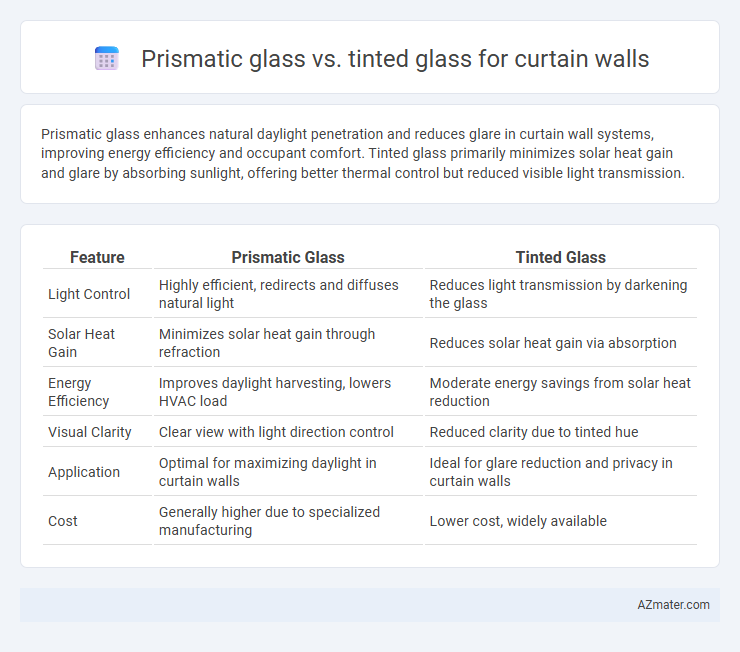
Prismatic glass enhances natural daylight penetration and reduces glare in curtain wall systems, improving energy efficiency and occupant comfort. Tinted glass primarily minimizes solar heat gain and glare by absorbing sunlight, offering better thermal control but reduced visible light transmission.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Prismatic Glass | Tinted Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Light Control | Highly efficient, redirects and diffuses natural light | Reduces light transmission by darkening the glass |
| Solar Heat Gain | Minimizes solar heat gain through refraction | Reduces solar heat gain via absorption |
| Energy Efficiency | Improves daylight harvesting, lowers HVAC load | Moderate energy savings from solar heat reduction |
| Visual Clarity | Clear view with light direction control | Reduced clarity due to tinted hue |
| Application | Optimal for maximizing daylight in curtain walls | Ideal for glare reduction and privacy in curtain walls |
| Cost | Generally higher due to specialized manufacturing | Lower cost, widely available |
Introduction to Curtain Wall Glass Options
Curtain wall glass options primarily include prismatic glass and tinted glass, each offering distinct functional benefits. Prismatic glass enhances natural daylight diffusion and visual comfort by redirecting sunlight, reducing glare without compromising transparency. Tinted glass improves energy efficiency by absorbing solar heat and reducing glare, making it ideal for controlling building temperature and enhancing occupant comfort.
What is Prismatic Glass?
Prismatic glass is engineered with embedded geometric patterns or micro-structures that refract and diffuse natural light, enhancing daylight performance and reducing glare in curtain wall applications. Unlike tinted glass, which simply absorbs and reduces solar heat gain by coloring the glass, prismatic glass optimizes light transmission to improve indoor illumination and energy efficiency. This innovation in facade technology supports sustainable building design by maximizing natural light while minimizing reliance on artificial lighting and cooling systems.
What is Tinted Glass?
Tinted glass is a type of architectural glazing that incorporates colorants to reduce solar heat gain and glare in curtain wall applications, enhancing energy efficiency and occupant comfort. It absorbs a portion of the solar spectrum, thereby lowering cooling loads and minimizing interior UV radiation without significantly compromising natural daylight. Compared to prismatic glass, tinted glass provides a uniform shading effect and improved privacy while maintaining structural performance and aesthetic integration within modern building facades.
Aesthetic Differences: Prismatic vs Tinted Glass
Prismatic glass enhances curtain walls with dynamic light refraction, creating vibrant patterns and shifting hues that change throughout the day, offering a visually engaging facade. Tinted glass provides a uniform, consistent color tone that reduces glare and controls solar heat gain, resulting in a sleek and subdued appearance. While prismatic glass emphasizes intricate optical effects and depth, tinted glass prioritizes subtlety and energy efficiency in the building's aesthetic.
Light Transmission and Daylighting Performance
Prismatic glass enhances daylighting performance by diffusing natural light uniformly, increasing light transmission while reducing glare in curtain wall applications. Tinted glass lowers light transmission by absorbing specific wavelengths, effectively controlling solar heat gain but potentially reducing interior brightness and altering color perception. Selecting prismatic glass optimizes natural light utilization and occupant comfort, whereas tinted glass prioritizes solar control and energy efficiency in building facades.
Energy Efficiency and Solar Control
Prismatic glass enhances energy efficiency by redirecting natural light deeper into interior spaces, reducing the need for artificial lighting while minimizing heat gain through selective light diffusion. Tinted glass provides solar control by absorbing and reflecting a portion of solar radiation, effectively lowering cooling loads but potentially reducing visible daylight transmission. Comparing both, prismatic glass optimizes daylight utilization and glare reduction without significant color distortion, whereas tinted glass mainly focuses on heat reduction at the expense of interior brightness.
Impact on Indoor Comfort and Glare Reduction
Prismatic glass enhances indoor comfort by diffusing sunlight, reducing glare while maintaining natural daylight levels, which creates a balanced and visually comfortable environment in curtain wall applications. Tinted glass lowers solar heat gain and glare by absorbing sunlight, but it can reduce daylight transmission, potentially impacting interior brightness and occupant comfort. Choosing prismatic glass maximizes daylight utilization and glare control, whereas tinted glass offers stronger solar heat and glare reduction at the expense of natural light.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Prismatic glass offers enhanced durability due to its engineered surface that resists scratches and environmental wear, making it ideal for curtain walls exposed to harsh weather conditions. Tinted glass, while effective in reducing solar heat gain, may require more frequent maintenance to prevent discoloration and fading over time from UV exposure. Choosing prismatic glass can lower long-term upkeep costs by maintaining optical clarity and structural integrity with less frequent cleaning and repair.
Cost Comparison: Prismatic vs Tinted Curtain Wall Glass
Prismatic glass for curtain walls typically incurs higher initial costs compared to tinted glass due to its advanced light-diffusing technology and specialized manufacturing processes. Tinted glass offers a more budget-friendly option with moderate solar control and reduced glare, though it may compromise natural light transmission more than prismatic glass. Over time, prismatic glass can provide energy savings that may offset its upfront cost difference by improving daylight efficiency and reducing cooling loads.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Curtain Wall Project
Prismatic glass enhances daylight distribution with high solar control, ideal for energy-efficient curtain walls, while tinted glass reduces glare and heat gain by absorbing solar radiation. Choosing the right glass depends on project-specific factors like climate, aesthetic preferences, and energy performance goals. Analyzing solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC) and visible light transmittance (VLT) values helps optimize comfort and sustainability in facade design.
Infographic: Prismatic glass vs Tinted glass for Curtain wall
 azmater.com
azmater.com