Nanoglass tableware offers superior scratch resistance and enhanced durability compared to potash glass, making it ideal for everyday use. Potash glass, while cost-effective and visually appealing, lacks the strength and longevity provided by nanoglass technology.
Table of Comparison
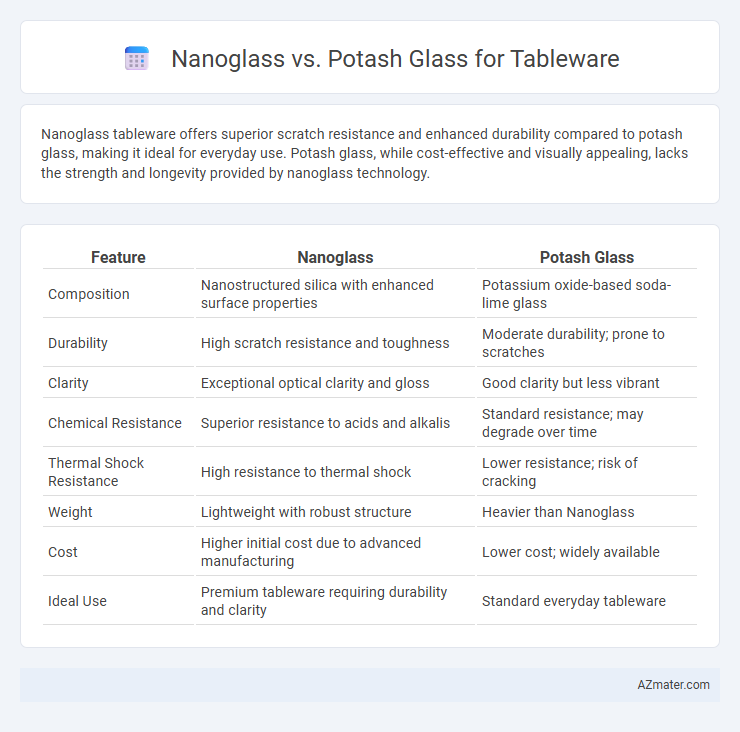
| Feature | Nanoglass | Potash Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Nanostructured silica with enhanced surface properties | Potassium oxide-based soda-lime glass |
| Durability | High scratch resistance and toughness | Moderate durability; prone to scratches |
| Clarity | Exceptional optical clarity and gloss | Good clarity but less vibrant |
| Chemical Resistance | Superior resistance to acids and alkalis | Standard resistance; may degrade over time |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | High resistance to thermal shock | Lower resistance; risk of cracking |
| Weight | Lightweight with robust structure | Heavier than Nanoglass |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to advanced manufacturing | Lower cost; widely available |
| Ideal Use | Premium tableware requiring durability and clarity | Standard everyday tableware |
Introduction to Nanoglass and Potash Glass
Nanoglass is an advanced, nano-engineered glass material known for its superior strength, scratch resistance, and enhanced clarity compared to conventional glass types. Potash glass, traditionally made using potassium carbonate, offers a higher refractive index and better chemical durability than soda-lime glass, making it a common choice for quality tableware. The comparison between Nanoglass and Potash glass highlights differences in durability, visual appeal, and manufacturing technologies used for premium tableware applications.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Nanoglass tableware typically incorporates nanoscale silica particles, enhancing strength and clarity through advanced sol-gel processes, while potash glass contains potassium oxide derived from potash, contributing to its durability and brilliance via traditional melting methods. The manufacturing of nanoglass involves controlled nanoparticle dispersion that improves scratch resistance and thermal stability, contrasting with potash glass production that relies on batch melting of raw materials like sand, soda ash, and potash in high-temperature furnaces. These compositional and processing variations result in nanoglass offering superior mechanical properties and clarity compared to the more conventional, chemically stable potash glass.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Nanoglass exhibits superior durability and strength compared to potash glass due to its nanoscale reinforcement that enhances resistance to scratches and impacts. Potash glass, while traditionally valued for its aesthetic qualities, tends to be more brittle and less resistant to mechanical stress and thermal shock. The advanced molecular structure of nanoglass ensures longer-lasting tableware, reducing breakage and maintaining clarity over time.
Aesthetic Qualities and Clarity
Nanoglass tableware exhibits superior aesthetic qualities characterized by its ultra-clear, brilliant transparency and enhanced scratch resistance, resulting from its nanostructured composition. Potash glass, while also clear and durable, typically offers a slightly warmer tone and less brilliance compared to the sharper clarity of nanoglass. The enhanced refractive index and reduced surface imperfections in nanoglass contribute to a visually striking clarity that elevates the presentation of tableware settings.
Thermal Resistance and Heat Tolerance
Nanoglass exhibits superior thermal resistance compared to potash glass, withstanding rapid temperature changes up to 150degC without cracking. Potash glass typically endures lower heat tolerance, around 100degC, making it less suitable for high-heat applications like oven use. The enhanced heat tolerance of Nanoglass ensures durability and safety in everyday tableware exposed to varied thermal conditions.
Safety and Toxicity Considerations
Nanoglass tableware offers superior safety due to its non-toxic, lead-free composition that resists chemical leaching, making it ideal for food contact applications. Potash glass, while historically valued for its clarity and durability, may contain trace heavy metals such as lead or arsenic, posing potential toxicity risks over prolonged use. Choosing nanoglass enhances consumer health protection by minimizing exposure to harmful substances and ensuring compliance with stringent food safety regulations.
Price and Cost-Effectiveness
Nanoglass tableware typically commands a higher price due to advanced manufacturing techniques and enhanced durability, offering superior resistance to scratches and breakage. Potash glass items are more affordable, making them a cost-effective choice for everyday use but with lower resistance to wear and tear. When evaluating long-term value, nanoglass provides better cost-effectiveness by reducing replacement frequency despite its upfront cost.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nanoglass tableware offers enhanced durability and longer lifespan compared to potash glass, reducing overall waste and the environmental footprint associated with frequent replacements. Potash glass production relies on potassium carbonate, often sourced from mining, which can contribute to resource depletion and higher energy consumption during manufacturing. Nanoglass's advanced material properties enable more sustainable use by minimizing raw material input and promoting recyclability, aligning better with eco-friendly practices.
Suitability for Tableware Applications
Nanoglass offers superior durability and scratch resistance compared to potash glass, making it highly suitable for tableware exposed to frequent use. Its enhanced transparency and resistance to thermal shock ensure long-lasting clarity and safety during temperature changes typically encountered in kitchens and dining settings. Potash glass, while traditional and cost-effective, tends to be less resilient and more prone to chipping, limiting its reliability for heavy-duty tableware applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Glass for Tableware
Nanoglass offers superior durability, scratch resistance, and a sleek modern appearance, making it ideal for high-end tableware that demands longevity and aesthetic appeal. Potash glass, with its traditional charm and affordability, suits everyday use where cost-effectiveness and classic design are priorities. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing budget, desired visual qualities, and durability requirements for optimal tableware performance.
Infographic: Nanoglass vs Potash glass for Tableware
 azmater.com
azmater.com