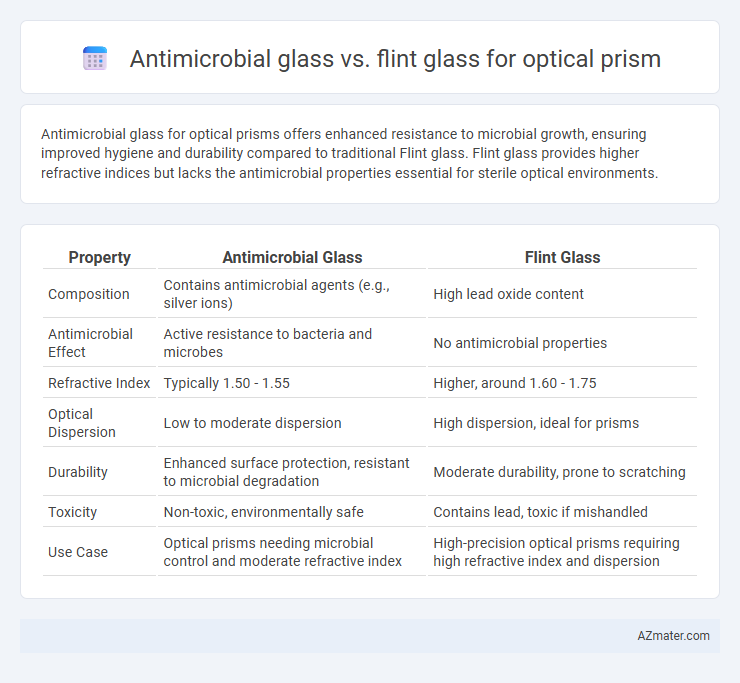
Antimicrobial glass for optical prisms offers enhanced resistance to microbial growth, ensuring improved hygiene and durability compared to traditional Flint glass. Flint glass provides higher refractive indices but lacks the antimicrobial properties essential for sterile optical environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Antimicrobial Glass | Flint Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Contains antimicrobial agents (e.g., silver ions) | High lead oxide content |
| Antimicrobial Effect | Active resistance to bacteria and microbes | No antimicrobial properties |
| Refractive Index | Typically 1.50 - 1.55 | Higher, around 1.60 - 1.75 |
| Optical Dispersion | Low to moderate dispersion | High dispersion, ideal for prisms |
| Durability | Enhanced surface protection, resistant to microbial degradation | Moderate durability, prone to scratching |
| Toxicity | Non-toxic, environmentally safe | Contains lead, toxic if mishandled |
| Use Case | Optical prisms needing microbial control and moderate refractive index | High-precision optical prisms requiring high refractive index and dispersion |
Introduction to Optical Prisms and Glass Types
Optical prisms are precision components designed to refract, reflect, and disperse light within devices such as cameras, microscopes, and spectrometers. Antimicrobial glass used for optical prisms offers enhanced durability and hygiene by inhibiting bacterial growth on surfaces, making it ideal for medical and laboratory applications. Flint glass, characterized by its high refractive index and dispersion due to lead oxide content, provides superior light-bending capabilities essential in high-precision optics.
What is Antimicrobial Glass?
Antimicrobial glass incorporates silver ions or other antimicrobial agents embedded within its surface to inhibit the growth of bacteria, fungi, and viruses, ensuring a cleaner and safer optical environment for prisms used in medical and laboratory applications. Flint glass, a traditional optical material known for its high refractive index and low dispersion, lacks inherent antimicrobial properties, potentially allowing microbial accumulation on optical surfaces over time. Integrating antimicrobial glass in optical prisms significantly enhances hygiene and durability without compromising optical clarity or performance.
Overview of Flint Glass Properties
Flint glass, characterized by its high refractive index and dispersion, is commonly used in optical prisms to enhance image clarity and color separation. Its dense lead content provides superior brightness and contrast, making it ideal for precise light refraction applications. Compared to antimicrobial glass, flint glass offers enhanced optical performance but lacks inherent antimicrobial properties, which may be critical in environments requiring hygiene control.
Light Transmission: Antimicrobial vs Flint Glass
Antimicrobial glass for optical prisms typically offers higher light transmission rates, ranging from 90% to 95%, due to its specially coated surface that reduces microbial growth without compromising clarity. Flint glass, known for its high refractive index and dispersion properties, transmits around 85% to 90% of light but may introduce slight chromatic aberrations affecting the prism's performance. The enhanced light transmission in antimicrobial glass ensures clearer image quality and improved optical efficiency compared to traditional flint glass prisms.
Antimicrobial Features and Benefits in Optical Applications
Antimicrobial glass for optical prisms incorporates silver ions or copper nanoparticles to inhibit microbial growth, ensuring enhanced hygiene and reducing contamination risks in medical and laboratory settings. This antimicrobial property preserves optical clarity and reduces maintenance frequency compared to traditional flint glass, which lacks inherent antimicrobial features and is prone to microbial buildup. The integration of antimicrobial technology in optical prisms significantly benefits applications requiring sterile environments while maintaining superior light transmission and refractive index stability.
Dispersion and Refractive Index Comparison
Antimicrobial glass for optical prisms typically exhibits a refractive index ranging from 1.50 to 1.55 with moderate dispersion values, enhancing image clarity while inhibiting microbial growth. Flint glass, known for its higher refractive index between 1.60 and 1.75 and greater dispersion coefficients, provides superior chromatic aberration correction but lacks inherent antimicrobial properties. The choice between antimicrobial and flint glass involves balancing lower dispersion and antimicrobial benefits against the higher refractive index and dispersion necessary for advanced optical applications.
Durability and Chemical Resistance
Antimicrobial glass for optical prisms offers enhanced chemical resistance by preventing microbial growth, maintaining surface integrity in harsh environments compared to flint glass, which is more susceptible to chemical wear and microbial contamination. Flint glass, known for its high refractive index, generally exhibits lower durability under corrosive conditions, leading to potential degradation and reduced optical performance over time. The superior chemical resilience of antimicrobial glass ensures longer-lasting durability and consistent optical clarity in demanding applications.
Cost Analysis: Antimicrobial Glass vs Flint Glass
Antimicrobial glass for optical prisms typically incurs higher initial costs compared to flint glass due to advanced coating technologies and enhanced material properties. Flint glass, while more cost-effective, lacks antimicrobial features, making it less suitable for applications requiring hygienic surfaces. Long-term cost benefits of antimicrobial glass arise from reduced maintenance, lower contamination risks, and extended product lifespan, offsetting the upfront price difference.
Application Suitability in Modern Optics
Antimicrobial glass offers superior resistance to microbial growth, making it highly suitable for optical prisms used in medical diagnostics and laboratory settings where hygiene is critical. Flint glass, known for its high refractive index and low dispersion, remains ideal for precision optical instruments requiring enhanced light bending and color correction, such as high-performance cameras and telescopes. The choice between antimicrobial and flint glass hinges on specific application demands, balancing optical clarity and contamination control in modern optics.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Glass for Optical Prisms
Antimicrobial glass offers enhanced durability and hygiene benefits, making it ideal for medical and laboratory optical prisms where contamination control is critical. Flint glass provides superior refractive properties and higher dispersion, favored in precision optics requiring accurate light manipulation. Selecting the right glass depends on balancing antimicrobial needs against optical performance requirements, with antimicrobial glass suited for sterile environments and flint glass excelling in high-precision optical applications.
Infographic: Antimicrobial glass vs Flint glass for Optical prism
 azmater.com
azmater.com