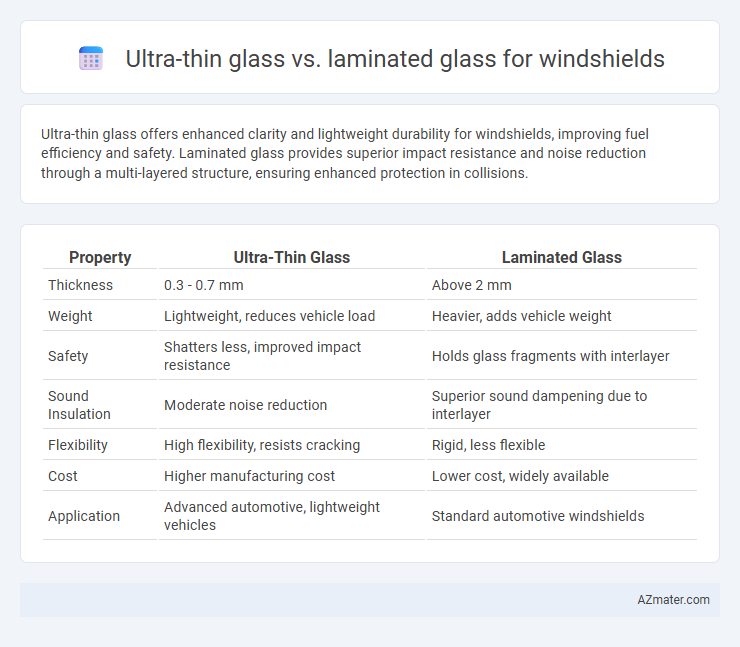
Ultra-thin glass offers enhanced clarity and lightweight durability for windshields, improving fuel efficiency and safety. Laminated glass provides superior impact resistance and noise reduction through a multi-layered structure, ensuring enhanced protection in collisions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ultra-Thin Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | 0.3 - 0.7 mm | Above 2 mm |
| Weight | Lightweight, reduces vehicle load | Heavier, adds vehicle weight |
| Safety | Shatters less, improved impact resistance | Holds glass fragments with interlayer |
| Sound Insulation | Moderate noise reduction | Superior sound dampening due to interlayer |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, resists cracking | Rigid, less flexible |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost | Lower cost, widely available |
| Application | Advanced automotive, lightweight vehicles | Standard automotive windshields |
Introduction: The Evolving Landscape of Windshield Technologies
Ultra-thin glass offers enhanced durability and weight reduction compared to traditional laminated glass, revolutionizing windshield technology in automotive design. Laminated glass, composed of multiple layers including a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, provides superior safety by preventing shattering upon impact. The shift towards ultra-thin glass enables manufacturers to achieve lighter vehicles with improved fuel efficiency while maintaining structural integrity and safety standards.
What is Ultra-Thin Glass?
Ultra-thin glass refers to glass sheets with thicknesses typically under 0.5 millimeters, offering superior lightweight properties compared to traditional laminated glass used in windshields. This type of glass improves vehicle fuel efficiency and enhances safety by providing better shatter resistance through advanced tempering and coating technologies. Automotive manufacturers increasingly adopt ultra-thin glass in windshields to reduce overall weight without compromising strength or optical clarity.
Understanding Laminated Glass
Laminated glass for windshields consists of two or more glass layers bonded with an inner layer of polyvinyl butyral (PVB), providing enhanced safety by preventing shattering upon impact. Compared to ultra-thin glass, laminated glass offers superior structural integrity and noise reduction, maintaining visibility even when damaged. Its multi-layer construction also improves UV protection and durability, making it a preferred choice for automotive windshields.
Key Differences Between Ultra-Thin and Laminated Glass
Ultra-thin glass for windshields typically measures less than 0.5 mm in thickness, offering enhanced visibility and reduced weight compared to laminated glass, which usually consists of two or more glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer. Laminated glass excels in impact resistance and safety by preventing shattering upon collision, whereas ultra-thin glass prioritizes flexibility and weight reduction, making it ideal for improving fuel efficiency and vehicle dynamics. Differences in manufacturing processes, cost, and durability also distinguish ultra-thin glass, which is more fragile without lamination, from laminated glass's well-established robustness and widespread automotive use.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Ultra-thin glass offers enhanced impact resistance due to its higher flexibility and advanced chemical strengthening processes, making it less prone to shattering compared to traditional laminated glass. Laminated glass provides superior structural integrity by combining multiple layers with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, which holds fragments together upon impact, reducing injury risks. When comparing strength and durability, ultra-thin glass excels in lightweight resilience, while laminated glass delivers better long-term protection against penetration and environmental stresses.
Safety Features and Crash Performance
Ultra-thin glass offers enhanced impact resistance and better shatter absorption compared to traditional laminated glass, improving occupant safety during collisions. Laminated glass features multiple layers including a plastic interlayer that holds shards together, reducing the risk of injury from glass fragments. Both materials are engineered to meet stringent safety standards, but ultra-thin glass provides superior crash energy dissipation and clearer visibility post-impact.
Impact on Vehicle Weight and Fuel Efficiency
Ultra-thin glass significantly reduces vehicle weight compared to laminated glass due to its thinner profile while maintaining strength and safety standards. This weight reduction enhances fuel efficiency by decreasing the overall mass the engine needs to propel, leading to lower fuel consumption. Laminated glass, being heavier, adds more mass and can negatively impact fuel economy, especially in lightweight and electric vehicles where every kilogram counts.
Cost Considerations and Market Availability
Ultra-thin glass offers cost advantages over laminated glass due to reduced material thickness and lower production expenses, making it an economical choice for automotive windshields. Laminated glass, widely available in the market, typically incurs higher costs because of its multi-layer construction and enhanced safety features. Market availability of ultra-thin glass is expanding but remains limited compared to the well-established laminated glass segment in automotive applications.
Future Trends in Automotive Windshield Materials
Ultra-thin glass offers significant weight reduction and enhanced clarity compared to laminated glass, making it a leading candidate for future automotive windshields aimed at improving fuel efficiency and visibility. Incorporation of smart technologies such as embedded sensors and heads-up displays is more compatible with ultra-thin glass due to its flexibility and superior surface quality. As electric and autonomous vehicles rise, ultra-thin glass adoption is expected to accelerate, driven by its potential to integrate advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and improve overall vehicle aerodynamics.
Which Windshield Glass is Right for You?
Ultra-thin glass offers superior clarity and lightweight durability, making it ideal for enhancing fuel efficiency and visibility in modern vehicles. Laminated glass excels in safety with its multi-layer construction that resists shattering and provides enhanced impact protection. Choosing the right windshield glass depends on prioritizing either advanced performance and lightness with ultra-thin glass or maximum safety and sturdiness with laminated glass.
Infographic: Ultra-thin glass vs Laminated glass for Windshield
 azmater.com
azmater.com