Automotive windshields typically use laminated safety glass, combining a tough outer glass with an inner plastic layer for impact resistance and shatter prevention. Screen glass, often used in electronics, lacks the durability and safety features required for automotive applications, making safety glass the preferred material for windshields.
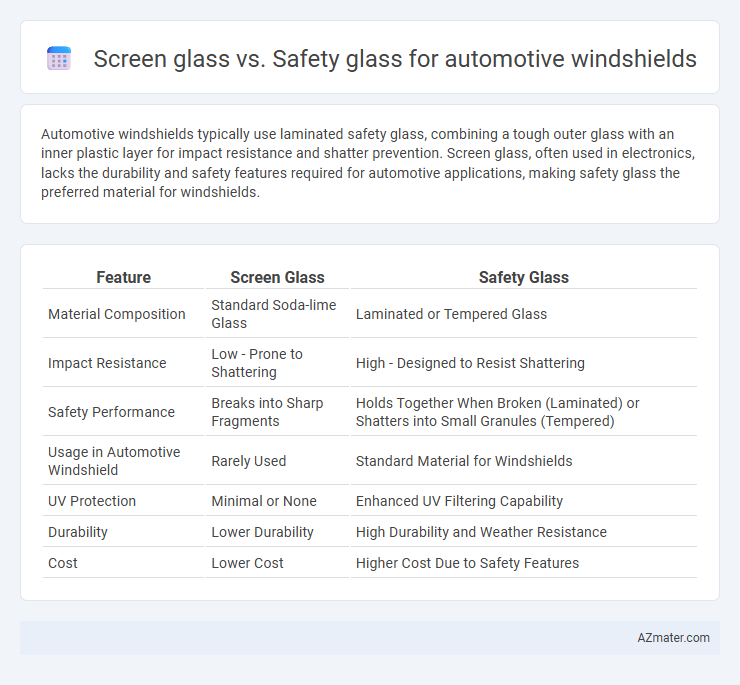
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Screen Glass | Safety Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Standard Soda-lime Glass | Laminated or Tempered Glass |
| Impact Resistance | Low - Prone to Shattering | High - Designed to Resist Shattering |
| Safety Performance | Breaks into Sharp Fragments | Holds Together When Broken (Laminated) or Shatters into Small Granules (Tempered) |
| Usage in Automotive Windshield | Rarely Used | Standard Material for Windshields |
| UV Protection | Minimal or None | Enhanced UV Filtering Capability |
| Durability | Lower Durability | High Durability and Weather Resistance |
| Cost | Lower Cost | Higher Cost Due to Safety Features |
Introduction to Automotive Windshield Technologies
Automotive windshield technologies primarily include screen glass and safety glass, each designed to enhance visibility and protection. Safety glass, typically laminated with a plastic interlayer, provides superior impact resistance and prevents shattering, ensuring passenger safety during collisions. Screen glass, more common in older models, offers basic transparency but lacks the structural integrity and durability essential for modern automotive safety standards.
What is Screen Glass?
Screen glass is a specialized type of automotive glass designed primarily for display screens rather than vehicle windshields, featuring enhanced clarity and scratch resistance to protect sensitive LCD or OLED panels. Unlike safety glass used in windshields, which incorporates laminated or tempered layers to prevent shattering and provide impact resistance, screen glass prioritizes optical performance and touch sensitivity. In automotive applications, safety glass is critical for occupant protection during collisions, whereas screen glass ensures durability and visibility for in-car infotainment systems.
What is Safety Glass?
Safety glass used in automotive windshields is designed to minimize injury during accidents by incorporating laminated or tempered glass layers that prevent shattering into sharp pieces. Laminated safety glass consists of two glass sheets bonded with a plastic interlayer, which holds fragments together upon impact, enhancing occupant protection. This contrasts with ordinary screen glass, which lacks impact-resistant features and poses higher risks of injury when broken.
Key Differences Between Screen Glass and Safety Glass
Screen glass typically refers to laminated or tempered glass used in automotive windshields, designed to provide clear visibility and basic protection, while safety glass is specifically engineered to reduce injury risks during accidents by shattering into small, less harmful pieces. Key differences include impact resistance, with safety glass offering superior durability and compliance with automotive safety standards like ASTM and DOT. Screen glass prioritizes optical clarity for display and screen integration, whereas safety glass emphasizes passenger protection and structural integrity.
Impact Resistance and Durability Comparison
Safety glass, commonly laminated for automotive windshields, offers superior impact resistance by preventing shattering upon collision, enhancing passenger safety. Screen glass, often tempered, provides high durability and scratch resistance but lacks the same level of impact protection, as it can break into sharp shards. Laminated safety glass combines multiple layers to absorb impact energy and maintain structural integrity, making it the preferred choice for automotive windshield applications.
Safety Considerations for Drivers and Passengers
Safety glass for automotive windshields, such as laminated glass, offers enhanced protection by preventing shattering upon impact, thereby reducing the risk of injury to drivers and passengers. In contrast, screen glass, typically made from tempered glass, can break into sharp shards, posing a higher risk during collisions. Laminated safety glass also maintains structural integrity, supporting the vehicle's frame and preventing occupant ejection in accidents.
Cost Factors: Screen Glass vs Safety Glass
Screen glass for automotive windshields generally costs less upfront but lacks the durability and impact resistance of safety glass, potentially leading to higher replacement expenses over time. Safety glass, which includes laminated and tempered variants, offers superior strength and shatterproof properties, justifying its higher initial investment with enhanced safety and longevity. Choosing safety glass reduces long-term maintenance and liability costs, making it more cost-effective despite the higher purchase price.
Legal Requirements and Industry Standards
Safety glass used in automotive windshields meets strict legal requirements such as the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard (FMVSS) 205 in the United States, ensuring impact resistance and shatter protection. Screen glass, typically non-laminated and lacking safety certifications, fails to comply with these industry standards and is unsuitable for automotive applications due to its fragility and lack of controlled breakage. Compliance with regulations like FMVSS 205 and ECE R43 mandates the use of laminated safety glass, enhancing driver protection through reduced injury risk during collisions.
Maintenance and Repair Implications
Screen glass in automotive windshields often requires frequent maintenance due to its susceptibility to scratches and chips, which can impair visibility and compromise safety. Safety glass, such as laminated or tempered glass, provides enhanced durability with a higher resistance to impact and easier repair options, reducing the frequency and cost of maintenance. Repair implications favor safety glass because small cracks or chips can be professionally fixed without full windshield replacement, unlike screen glass which often demands more extensive repairs or replacement.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Vehicle
Choosing the right glass for your vehicle windshield involves understanding the differences between screen glass and safety glass; safety glass, typically laminated or tempered, offers enhanced impact resistance and prevents shattering, ensuring passenger protection. Screen glass, often used in non-automotive applications, lacks the structural integrity and safety features required for automotive windshields. Opting for certified automotive safety glass guarantees compliance with safety standards and improves durability under various driving conditions.
Infographic: Screen glass vs Safety glass for Automotive windshield
 azmater.com
azmater.com