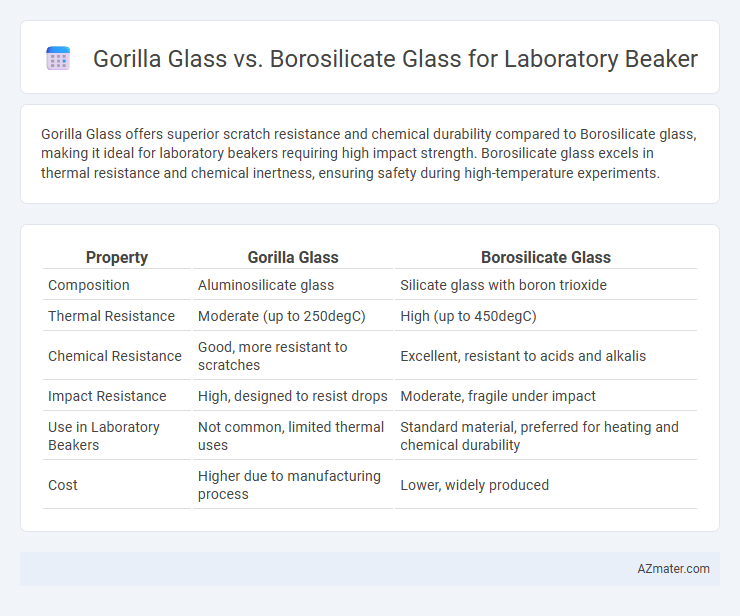
Gorilla Glass offers superior scratch resistance and chemical durability compared to Borosilicate glass, making it ideal for laboratory beakers requiring high impact strength. Borosilicate glass excels in thermal resistance and chemical inertness, ensuring safety during high-temperature experiments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Gorilla Glass | Borosilicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Aluminosilicate glass | Silicate glass with boron trioxide |
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate (up to 250degC) | High (up to 450degC) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good, more resistant to scratches | Excellent, resistant to acids and alkalis |
| Impact Resistance | High, designed to resist drops | Moderate, fragile under impact |
| Use in Laboratory Beakers | Not common, limited thermal uses | Standard material, preferred for heating and chemical durability |
| Cost | Higher due to manufacturing process | Lower, widely produced |
Introduction to Laboratory Glassware Materials
Laboratory glassware materials like Gorilla Glass and Borosilicate Glass offer distinct advantages based on chemical resistance and thermal stability. Borosilicate Glass, with its low thermal expansion coefficient (~3.3 x 10^-6 /degC), is highly resistant to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, making it the preferred choice for laboratory beakers. Gorilla Glass, primarily engineered for impact resistance and scratch hardness in consumer electronics, lacks the chemical inertness and thermal stability essential for laboratory applications.
What is Gorilla Glass?
Gorilla Glass is an aluminosilicate glass developed by Corning, known for its high scratch resistance and durability due to ion-exchange processes that strengthen its surface. Unlike traditional Borosilicate glass, commonly used in laboratory beakers for its thermal shock resistance and chemical stability, Gorilla Glass offers enhanced toughness but lower resistance to rapid temperature changes. This makes Gorilla Glass ideal for devices requiring impact resistance, while Borosilicate glass remains preferred for laboratory applications requiring heat resistance.
What is Borosilicate Glass?
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass known for its exceptional thermal resistance and chemical durability, making it ideal for laboratory beakers used in high-temperature experiments. Unlike Gorilla glass, which is chemically strengthened for scratch resistance and primarily used in consumer electronics, borosilicate glass withstands thermal shock and corrosive chemicals without cracking or breaking. This makes borosilicate glass the preferred choice for lab applications requiring reliability under rigorous conditions.
Chemical Resistance: Gorilla Glass vs Borosilicate Glass
Borosilicate glass exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to Gorilla glass, making it the preferred choice for laboratory beakers exposed to strong acids, bases, and solvents. Its low thermal expansion coefficient ensures minimal chemical reactivity and enhanced durability under rapid temperature changes. Gorilla glass, primarily designed for scratch resistance and impact strength in consumer electronics, lacks the extensive chemical stability required for rigorous lab environments.
Thermal Stability and Heat Tolerance
Gorilla Glass offers moderate thermal stability with a heat tolerance typically up to 300degC, making it suitable for everyday laboratory use but vulnerable to sudden thermal shocks. Borosilicate glass exhibits superior thermal stability and high heat tolerance, often withstanding temperatures up to 500degC and rapid temperature changes without cracking. For laboratory beakers requiring consistent exposure to high heat and thermal cycling, borosilicate glass remains the preferred material due to its enhanced durability and resistance to thermal stress.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Gorilla glass exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to borosilicate glass, offering higher resistance to impact and scratches, making it more durable for laboratory beakers subjected to frequent handling and accidental drops. Borosilicate glass, while less impact-resistant, excels in thermal shock resistance and chemical durability, maintaining integrity during rapid temperature changes and exposure to corrosive substances common in laboratory environments. For applications demanding high mechanical toughness and surface resilience, Gorilla glass provides enhanced durability, whereas borosilicate glass remains preferred for thermal and chemical stability.
Transparency and Optical Clarity
Gorilla Glass offers superior transparency and optical clarity compared to borosilicate glass, making it ideal for applications requiring precise visual observation. Its chemically strengthened surface enhances scratch resistance without compromising light transmission, ensuring clear visibility of contents in laboratory beakers. Borosilicate glass provides good clarity but may slightly distort light due to its composition, while Gorilla Glass maintains consistent optical performance under stress.
Safety and Breakage Risk
Gorilla Glass offers superior impact resistance and scratch durability compared to Borosilicate glass, significantly reducing the risk of breakage in laboratory beakers under mechanical stress. Borosilicate glass, while highly resistant to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, is more prone to shattering upon sudden impacts or drops, posing higher safety concerns in dynamic lab environments. Choosing Gorilla Glass enhances overall safety by minimizing breakage incidents and ensuring longer-lasting, safer laboratory glassware.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Gorilla Glass offers high scratch resistance and strength but comes at a significantly higher cost compared to borosilicate glass, which is more affordable and widely used in laboratory beakers. Borosilicate glass provides excellent thermal resistance and chemical durability, making it readily available from numerous suppliers at lower prices. The cost difference and greater market availability of borosilicate glass make it the preferred choice for most laboratory applications over Gorilla Glass.
Conclusion: Best Choice for Laboratory Beakers
Gorilla Glass offers superior scratch resistance and impact durability compared to borosilicate glass, making it ideal for high-use laboratory environments where strength and safety are priorities. Borosilicate glass excels in thermal resistance and chemical inertness, essential for experiments involving rapid temperature changes and reactive substances. For laboratory beakers, borosilicate glass remains the best choice due to its proven performance in heat tolerance and chemical stability, crucial for accurate and safe experimental results.
Infographic: Gorilla glass vs Borosilicate glass for Laboratory beaker
 azmater.com
azmater.com