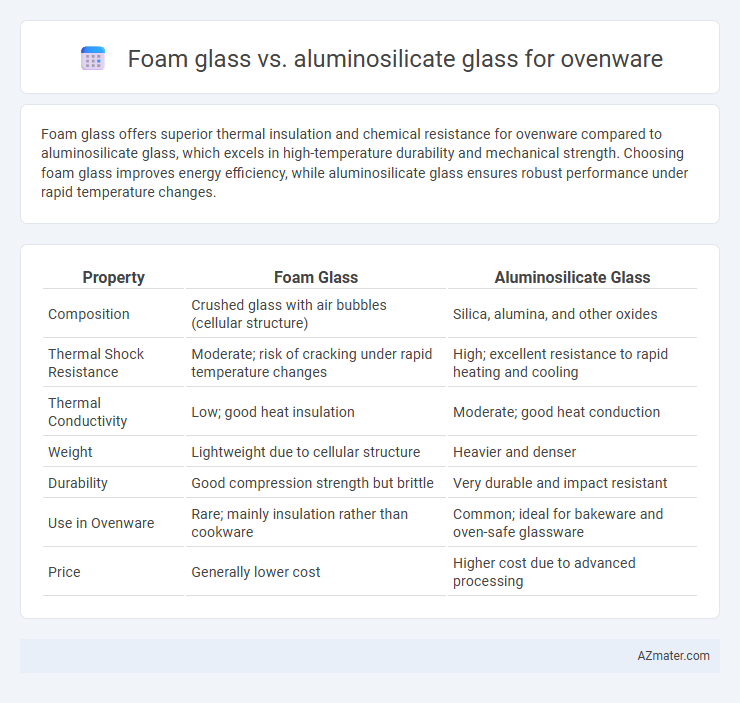
Foam glass offers superior thermal insulation and chemical resistance for ovenware compared to aluminosilicate glass, which excels in high-temperature durability and mechanical strength. Choosing foam glass improves energy efficiency, while aluminosilicate glass ensures robust performance under rapid temperature changes.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Foam Glass | Aluminosilicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Crushed glass with air bubbles (cellular structure) | Silica, alumina, and other oxides |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Moderate; risk of cracking under rapid temperature changes | High; excellent resistance to rapid heating and cooling |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low; good heat insulation | Moderate; good heat conduction |
| Weight | Lightweight due to cellular structure | Heavier and denser |
| Durability | Good compression strength but brittle | Very durable and impact resistant |
| Use in Ovenware | Rare; mainly insulation rather than cookware | Common; ideal for bakeware and oven-safe glassware |
| Price | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to advanced processing |
Introduction to Ovenware Materials
Foam glass and aluminosilicate glass are key materials used in ovenware, each offering distinct thermal and mechanical properties. Foam glass provides excellent insulation and lightweight characteristics due to its porous structure, making it ideal for energy-efficient oven components. Aluminosilicate glass offers superior thermal shock resistance and durability, ensuring safe use at high temperatures in cookware and bakeware applications.
What is Foam Glass?
Foam glass is a lightweight, porous material made by heating crushed glass with a foaming agent, resulting in excellent thermal insulation and resistance to high temperatures, making it suitable for ovenware. Aluminosilicate glass, in contrast, is a dense, heat-resistant glass composed of aluminum oxide and silica, known for its durability and thermal shock resistance but lacks the insulating properties of foam glass. For ovenware, foam glass provides superior insulation, reducing heat transfer, while aluminosilicate glass offers strength and direct heat resistance.
What is Aluminosilicate Glass?
Aluminosilicate glass is a type of glass composed primarily of aluminum oxide and silicon dioxide, known for its exceptional thermal resistance and mechanical strength, making it ideal for ovenware applications. Compared to foam glass, aluminosilicate glass withstands rapid temperature changes without cracking and offers greater durability under extreme heat conditions. Its low thermal expansion coefficient ensures reliable performance in high-temperature environments, enhancing safety and longevity in kitchenware products.
Thermal Resistance Comparison
Foam glass exhibits superior thermal insulation properties with a low thermal conductivity of approximately 0.04 W/m*K, making it ideal for maintaining steady oven temperatures and minimizing heat loss. Aluminosilicate glass withstands high thermal shock and operates effectively at temperatures up to 1500degC, thanks to its low coefficient of thermal expansion around 3.3 x 10^-6 /degC. When comparing thermal resistance, foam glass excels in insulating performance, while aluminosilicate glass provides greater durability under rapid temperature changes and extreme heat conditions.
Durability and Strength Differences
Foam glass, known for its cellular structure, offers excellent thermal insulation but has lower mechanical strength compared to aluminosilicate glass, which exhibits superior durability due to its dense, non-porous composition. Aluminosilicate glass withstands high thermal shock and mechanical stress better, making it more suitable for ovenware applications requiring resistance to sudden temperature changes and heavy use. The inherent brittleness of foam glass limits its ability to endure impact and pressure, whereas aluminosilicate glass maintains structural integrity under rigorous cooking conditions.
Heat Distribution Performance
Foam glass offers excellent insulation but has limited heat distribution due to its porous structure, making it less effective for uniform cooking in ovenware. Aluminosilicate glass exhibits superior heat distribution and thermal shock resistance, ensuring even heat transfer and durability under rapid temperature changes. Therefore, aluminosilicate glass is preferred for ovenware requiring consistent heat performance and longevity.
Chemical and Stain Resistance
Foam glass exhibits superior chemical resistance and stain resistance compared to aluminosilicate glass due to its non-porous, inert silica-based matrix that prevents absorption of acids, alkalis, and organic compounds. Aluminosilicate glass, while robust and thermal shock-resistant, can be more susceptible to staining and chemical etching over time when exposed to harsh detergents or acidic food residues. The closed-cell structure of foam glass provides enhanced durability in maintaining clarity and hygiene, making it ideal for ovenware applications requiring long-term chemical stability.
Safety and Health Considerations
Foam glass offers superior thermal insulation and chemical inertness, reducing the risk of toxic emissions or contamination during high-temperature cooking, making it a safer choice for ovenware. Aluminosilicate glass provides excellent thermal shock resistance and durability but may release trace amounts of aluminum compounds when exposed to extreme conditions, which raises concerns regarding long-term health safety. Both materials require rigorous testing for leachables and heat exposure, yet foam glass's non-porous structure tends to minimize bacterial growth and allergenic risks in ovenware applications.
Cost and Availability
Foam glass offers a cost-effective solution for ovenware due to its inexpensive raw materials and straightforward manufacturing process, resulting in lower market prices compared to aluminosilicate glass. Aluminosilicate glass, while more expensive, provides superior thermal shock resistance and durability, making it less common but preferred for high-end or professional cookware applications. Availability of foam glass is widespread due to its use in insulation and construction, whereas aluminosilicate glass is more specialized and typically available through niche suppliers catering to premium ovenware markets.
Which Glass is Best for Ovenware?
Foam glass offers excellent thermal insulation and lightweight properties, making it suitable for ovenware that requires heat retention and energy efficiency. Aluminosilicate glass excels in thermal shock resistance and durability at high temperatures, ensuring safety and longevity during rapid temperature changes. For ovenware, aluminosilicate glass is generally preferred due to its superior strength and ability to withstand direct exposure to high heat without cracking.
Infographic: Foam glass vs Aluminosilicate glass for Ovenware
 azmater.com
azmater.com