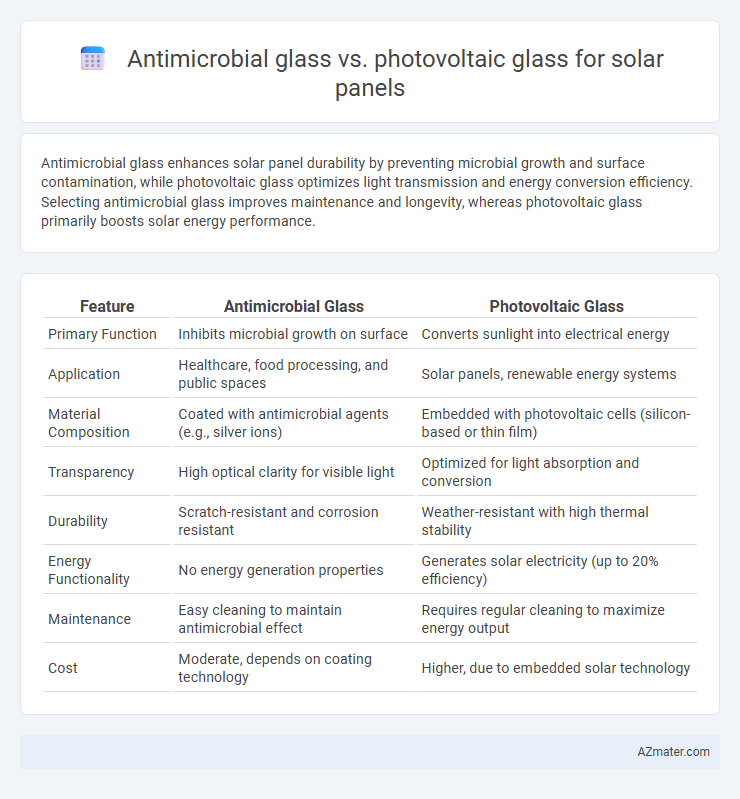
Antimicrobial glass enhances solar panel durability by preventing microbial growth and surface contamination, while photovoltaic glass optimizes light transmission and energy conversion efficiency. Selecting antimicrobial glass improves maintenance and longevity, whereas photovoltaic glass primarily boosts solar energy performance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Antimicrobial Glass | Photovoltaic Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Inhibits microbial growth on surface | Converts sunlight into electrical energy |
| Application | Healthcare, food processing, and public spaces | Solar panels, renewable energy systems |
| Material Composition | Coated with antimicrobial agents (e.g., silver ions) | Embedded with photovoltaic cells (silicon-based or thin film) |
| Transparency | High optical clarity for visible light | Optimized for light absorption and conversion |
| Durability | Scratch-resistant and corrosion resistant | Weather-resistant with high thermal stability |
| Energy Functionality | No energy generation properties | Generates solar electricity (up to 20% efficiency) |
| Maintenance | Easy cleaning to maintain antimicrobial effect | Requires regular cleaning to maximize energy output |
| Cost | Moderate, depends on coating technology | Higher, due to embedded solar technology |
Introduction to Solar Panel Glass Technologies
Solar panel glass technologies primarily include antimicrobial glass and photovoltaic glass, each serving distinct roles in enhancing solar panel efficiency and durability. Antimicrobial glass integrates coatings that inhibit microbial growth, improving panel longevity and reducing maintenance in humid or polluted environments. Photovoltaic glass is designed to maximize light transmission and withstand environmental stresses, directly impacting the energy conversion efficiency and structural integrity of solar panels.
What is Antimicrobial Glass?
Antimicrobial glass incorporates agents such as silver ions or copper nanoparticles to inhibit the growth of bacteria, viruses, and fungi on its surface, ensuring cleaner and safer solar panel installations. Unlike photovoltaic glass, which primarily focuses on maximizing light transmission and energy conversion efficiency, antimicrobial glass enhances durability and reduces maintenance by preventing microbial biofilm formation. This functional glass is especially valuable in environments prone to contamination, safeguarding solar panels from bio-degradation without compromising transparency or energy output.
What is Photovoltaic Glass?
Photovoltaic glass is a specialized type of glass designed to maximize the efficiency and durability of solar panels by allowing optimal sunlight transmission while protecting the photovoltaic cells beneath it. It is engineered with anti-reflective coatings and high solar transmittance properties to enhance energy conversion rates. Unlike antimicrobial glass, which primarily inhibits microbial growth on surfaces, photovoltaic glass focuses on maximizing solar energy capture for renewable power generation.
Key Characteristics of Antimicrobial Glass
Antimicrobial glass for solar panels features a surface treatment that inhibits the growth of bacteria, fungi, and algae, enhancing hygiene and reducing maintenance frequency. This glass type often incorporates silver ions or other biocidal agents embedded within its coating, providing long-lasting protection without compromising transparency or energy efficiency. Compared to photovoltaic glass, antimicrobial glass prioritizes cleanliness and microbial resistance, making it ideal for environments where biological contamination can impact panel performance.
Core Advantages of Photovoltaic Glass
Photovoltaic glass offers superior energy conversion efficiency by integrating photovoltaic cells that generate electricity directly from sunlight, significantly enhancing solar panel performance. Its durability and weather resistance protect solar modules from environmental damage, ensuring long-term operational stability and reduced maintenance costs. Unlike antimicrobial glass primarily designed for hygiene, photovoltaic glass maximizes renewable energy output, making it a critical component in sustainable energy solutions.
Antimicrobial Glass in Solar Panel Applications
Antimicrobial glass in solar panel applications enhances durability by inhibiting microbial growth, which can cause surface degradation and reduce light transmittance. This glass type maintains optimal efficiency and cleanliness without frequent maintenance, crucial for panels in humid or polluted environments. Compared to photovoltaic glass primarily designed for energy conversion, antimicrobial glass prioritizes long-term performance and reduced biofouling in solar installations.
Photovoltaic Glass in Energy Generation
Photovoltaic glass enhances solar panel efficiency by maximizing light transmission while protecting solar cells from environmental damage and mechanical stress. Its advanced coatings reduce reflection and increase energy conversion rates, contributing significantly to sustainable energy generation. Unlike antimicrobial glass, which primarily inhibits microbial growth, photovoltaic glass directly impacts solar power output and longevity.
Comparative Analysis: Efficiency and Longevity
Antimicrobial glass for solar panels offers enhanced surface cleanliness by inhibiting microbial growth, potentially reducing maintenance needs and preserving light transmittance over time. Photovoltaic glass is primarily engineered for maximum light transmission and durability under environmental stress, optimizing energy conversion efficiency and structural longevity in solar modules. Comparative analysis shows photovoltaic glass typically outperforms antimicrobial variants in energy efficiency due to specialized coatings, while antimicrobial glass contributes to longer operational life by minimizing contamination-related degradation.
Cost Implications: Antimicrobial vs Photovoltaic Glass
Antimicrobial glass for solar panels generally incurs higher upfront costs due to specialized coatings that inhibit microbial growth and maintain panel efficiency by reducing dirt and biofilm accumulation. Photovoltaic glass, designed primarily for optimal light transmission and durability, typically offers lower production costs but may require more frequent cleaning and maintenance, potentially increasing long-term expenses. Cost implications hinge on the balance between initial investment in antimicrobial treatment and savings from improved panel performance and reduced maintenance over the solar panel's lifespan.
Future Trends and Innovations in Solar Panel Glass
Future trends in solar panel glass emphasize multifunctional surfaces, with antimicrobial glass providing added protection against microbial contamination, enhancing panel longevity in humid or polluted environments. Innovations in photovoltaic glass focus on improving light transmittance and durability through advanced coatings and nanostructures, enabling higher energy conversion efficiencies. The convergence of these technologies points toward solar panels with integrated antimicrobial properties and enhanced photovoltaic performance, driving sustainable energy solutions in diverse climates.
Infographic: Antimicrobial glass vs Photovoltaic glass for Solar panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com