Tempered glass offers enhanced strength and shatter resistance, improving safety in automobile windows, while tinted glass reduces glare and UV exposure, enhancing comfort and protecting the vehicle's interior. Choosing between them depends on prioritizing safety features or passenger comfort and privacy.
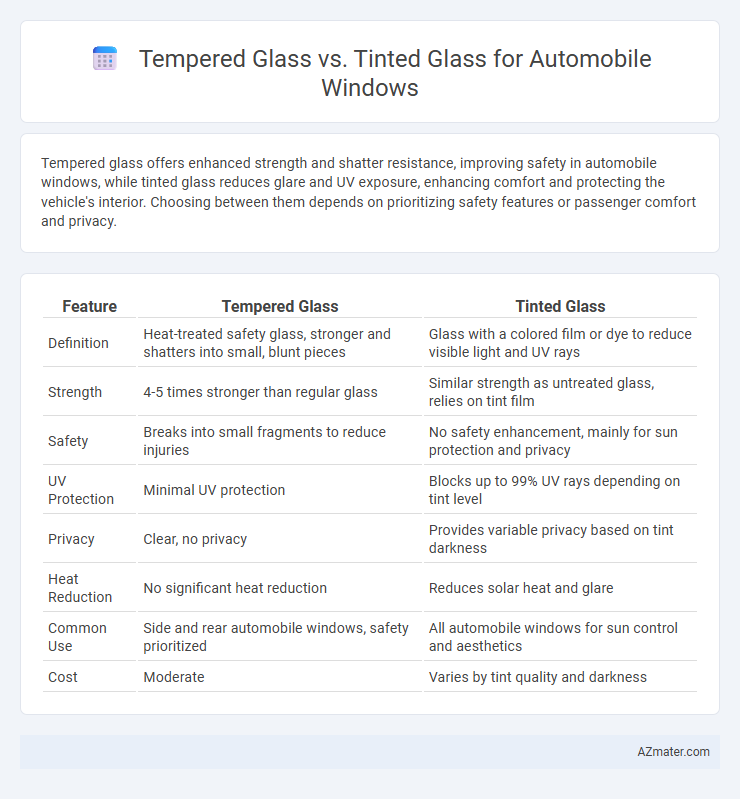
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tempered Glass | Tinted Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Heat-treated safety glass, stronger and shatters into small, blunt pieces | Glass with a colored film or dye to reduce visible light and UV rays |
| Strength | 4-5 times stronger than regular glass | Similar strength as untreated glass, relies on tint film |
| Safety | Breaks into small fragments to reduce injuries | No safety enhancement, mainly for sun protection and privacy |
| UV Protection | Minimal UV protection | Blocks up to 99% UV rays depending on tint level |
| Privacy | Clear, no privacy | Provides variable privacy based on tint darkness |
| Heat Reduction | No significant heat reduction | Reduces solar heat and glare |
| Common Use | Side and rear automobile windows, safety prioritized | All automobile windows for sun control and aesthetics |
| Cost | Moderate | Varies by tint quality and darkness |
Introduction to Automobile Window Glass Types
Automobile window glass primarily consists of tempered glass and tinted glass, each serving distinct functional and safety purposes. Tempered glass is heat-treated to enhance its strength and shatters into small, blunt pieces to reduce injury risk during accidents, making it standard for side and rear windows. Tinted glass incorporates a film or coating to reduce glare, UV radiation, and heat inside the vehicle, enhancing comfort and protecting the interior without compromising visibility.
What is Tempered Glass?
Tempered glass, also known as toughened glass, is a type of safety glass engineered through controlled thermal or chemical treatments to increase its strength compared to normal glass. It is designed to shatter into small, blunt pieces rather than sharp shards upon impact, minimizing the risk of injury during accidents. Commonly used in automobile windows, tempered glass provides enhanced durability, heat resistance, and improved passenger safety without compromising visibility.
What is Tinted Glass?
Tinted glass in automobiles is specially treated glass infused with dyes or chemicals that reduce visible light transmission, enhancing privacy and blocking harmful UV rays. Compared to tempered glass, which is heat-strengthened for safety and shatters into small blunt pieces upon impact, tinted glass primarily offers solar heat rejection and glare reduction without compromising clarity or structural integrity. This makes tinted glass ideal for improving driver comfort and protecting interior components from sun damage while maintaining safety standards.
Key Differences Between Tempered and Tinted Glass
Tempered glass is heat-treated to increase strength and shatters into small, blunt pieces upon impact, enhancing passenger safety, while tinted glass involves applying a film or dye to reduce glare and UV exposure. Tempered glass primarily provides structural integrity and safety benefits in automobile windows, whereas tinted glass focuses on privacy, heat reduction, and aesthetic appeal. The key differences lie in their manufacturing process, purpose, and functional properties: tempered glass is engineered for durability and safety, and tinted glass is designed mainly for light control and comfort.
Safety Features: Tempered vs Tinted Glass
Tempered glass for automobile windows is engineered to shatter into small, blunt pieces upon impact, significantly reducing the risk of injury during accidents, while tinted glass primarily provides UV protection and glare reduction but does not improve impact resistance. Tempered glass undergoes a thermal treatment process that enhances its strength and safety compliance standards, making it the preferred choice for side and rear windows due to its shatter-resistant properties. Tinted glass may add some privacy and heat reduction benefits but lacks the safety features of tempered glass, which is critical for minimizing harm in collisions.
UV Protection and Heat Reduction Comparison
Tempered glass offers strong UV protection by blocking up to 99% of harmful ultraviolet rays, enhancing passenger safety and preventing interior fading. Tinted glass not only reduces UV exposure but also provides superior heat reduction by absorbing and reflecting solar energy, significantly lowering cabin temperature and improving fuel efficiency. Both options contribute to vehicle comfort, but tinted glass excels in minimizing heat buildup, while tempered glass prioritizes impact resistance and UV shielding.
Legal Considerations for Automotive Glass
Automotive window regulations mandate specific transparency levels, where tempered glass typically meets minimum light transmission standards required by law, while tinted glass often faces restrictions based on tint darkness and reflectivity. Legal considerations vary by jurisdiction, with many regions imposing limits on visible light transmission (VLT) percentages for side and front windows to ensure driver visibility and safety. Compliance with vehicle safety regulations and inspection requirements is essential when choosing between tempered and tinted glass for automotive applications, preventing potential fines or safety violations.
Aesthetic and Privacy Benefits
Tempered glass provides a clear, sleek appearance that enhances the car's modern aesthetic with high durability and shatter resistance, while tinted glass offers a customizable look by varying shades, contributing to a sportier or more sophisticated style. Tinted glass significantly improves privacy by reducing visibility into the vehicle's interior, protecting occupants from outside view and minimizing glare from sunlight. The combination of tempered glass's strength and tinted glass's privacy benefits addresses both safety and personal space preferences for automobile windows.
Cost and Installation Factors
Tempered glass for automobile windows typically costs more due to its heat-strengthening process, but it offers higher safety and durability, making installation more straightforward with standard tools. Tinted glass tends to be less expensive upfront but may require additional labor and materials during installation, especially if aftermarket tint films are applied, increasing overall costs. Choosing between tempered and tinted glass should consider both initial price and the complexity of fitting or retrofitting windows to ensure optimal long-term value.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Vehicle
Choosing the right glass for your vehicle involves understanding the differences between tempered glass and tinted glass, as tempered glass offers enhanced safety by shattering into small, blunt pieces upon impact, minimizing injury risks. Tinted glass provides UV protection and reduces glare, improving comfort and privacy while helping to regulate interior temperatures. Combining tempered glass with tinting can optimize both safety and comfort, making your automobile window more functional and secure.
Infographic: Tempered glass vs Tinted glass for Automobile window
 azmater.com
azmater.com