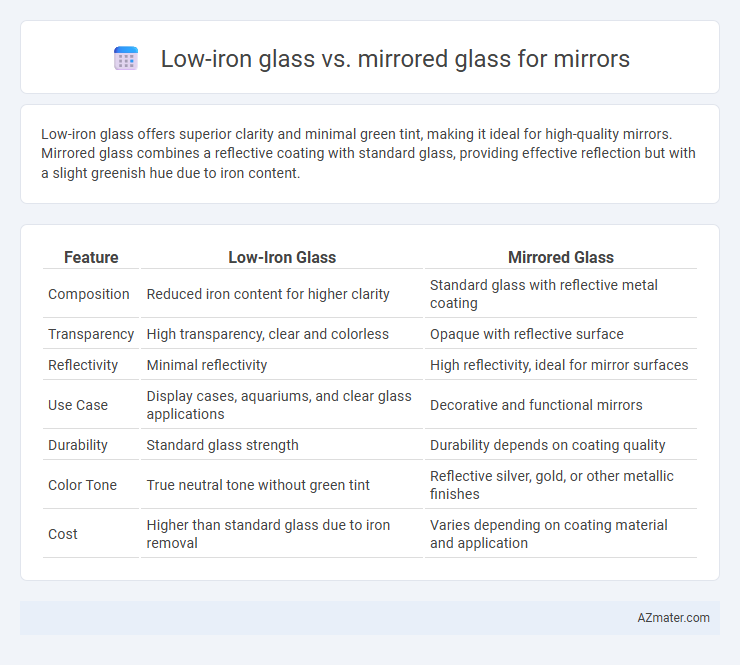
Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and minimal green tint, making it ideal for high-quality mirrors. Mirrored glass combines a reflective coating with standard glass, providing effective reflection but with a slight greenish hue due to iron content.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Low-Iron Glass | Mirrored Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Reduced iron content for higher clarity | Standard glass with reflective metal coating |
| Transparency | High transparency, clear and colorless | Opaque with reflective surface |
| Reflectivity | Minimal reflectivity | High reflectivity, ideal for mirror surfaces |
| Use Case | Display cases, aquariums, and clear glass applications | Decorative and functional mirrors |
| Durability | Standard glass strength | Durability depends on coating quality |
| Color Tone | True neutral tone without green tint | Reflective silver, gold, or other metallic finishes |
| Cost | Higher than standard glass due to iron removal | Varies depending on coating material and application |
Understanding Low-Iron Glass: Definition and Characteristics
Low-iron glass, also known as extra-clear glass, is distinguished by its reduced iron oxide content, typically less than 0.03%, resulting in higher light transmission and minimal greenish tint compared to standard clear glass. This clarity enhances the true reflection quality, making it ideal for high-precision mirrors where color accuracy and brightness are critical. In contrast, mirrored glass typically uses standard glass with a reflective coating, which may exhibit slight green hues and less optical purity than mirrors made from low-iron glass substrates.
Mirrored Glass Explained: Features and Common Uses
Mirrored glass features a reflective coating applied to a base glass, creating a highly reflective surface ideal for decorative and functional applications. Common uses include bathroom mirrors, interior design elements, and architectural facades, where both aesthetics and durability are crucial. Unlike low-iron glass, which enhances clarity and reduces green tint, mirrored glass emphasizes reflectivity and can incorporate various finishes such as silver or bronze to suit specific design needs.
Visual Clarity: Low-Iron Glass vs. Traditional Mirrored Glass
Low-iron glass offers superior visual clarity compared to traditional mirrored glass due to its reduced iron content, which minimizes the greenish tint commonly seen in standard mirrors. This results in a more true-to-color reflection and enhanced brightness, making it ideal for applications requiring precise color accuracy. Traditional mirrored glass, while cost-effective, often distorts colors and decreases clarity because of its higher iron oxide levels.
Color Accuracy and Reflection Quality
Low-iron glass offers superior color accuracy by minimizing the greenish tint typical in standard glass, resulting in clearer and more true-to-life reflections ideal for high-end mirrors. Mirrored glass, often produced with a reflective coating on regular glass, tends to have slight color distortions but provides strong reflection quality and durability. Choosing low-iron glass enhances visual clarity and precision, while mirrored glass emphasizes reflective brightness and structural resilience.
Thickness and Durability Comparison
Low-iron glass typically offers higher clarity and minimal green tint compared to mirrored glass, making it a preferred choice for high-quality mirrors requiring optimal visual accuracy. In terms of thickness, low-iron glass mirrors are often available in standard thicknesses ranging from 3mm to 6mm, providing good durability, while mirrored glass can vary more widely but generally requires additional backing to enhance strength and longevity. Durability-wise, low-iron glass has superior resistance to scratching and environmental degradation, whereas mirrored glass relies heavily on its reflective coating, which can be prone to tarnishing and damage over time.
Light Transmission and Brightness Differences
Low-iron glass offers higher light transmission, typically around 91%, compared to standard mirrored glass, which reduces light due to its reflective backing. This increased transparency results in brighter, clearer reflections when used in mirrors, enhancing natural light within spaces. Mirrored glass, while providing reflective properties, generally lowers brightness and can create a slightly darker appearance because of its metallic coating.
Applications: Where Each Glass Type Excels
Low-iron glass is ideal for applications requiring high clarity and true color representation, such as decorative mirrors, luxury retail displays, and museum exhibits where minimal green tint enhances visual accuracy. Mirrored glass excels in functional applications like architectural facades, privacy screens, and solar control windows, benefiting from its reflective coating that provides glare reduction and heat rejection. Choosing between these glass types depends on whether clarity and color fidelity or reflective functionality and energy efficiency are the primary application needs.
Cost Considerations: Low-Iron Glass vs. Mirrored Glass
Low-iron glass typically costs more than standard mirrored glass due to its higher clarity and reduced green tint, making it ideal for premium mirror applications. Mirrored glass, which incorporates a reflective coating on standard glass, offers a more budget-friendly option but may have slight color distortion and lower optical purity. When considering costs, low-iron glass demands a higher initial investment, but its superior visual quality and longevity can provide better value in high-end installations.
Maintenance and Longevity Factors
Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and reduces the greenish tint seen in standard glass, making mirrors appear brighter and more reflective while requiring less frequent cleaning due to its smoother surface. Mirrored glass typically includes a reflective coating that may degrade over time if exposed to moisture or abrasive cleaning agents, necessitating careful maintenance to preserve longevity. Selecting low-iron glass enhances durability and ease of upkeep, as it resists yellowing and corrosion better than traditional mirrored glass, extending the mirror's lifespan in various environments.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Mirror Project
Low-iron glass offers superior clarity and minimal green tint, making it ideal for high-quality mirror projects that require true color reflection and enhanced brightness. Mirrored glass, coated with a reflective metallic layer, provides excellent reflectivity and is often more cost-effective, suitable for general decorative or functional mirror applications. Selecting the right glass depends on the project's visual clarity needs, budget constraints, and overall aesthetic goals.
Infographic: Low-iron glass vs Mirrored glass for Mirror
 azmater.com
azmater.com