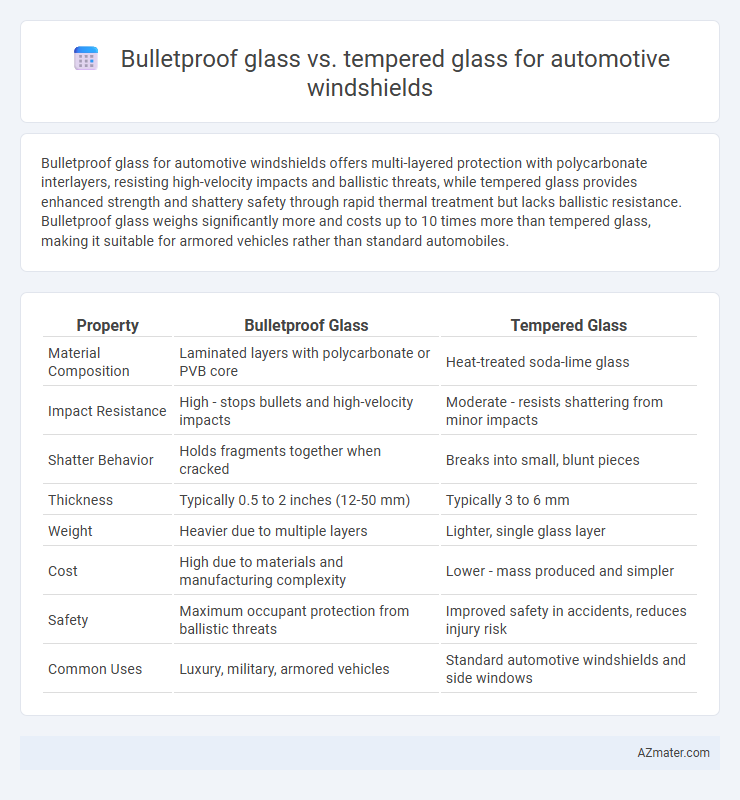
Bulletproof glass for automotive windshields offers multi-layered protection with polycarbonate interlayers, resisting high-velocity impacts and ballistic threats, while tempered glass provides enhanced strength and shattery safety through rapid thermal treatment but lacks ballistic resistance. Bulletproof glass weighs significantly more and costs up to 10 times more than tempered glass, making it suitable for armored vehicles rather than standard automobiles.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bulletproof Glass | Tempered Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Laminated layers with polycarbonate or PVB core | Heat-treated soda-lime glass |
| Impact Resistance | High - stops bullets and high-velocity impacts | Moderate - resists shattering from minor impacts |
| Shatter Behavior | Holds fragments together when cracked | Breaks into small, blunt pieces |
| Thickness | Typically 0.5 to 2 inches (12-50 mm) | Typically 3 to 6 mm |
| Weight | Heavier due to multiple layers | Lighter, single glass layer |
| Cost | High due to materials and manufacturing complexity | Lower - mass produced and simpler |
| Safety | Maximum occupant protection from ballistic threats | Improved safety in accidents, reduces injury risk |
| Common Uses | Luxury, military, armored vehicles | Standard automotive windshields and side windows |
Introduction: Bulletproof vs Tempered Glass in Automotive Windshields
Bulletproof glass in automotive windshields offers enhanced protection by combining multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate to resist high-velocity impacts and ballistic threats. Tempered glass, commonly used in standard windshields, undergoes controlled thermal or chemical treatments to increase strength and shatter into small, less harmful pieces upon breakage. Choosing between bulletproof and tempered glass depends on the required security level, with bulletproof glass providing superior defense in high-risk environments while tempered glass ensures durability and safety for everyday driving.
Key Material Differences
Bulletproof glass for automotive windshields is composed of multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate materials, providing enhanced resistance to ballistic impacts and preventing shattering. Tempered glass undergoes a heat treatment process that increases its strength, causing it to break into small, blunt pieces upon impact, but lacks the multi-layered structure found in bulletproof glass. The key material difference lies in bulletproof glass's multiple laminated layers and specialized polymers versus tempered glass's single, heat-strengthened glass layer.
How Each Glass Type Is Manufactured
Bulletproof glass for automotive windshields is manufactured using multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate materials, creating a composite structure designed to absorb and dissipate impact energy. Tempered glass is produced through a heat treatment process where the glass is rapidly cooled after being heated to around 620degC, resulting in increased strength and a characteristic shattering pattern into small, blunt pieces. The layered construction of bulletproof glass provides ballistic protection, while tempered glass emphasizes enhanced durability and safety during breakage.
Impact Resistance Comparison
Bulletproof glass offers significantly higher impact resistance than tempered glass due to its multi-layered construction of polycarbonate and laminated glass, designed to absorb and disperse energy from high-velocity projectiles and blunt force. Tempered glass, while stronger than regular glass and able to shatter into small, less dangerous pieces upon impact, lacks the ability to withstand sustained or high-powered impacts. In automotive windshields, bulletproof glass provides enhanced protection against ballistic threats and severe collisions, whereas tempered glass mainly protects against minor impacts and breakage.
Safety and Security Features
Bulletproof glass for automotive windshields consists of multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate, providing superior resistance against ballistic threats and forced entry, ensuring maximum occupant protection in high-risk environments. Tempered glass, while much stronger than regular glass due to its thermal treatment process, primarily offers enhanced impact resistance and shatters into small, blunt pieces to reduce injury during accidents but lacks the ability to stop bullets or heavy penetration. For safety and security, bulletproof glass excels in preventing penetration from firearms and blunt objects, whereas tempered glass focuses on minimizing injury from glass breakage and general impact resistance.
Cost Analysis and Affordability
Bulletproof glass for automotive windshields typically costs significantly more than tempered glass, with prices ranging from $200 to $500 per square foot compared to tempered glass which generally costs $50 to $150 per square foot. The higher expense of bulletproof glass is due to its multi-layered construction involving polycarbonate and laminated glass, providing enhanced protection against ballistic threats but impacting overall affordability for average consumers. Tempered glass remains the most cost-effective solution for standard automotive safety requirements, making it the preferred choice for most manufacturers and consumers focused on budget-friendly windshield replacement or manufacturing.
Weight and Installation Considerations
Bulletproof glass for automotive windshields is significantly heavier than tempered glass due to its multiple layers of laminated polycarbonate and glass, which impacts overall vehicle weight and fuel efficiency. Installation of bulletproof glass requires specialized techniques and reinforced frames to securely handle its thickness and weight, increasing labor and cost compared to tempered glass, which is lighter and easier to fit with standard mounting methods. Choosing between bulletproof and tempered glass involves balancing enhanced security needs against added weight and installation complexity.
Visibility and Optical Clarity
Bulletproof glass for automotive windshields consists of multiple laminated layers that significantly enhance ballistic protection without compromising visibility, maintaining high optical clarity even under impact. Tempered glass is heat-treated to improve strength and shatter into small, blunt pieces, offering good visibility but lower resistance to penetration and slightly reduced optical clarity due to internal stresses. The multilayer construction of bulletproof glass provides superior transparency and minimal distortion, making it ideal for applications requiring maximum security and clear vision.
Regulatory and Legal Requirements
Bulletproof glass for automotive windshields must comply with stringent federal safety standards such as FMVSS 205, ensuring ballistic resistance while maintaining visibility and impact absorption for occupant protection. Tempered glass, regulated under the same FMVSS 205, is engineered to shatter into small, less harmful fragments upon impact, addressing legal mandates for passenger safety in everyday driving conditions. Regulatory requirements dictate specific thickness, laminated structure, and performance tests for both types of glass to meet crashworthiness and pedestrian safety laws set by agencies like NHTSA.
Choosing the Right Glass for Automotive Windshields
Bulletproof glass provides superior protection by combining multiple layers of polycarbonate and laminated glass, making it ideal for high-security vehicles but significantly heavier and more expensive than tempered glass. Tempered glass, commonly used in standard automotive windshields, offers excellent shatter resistance and safety by breaking into small, less harmful pieces upon impact but lacks ballistic protection. Choosing the right glass for automotive windshields depends on balancing security needs, cost, weight considerations, and compliance with vehicle safety standards.
Infographic: Bulletproof glass vs Tempered glass for Automotive windshield
 azmater.com
azmater.com