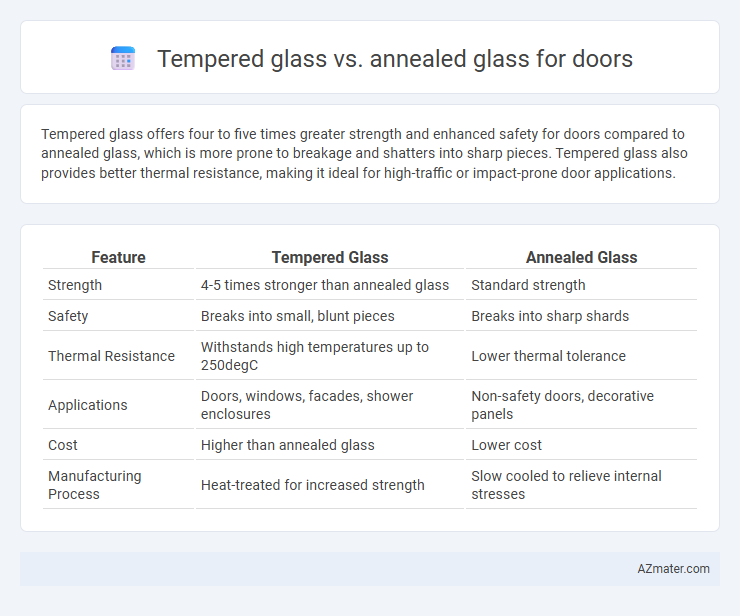
Tempered glass offers four to five times greater strength and enhanced safety for doors compared to annealed glass, which is more prone to breakage and shatters into sharp pieces. Tempered glass also provides better thermal resistance, making it ideal for high-traffic or impact-prone door applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tempered Glass | Annealed Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | 4-5 times stronger than annealed glass | Standard strength |
| Safety | Breaks into small, blunt pieces | Breaks into sharp shards |
| Thermal Resistance | Withstands high temperatures up to 250degC | Lower thermal tolerance |
| Applications | Doors, windows, facades, shower enclosures | Non-safety doors, decorative panels |
| Cost | Higher than annealed glass | Lower cost |
| Manufacturing Process | Heat-treated for increased strength | Slow cooled to relieve internal stresses |
Overview: Tempered Glass vs Annealed Glass
Tempered glass offers enhanced strength and safety due to its heat treatment process, making it ideal for door applications requiring impact resistance and shatterproof properties. Annealed glass, cooled slowly to relieve internal stresses, is more prone to breakage and produces sharp shards, limiting its use in high-impact door environments. Choosing tempered glass ensures compliance with safety standards and durability, while annealed glass remains a cost-effective option for low-risk interior doors.
Key Differences Between Tempered and Annealed Glass
Tempered glass for doors is heat-treated to increase strength and shatter into small, blunt pieces upon impact, enhancing safety, whereas annealed glass is cooled slowly to relieve internal stresses and breaks into large, sharp shards. Tempered glass typically has four to five times the strength of annealed glass, making it more resistant to impacts and thermal stress. Annealed glass is easier to cut and shape, making it suitable for custom designs but less ideal for high-traffic areas where durability and safety are critical.
Safety Features: Which Glass Is Safer for Doors?
Tempered glass offers superior safety features for doors due to its high strength and ability to shatter into small, blunt pieces that reduce injury risk upon breakage. Annealed glass, while less expensive, breaks into large, sharp shards that pose greater danger. Building codes and safety standards often favor tempered glass for door applications, especially in high-traffic or impact-prone areas.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Tempered glass offers significantly higher strength, with a tensile strength up to four times greater than annealed glass, making it more resistant to impact and thermal stress. Its durability is enhanced by a heat treatment process that creates compressive surface stresses, preventing catastrophic breakage and causing it to crumble into small, blunt pieces. In contrast, annealed glass lacks this reinforcement, making it more prone to shattering into sharp shards and less suitable for high-traffic or safety-critical door applications.
Impact and Shatter Resistance
Tempered glass offers significantly higher impact resistance compared to annealed glass due to its heat treatment process, making it ideal for doors in high-traffic or security-sensitive areas. When broken, tempered glass shatters into small, blunt pieces that reduce injury risk, whereas annealed glass breaks into large, sharp shards posing greater hazard. This enhanced shatter resistance and durability ensure tempered glass provides superior safety and longevity for door applications.
Thermal Performance and Heat Resistance
Tempered glass offers superior thermal performance and heat resistance compared to annealed glass, withstanding temperatures up to 470degF (243degC) without warping or cracking. Its thermal strength is achieved through rapid cooling during manufacturing, creating a durable, stress-resistant surface ideal for door applications exposed to fluctuating temperatures. Annealed glass, while more affordable, has a lower tolerance to heat and is prone to thermal stress fractures, making it less suitable for doors exposed to direct sunlight or high-heat environments.
Aesthetic Options and Design Flexibility
Tempered glass offers enhanced design flexibility by allowing intricate shapes and patterns due to its strength and safety features, making it ideal for modern, stylish door designs. Annealed glass provides broader aesthetic options such as custom etching and staining but lacks the same durability, limiting its use in high-traffic or safety-critical door applications. Choosing tempered glass ensures a blend of visual appeal and resilience, whereas annealed glass suits decorative doors with lower impact exposure.
Cost Analysis: Tempered vs Annealed Glass Doors
Tempered glass doors typically cost 30-50% more than annealed glass due to their enhanced safety features and heat treatment processes. Annealed glass offers a lower upfront price but may incur higher long-term expenses from potential breakage and replacement. Investing in tempered glass can reduce liability risks and maintenance costs, justifying the initial price differential for commercial and high-traffic door applications.
Building Codes and Legal Requirements
Tempered glass is often mandated by building codes for doors due to its enhanced strength and safety features, meeting requirements outlined in standards like ASTM C1048 and ANSI Z97.1. Annealed glass, lacking the same impact resistance, typically does not comply with these safety regulations for use in doors, especially in commercial and public buildings. Compliance with local building codes and glass safety standards is crucial to avoid legal liabilities and ensure occupant protection.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Door
Tempered glass offers superior strength and safety for doors, resisting impact and shattering into small, blunt pieces to reduce injury risk. Annealed glass is less durable, prone to break into sharp shards, making it less suitable for high-traffic or safety-critical door applications. Selecting tempered glass enhances security and longevity for residential and commercial doors where durability and safety are priorities.
Infographic: Tempered glass vs Annealed glass for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com