performance camera lenses in challenging environments.
Optical Clarity and Image Quality
Nanoglass offers superior optical clarity compared to traditional optical glass due to its nanoscale smoothness, reducing light scatter and enhancing image sharpness. This results in higher image quality with improved contrast and color fidelity, critical for professional camera lenses. Optical glass, while effective, often exhibits more internal reflections and slight imperfections that can degrade overall image performance.
Weight and Design Flexibility
Nanoglass offers significant weight reduction compared to traditional optical glass, making it ideal for lightweight camera lens designs. Its advanced material properties enable greater design flexibility, allowing for thinner, more compact lenses without compromising optical performance. This combination of reduced weight and customizable form factors enhances portability and versatility in modern camera systems.
Cost and Availability
Nanoglass offers advanced optical performance with enhanced durability but comes at a higher cost due to complex manufacturing processes compared to traditional optical glass. Optical glass remains more widely available and cost-effective, benefiting from established production techniques and widespread supply chains. Camera manufacturers often balance between the premium price of nanoglass and the affordable accessibility of optical glass based on budget constraints and application needs.
Practical Applications in Camera Lenses
Nanoglass offers superior scratch resistance and lightweight properties compared to traditional optical glass, making it ideal for rugged camera lenses used in outdoor photography. Its enhanced transmission of light and reduced chromatic aberration improve image clarity and color accuracy, benefiting professional photographers requiring precision. Optical glass remains popular for standard lenses due to cost-effectiveness and proven optical performance in controlled environments.
Which Glass is Better for Camera Lenses?
Nanoglass offers superior scratch resistance and enhanced light transmission compared to traditional optical glass, improving image clarity and durability for camera lenses. Optical glass, widely used in high-quality lenses, provides excellent refractive properties and cost-effectiveness but may lack the advanced durability of nanoglass coatings. For professional photography, nanoglass technology stands out as the better choice due to its enhanced protection and optical performance.
Infographic: Nanoglass vs Optical glass for Camera lens
 azmater.com
azmater.com