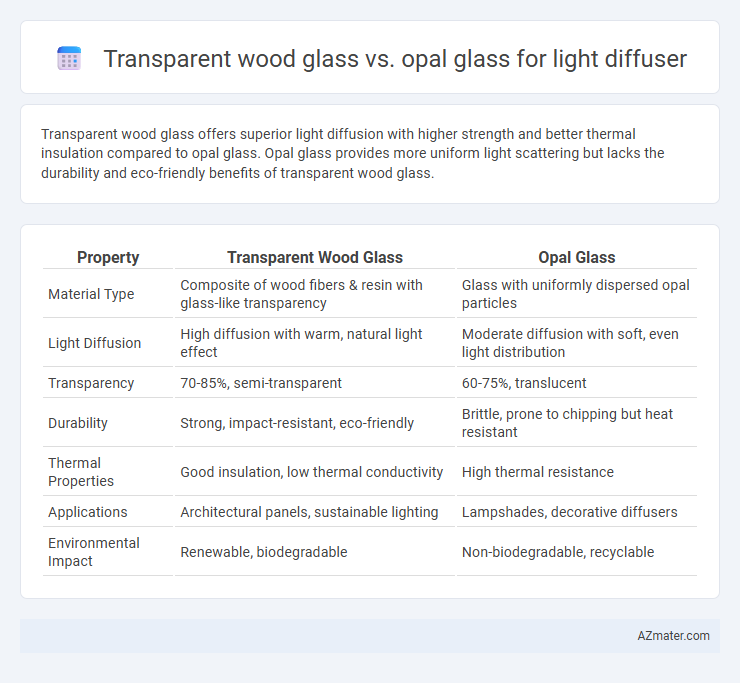
Transparent wood glass offers superior light diffusion with higher strength and better thermal insulation compared to opal glass. Opal glass provides more uniform light scattering but lacks the durability and eco-friendly benefits of transparent wood glass.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Transparent Wood Glass | Opal Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Composite of wood fibers & resin with glass-like transparency | Glass with uniformly dispersed opal particles |
| Light Diffusion | High diffusion with warm, natural light effect | Moderate diffusion with soft, even light distribution |
| Transparency | 70-85%, semi-transparent | 60-75%, translucent |
| Durability | Strong, impact-resistant, eco-friendly | Brittle, prone to chipping but heat resistant |
| Thermal Properties | Good insulation, low thermal conductivity | High thermal resistance |
| Applications | Architectural panels, sustainable lighting | Lampshades, decorative diffusers |
| Environmental Impact | Renewable, biodegradable | Non-biodegradable, recyclable |
Introduction to Light Diffusers: Transparent Wood Glass vs Opal Glass
Light diffusers enhance lighting quality by evenly distributing light and reducing glare. Transparent wood glass offers high mechanical strength, natural aesthetics, and superior light scattering through its unique nanostructure, making it ideal for eco-friendly lighting applications. Opal glass provides uniform diffusion with excellent heat resistance and durability, commonly used in traditional lighting fixtures requiring soft, consistent illumination.
Material Composition: Transparent Wood Glass Explained
Transparent wood glass is composed of natural wood fibers combined with a polymer resin, offering a unique balance of strength, light diffusion, and environmental sustainability. This material uses the natural cellular structure of wood to scatter light softly while maintaining higher translucency compared to opal glass, which is made from silica and alumina with a milky appearance that diffuses light uniformly. The organic composition of transparent wood glass results in better thermal insulation and a more eco-friendly profile, whereas opal glass focuses primarily on aesthetic diffusion without the same level of biodegradability or strength-to-weight ratio.
Understanding Opal Glass: Structure and Properties
Opal glass is a type of glass diffuser characterized by its milky, translucent appearance achieved through the inclusion of fine particles or opacifiers within the glass matrix, which scatter light to produce a soft, uniform glow. Unlike transparent wood glass, which preserves wood grain with high transparency and anisotropic light diffusion, opal glass provides isotropic diffusion by diffusing light evenly in all directions, eliminating glare and harsh shadows. Its chemical resistance, thermal stability, and high durability make opal glass ideal for lighting applications requiring consistent light diffusion and aesthetic versatility.
Light Transmission and Diffusion Efficiency
Transparent wood glass offers higher light transmission rates, typically exceeding 85%, compared to opal glass, which generally allows around 70-80%. The nanostructured cellulose fibers in transparent wood enhance diffusion efficiency by scattering light uniformly without significant loss, whereas opal glass relies on micro-structured particles to diffuse light but often results in lower clarity. This makes transparent wood glass more effective for applications requiring both high illumination and soft, even light distribution.
Aesthetic Qualities and Design Versatility
Transparent wood glass offers a unique aesthetic with its natural wood grain visible through a clear, durable surface, creating a warm, organic ambiance ideal for modern and eco-friendly interiors. Opal glass provides a smooth, uniform diffusion of light with a soft, matte finish that complements minimalist and contemporary designs by evenly distributing illumination without glare. Both materials enhance design versatility, with transparent wood glass allowing for customization in wood types and finishes, while opal glass suits various shapes and applications due to its consistent light diffusion properties.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Transparent wood glass offers superior durability due to its enhanced resistance to cracking and shattering, making it ideal for long-term light diffuser applications. Its natural lignin content provides improved impact strength compared to opal glass, which is more prone to surface scratches and brittleness over time. Opal glass, while aesthetically pleasing, generally exhibits a shorter lifespan under high mechanical stress and environmental exposure than transparent wood glass.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Transparent wood glass offers superior sustainability by utilizing renewable wood fibers combined with eco-friendly resins, resulting in a biodegradable and low carbon footprint material for light diffusers. Opal glass, while recyclable, involves energy-intensive production processes and raw materials with higher environmental costs, limiting its eco-friendliness compared to transparent wood glass. The biodegradable nature and reduced greenhouse gas emissions of transparent wood glass position it as a more environmentally responsible choice for sustainable lighting solutions.
Applications in Modern Architecture and Lighting
Transparent wood glass offers superior mechanical strength and thermal insulation compared to opal glass, making it ideal for sustainable architectural projects that emphasize energy efficiency. Opal glass provides more uniform light diffusion, favored in commercial lighting for creating soft, glare-free illumination in office spaces and retail environments. Modern architecture leverages transparent wood glass in skylights and facades to combine natural aesthetics with daylight harvesting, while opal glass is preferred in pendant fixtures and wall sconces for consistent ambient lighting.
Cost Implications and Scalability
Transparent wood glass offers higher scalability potential due to its raw material abundance and simpler processing, reducing overall production costs compared to opal glass. Opal glass requires specialized manufacturing and higher energy consumption, significantly increasing cost implications, especially for large-scale applications. The cost efficiency of transparent wood glass makes it a more viable option for mass production in light diffuser technology.
Future Trends in Light Diffuser Materials
Transparent wood glass offers enhanced sustainability and natural aesthetics, making it a promising alternative to traditional opal glass in light diffusers. Future trends emphasize eco-friendly, biodegradable materials with improved light diffusion efficiency and mechanical strength, where transparent wood's renewable origin and tunable optical properties align with these demands. Innovations in nanostructured coatings and cellulose-based composites are expected to further enhance light diffusion and durability, positioning transparent wood as a leading material in next-generation light diffuser applications.
Infographic: Transparent wood glass vs Opal glass for Light diffuser
 azmater.com
azmater.com