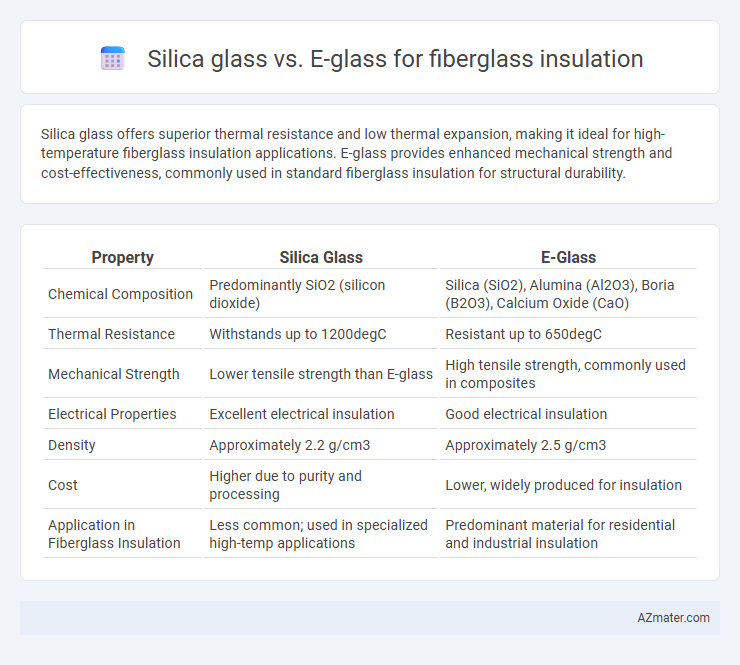
Silica glass offers superior thermal resistance and low thermal expansion, making it ideal for high-temperature fiberglass insulation applications. E-glass provides enhanced mechanical strength and cost-effectiveness, commonly used in standard fiberglass insulation for structural durability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Silica Glass | E-Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Predominantly SiO2 (silicon dioxide) | Silica (SiO2), Alumina (Al2O3), Boria (B2O3), Calcium Oxide (CaO) |
| Thermal Resistance | Withstands up to 1200degC | Resistant up to 650degC |
| Mechanical Strength | Lower tensile strength than E-glass | High tensile strength, commonly used in composites |
| Electrical Properties | Excellent electrical insulation | Good electrical insulation |
| Density | Approximately 2.2 g/cm3 | Approximately 2.5 g/cm3 |
| Cost | Higher due to purity and processing | Lower, widely produced for insulation |
| Application in Fiberglass Insulation | Less common; used in specialized high-temp applications | Predominant material for residential and industrial insulation |
Introduction to Fiberglass Insulation
Fiberglass insulation primarily uses E-glass, a type of alumino-borosilicate glass known for its strength and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for thermal and acoustic insulation in buildings. Silica glass, composed of nearly pure silicon dioxide, offers superior thermal resistance and chemical durability but is less common in standard fiberglass insulation due to higher cost and brittleness. E-glass fibers provide a balanced combination of mechanical performance and affordability, driving their widespread use in residential and commercial insulation applications.
What is Silica Glass?
Silica glass, primarily composed of silicon dioxide (SiO2), is a high-purity, heat-resistant material often used for advanced fiberglass insulation due to its superior thermal stability and chemical durability compared to E-glass. Unlike E-glass, which contains alumina and boron additives making it more cost-effective but less resistant to high temperatures, silica glass can withstand temperatures above 1000degC, making it ideal for demanding industrial applications. Its low thermal expansion and excellent electrical insulation properties ensure enhanced performance in extreme environments where traditional E-glass insulation might degrade over time.
What is E-Glass?
E-Glass, short for electrical glass, is a type of fiberglass made from alumino-borosilicate composition, offering excellent electrical insulation properties and high mechanical strength. It is widely used in fiberglass insulation due to its low cost, good thermal resistance, and durability in various environmental conditions. Compared to silica glass, E-Glass provides a balance of strength and thermal performance, making it a preferred choice for insulation applications.
Key Material Properties: Silica Glass vs E-Glass
Silica glass exhibits exceptional thermal resistance, high melting points above 1700degC, and excellent chemical inertness, making it ideal for high-temperature fiberglass insulation applications. E-glass offers a balanced combination of mechanical strength, moderate thermal resistance up to 540degC, and cost-effectiveness, commonly used in general-purpose fiberglass insulation. Both materials differ significantly in density and tensile strength, with silica glass being more brittle but more thermally stable, whereas E-glass provides improved toughness and electrical insulation properties.
Thermal Insulation Performance Comparison
Silica glass exhibits superior thermal insulation performance compared to E-glass due to its higher melting point and lower thermal conductivity, making it ideal for high-temperature applications. E-glass, while more cost-effective and widely used, has a thermal conductivity typically around 0.04 W/m*K, whereas silica glass can achieve values below 0.02 W/m*K, enhancing energy efficiency in insulation. The enhanced thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock of silica glass fibers contribute to better long-term insulation performance under extreme heat conditions.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Silica glass exhibits superior mechanical strength and high-temperature resistance compared to E-glass, making it ideal for applications requiring enhanced durability and thermal stability in fiberglass insulation. E-glass, while cost-effective and possessing good tensile strength, has lower resistance to chemical and thermal degradation, which can reduce its long-term durability in harsh environments. The choice between silica glass and E-glass directly impacts the insulation's ability to maintain structural integrity and performance under mechanical stress and prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures.
Chemical Resistance and Stability
Silica glass offers superior chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to E-glass, making it ideal for applications requiring durability in harsh chemical environments and high temperatures. E-glass, while widely used in fiberglass insulation due to its cost-effectiveness and good mechanical properties, exhibits lower resistance to alkaline and acidic substances, leading to potential degradation over time. The enhanced chemical stability of silica glass stems from its high purity and amorphous structure, ensuring longer lifespan and consistent performance in chemically aggressive conditions.
Cost and Availability
E-glass is widely favored for fiberglass insulation due to its lower cost and broad availability, making it a cost-effective solution for large-scale applications. Silica glass, while offering superior thermal resistance and durability, tends to be significantly more expensive and harder to source in bulk. The economic advantage and easy procurement of E-glass drive its predominant use in residential and commercial insulation projects.
Typical Applications in Construction and Industry
Silica glass is predominantly used in high-temperature insulation applications and refractory linings due to its exceptional thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock. E-glass, with its balanced strength, electrical insulation properties, and cost-effectiveness, is commonly utilized in standard fiberglass insulation for walls, roofing, and ductwork in residential and commercial construction. Industrial uses of E-glass include reinforcement in composite materials for automotive, marine, and wind energy sectors, whereas silica glass finds specialized roles in furnaces and kilns where extreme heat resistance is critical.
Choosing the Right Glass Fiber for Insulation Needs
Silica glass offers superior thermal resistance and low thermal expansion, making it ideal for high-temperature fiberglass insulation applications where durability and heat stability are critical. E-glass, composed of alumino-borosilicate, provides excellent electrical insulation, mechanical strength, and cost-effectiveness, making it the standard choice for most general fiberglass insulation projects. Selecting between silica glass and E-glass depends on balancing performance requirements such as thermal endurance and insulation efficiency against budget constraints and application-specific needs.
Infographic: Silica glass vs E-glass for Fiberglass insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com