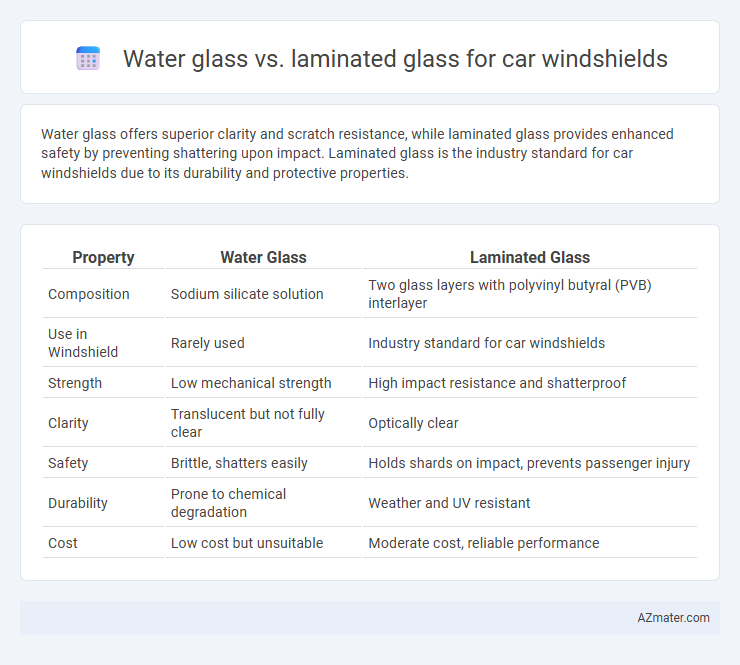
Water glass offers superior clarity and scratch resistance, while laminated glass provides enhanced safety by preventing shattering upon impact. Laminated glass is the industry standard for car windshields due to its durability and protective properties.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Water Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Sodium silicate solution | Two glass layers with polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer |
| Use in Windshield | Rarely used | Industry standard for car windshields |
| Strength | Low mechanical strength | High impact resistance and shatterproof |
| Clarity | Translucent but not fully clear | Optically clear |
| Safety | Brittle, shatters easily | Holds shards on impact, prevents passenger injury |
| Durability | Prone to chemical degradation | Weather and UV resistant |
| Cost | Low cost but unsuitable | Moderate cost, reliable performance |
Introduction to Car Windshield Materials
Car windshields commonly use laminated glass, which consists of two glass layers bonded with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, providing enhanced safety and impact resistance. Water glass, or sodium silicate coatings, offer hydrophobic properties to improve visibility during rain but are not structural materials for windshields. Laminated glass remains the industry standard due to its ability to prevent shattering while maintaining optical clarity and durability under various driving conditions.
What is Water Glass?
Water glass, also known as sodium silicate, is a chemical compound used in automotive applications for its adhesive and sealing properties, offering an alternative to traditional laminated glass in specific windshield installations. Unlike laminated glass, which consists of two glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer for impact resistance and safety, water glass provides a transparent, durable coating that enhances water resistance and structural integrity. This compound helps prevent seal failure and glass delamination, improving windshield lifespan and reducing repair costs.
What is Laminated Glass?
Laminated glass is a type of safety glass commonly used for car windshields, composed of two or more layers of glass bonded together with an interlayer, usually made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB). This construction helps the glass hold together upon impact, reducing the risk of shattering and enhancing passenger safety. Unlike water glass, which typically involves surface treatments, laminated glass offers superior strength and resistance against penetration and UV radiation.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Laminated glass offers superior strength and durability compared to water glass for car windshields due to its construction of two glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer that prevents shattering upon impact. Water glass, primarily used for insulating or sealing purposes, lacks the structural integrity and impact resistance required for automotive safety. Laminated glass fulfills safety standards by maintaining windshield integrity during collisions, reducing the risk of injury and improving overall vehicle durability.
Safety Features: Impact Resistance
Water glass, composed of tempered glass, offers excellent shatter resistance by breaking into small, blunt pieces upon impact, reducing injury risk during collisions. Laminated glass consists of two glass layers bonded with a plastic interlayer, maintaining structural integrity by holding shards together and preventing penetration from debris or collision forces. The laminated glass is superior in impact resistance and safety performance for car windshields, providing enhanced protection by minimizing fragmentation and maintaining visibility after impact.
Visibility and Optical Clarity
Water glass offers superior visibility for car windshields due to its uniform surface and high optical clarity, minimizing distortions and glare. Laminated glass, composed of two glass layers with a plastic interlayer, provides enhanced safety but may slightly reduce optical clarity compared to water glass. The plastic interlayer in laminated glass can cause minor visual distortions under certain lighting conditions, impacting overall visibility.
UV and Sound Protection
Laminated glass for car windshields offers superior UV protection by incorporating a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer that blocks up to 99% of harmful ultraviolet rays, reducing interior fading and skin exposure. Water glass, also known as borosilicate glass, lacks this specialized interlayer and offers minimal UV filtering, making it less effective against sun damage. In terms of sound protection, laminated glass significantly reduces external noise due to its layered construction, whereas water glass provides lower acoustic insulation, resulting in a noisier cabin environment.
Cost Differences and Affordability
Water glass windshields generally cost less than laminated glass due to simpler manufacturing processes and lower material expenses. Laminated glass offers enhanced safety and durability but comes at a higher price point, often 30-50% more expensive than water glass options. Choosing the more affordable water glass can reduce initial replacement costs, but laminated glass provides better long-term value through improved impact resistance and noise reduction.
Repair and Replacement Considerations
Water glass windshields, composed mainly of silica-based materials, offer limited flexibility when it comes to repairs due to their rigid structure, often necessitating full replacement after damage. Laminated glass, featuring a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer between two glass sheets, is more amenable to repairs from minor chips and cracks, enhancing safety while reducing replacement frequency. The repair process for laminated glass seals cracks to prevent spreading, preserving structural integrity and lowering overall maintenance costs compared to water glass windshields.
Which Windshield Glass is Best for Your Car?
Laminated glass is widely regarded as the best choice for car windshields due to its safety features, as it consists of two layers of glass with a plastic interlayer that holds shards together upon impact, reducing injury risk. Water glass, although more resistant to scratches and chemical damage, lacks the structural integrity and impact resistance essential for automotive safety standards. For optimal protection, durability, and compliance with automotive regulations, laminated glass remains the preferred material for windshields.
Infographic: Water glass vs Laminated glass for Car windshield
 azmater.com
azmater.com