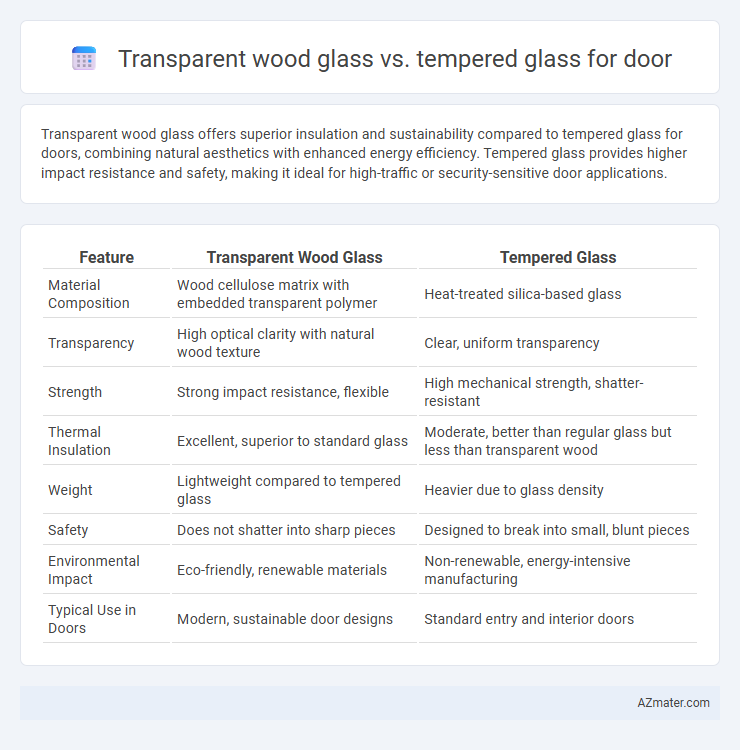
Transparent wood glass offers superior insulation and sustainability compared to tempered glass for doors, combining natural aesthetics with enhanced energy efficiency. Tempered glass provides higher impact resistance and safety, making it ideal for high-traffic or security-sensitive door applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Transparent Wood Glass | Tempered Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Wood cellulose matrix with embedded transparent polymer | Heat-treated silica-based glass |
| Transparency | High optical clarity with natural wood texture | Clear, uniform transparency |
| Strength | Strong impact resistance, flexible | High mechanical strength, shatter-resistant |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent, superior to standard glass | Moderate, better than regular glass but less than transparent wood |
| Weight | Lightweight compared to tempered glass | Heavier due to glass density |
| Safety | Does not shatter into sharp pieces | Designed to break into small, blunt pieces |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, renewable materials | Non-renewable, energy-intensive manufacturing |
| Typical Use in Doors | Modern, sustainable door designs | Standard entry and interior doors |
Introduction to Transparent Wood Glass and Tempered Glass
Transparent wood glass combines natural wood fibers with transparent polymers, offering high strength, lightweight properties, and eco-friendly benefits for door applications. Tempered glass is heat-treated to enhance durability and safety, providing excellent impact resistance and thermal strength commonly used in door panels. Both materials support modern design aesthetics, but transparent wood glass emphasizes sustainability and insulation, while tempered glass prioritizes clarity and toughness.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Transparent wood glass combines cellulose fibers from wood with polymer resins, creating a hybrid material that offers both natural aesthetics and enhanced strength through chemical treatment and impregnation processes. Tempered glass is manufactured by heating standard glass to around 620degC and rapidly cooling it, increasing its strength and making it more resistant to impact and thermal stress. The fabrication of transparent wood involves delignification and resin infiltration, while tempered glass relies on controlled thermal tempering to achieve its durability and safety features.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
Transparent wood glass offers superior optical clarity with natural diffused light transmission, reducing glare while maintaining visibility, making it ideal for creating warm, inviting door panels. Tempered glass provides high clarity with almost 90% light transmission but can cause sharp reflections and glare due to its smooth surface. For door applications emphasizing both aesthetics and functional light diffusion, transparent wood glass enhances ambiance, whereas tempered glass excels in strength and clear visibility.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Transparent wood glass offers a unique combination of lightweight strength and impact resistance due to its reinforced cellulose fibers, providing enhanced durability compared to traditional glass. Tempered glass, treated through controlled thermal or chemical processes, delivers superior hardness and shatter-resistance, making it highly reliable for safety in door applications. While tempered glass excels in resisting sudden impacts and thermal stress, transparent wood glass offers better flexibility and sustainability, making it a viable alternative for eco-friendly, durable door solutions.
Energy Efficiency and Insulation Properties
Transparent wood glass offers superior energy efficiency compared to tempered glass due to its natural insulating properties, which reduce heat transfer and maintain indoor temperature stability. Its cellular structure provides enhanced thermal insulation, lowering energy consumption for heating and cooling in door applications. Tempered glass, while durable and impact-resistant, lacks the same level of insulation and is less effective at preventing heat loss or gain.
Safety Features for Door Applications
Transparent wood glass offers enhanced safety features for door applications due to its higher resistance to shattering and impact compared to traditional tempered glass. It combines the strength of wood fibers with clear resin, providing a durable, flexible material that reduces injury risks from sharp shards if broken. Tempered glass, while strong and heat-treated to resist breakage, tends to shatter into small, blunt pieces, yet it is more brittle and susceptible to cracking under sharp impacts than transparent wood glass.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Transparent wood glass offers a significantly lower carbon footprint compared to tempered glass, as it is derived from renewable biomass and requires less energy-intensive processing. Its biodegradability and potential for carbon sequestration make it a more sustainable choice, reducing landfill waste and greenhouse gas emissions. Tempered glass, while durable and recyclable, demands higher energy consumption during production and is less environmentally friendly due to the extensive mining and processing of raw materials.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetics
Transparent wood glass offers exceptional design flexibility by combining natural wood grain patterns with translucent properties, allowing for customizable shapes, colors, and patterns that enhance door aesthetics with a warm, organic appeal. Tempered glass provides a sleek, modern look with high clarity and strength, but its design options are typically limited to clear or frosted finishes and standard shapes, restricting creative expression. Transparent wood glass uniquely integrates texture and light diffusion, making it ideal for doors that demand both durability and visually striking, nature-inspired designs.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Transparent wood glass offers a unique aesthetic and improved insulation but generally comes at a higher cost due to advanced manufacturing processes and limited suppliers. Tempered glass is widely available, more affordable, and extensively used in door applications, benefiting from established production scales and distribution networks. Market analysis reveals tempered glass dominates availability and cost-effectiveness, whereas transparent wood glass remains a niche, premium option with potential for growth as demand for sustainable materials increases.
Future Trends in Door Materials
Transparent wood glass combines renewable materials with high strength and thermal insulation, positioning it as a sustainable alternative to traditional tempered glass in door manufacturing. Its ability to offer both durability and energy efficiency supports growing trends towards eco-friendly and smart building solutions. Innovations in nanotechnology and bio-based resins are expected to further enhance the mechanical properties and transparency of transparent wood glass, accelerating its adoption in futuristic door designs.
Infographic: Transparent wood glass vs Tempered glass for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com