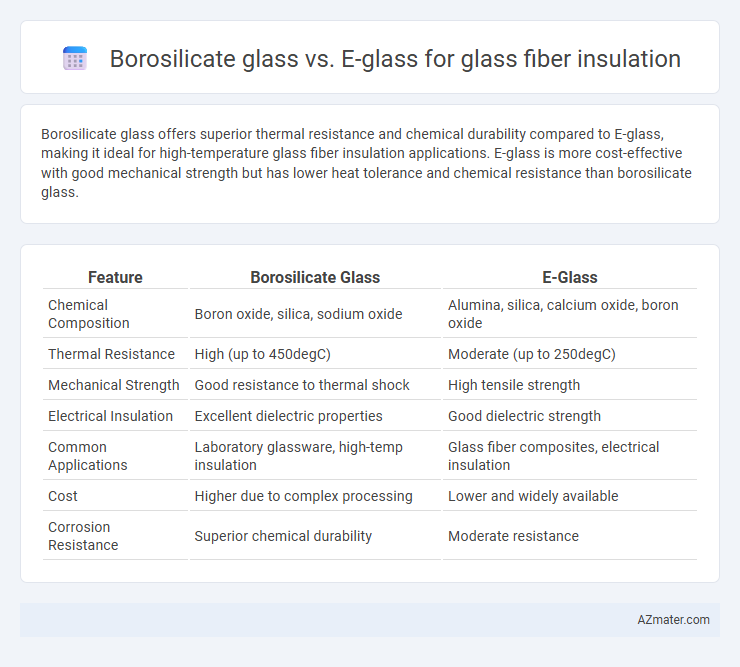
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and chemical durability compared to E-glass, making it ideal for high-temperature glass fiber insulation applications. E-glass is more cost-effective with good mechanical strength but has lower heat tolerance and chemical resistance than borosilicate glass.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Borosilicate Glass | E-Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Boron oxide, silica, sodium oxide | Alumina, silica, calcium oxide, boron oxide |
| Thermal Resistance | High (up to 450degC) | Moderate (up to 250degC) |
| Mechanical Strength | Good resistance to thermal shock | High tensile strength |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent dielectric properties | Good dielectric strength |
| Common Applications | Laboratory glassware, high-temp insulation | Glass fiber composites, electrical insulation |
| Cost | Higher due to complex processing | Lower and widely available |
| Corrosion Resistance | Superior chemical durability | Moderate resistance |
Introduction to Glass Fiber Insulation
Glass fiber insulation commonly utilizes E-glass due to its excellent electrical insulation, high tensile strength, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for thermal and acoustic applications. Borosilicate glass fibers offer superior chemical resistance and thermal stability, suitable for environments demanding higher durability against corrosion and heat. Choosing between borosilicate and E-glass depends on specific insulation requirements, balancing performance characteristics with economic considerations.
What is Borosilicate Glass?
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass composed primarily of silica and boron trioxide, renowned for its high thermal resistance and low thermal expansion, making it ideal for glass fiber insulation in high-temperature environments. Compared to E-glass, which is commonly used for electrical insulation due to its good strength and affordability, borosilicate glass fibers offer superior resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion. This makes borosilicate glass particularly suitable for applications requiring durability under extreme heat and harsh chemical exposure.
What is E-glass?
E-glass, or electrical-grade glass, is a type of fiberglass made primarily from alumino-borosilicate materials, known for its excellent electrical insulating properties and high mechanical strength. It is widely used in glass fiber insulation due to its durability, resistance to thermal shock, and cost-effectiveness compared to Borosilicate glass. While Borosilicate glass offers superior chemical and thermal resistance, E-glass remains the preferred choice for reinforcement in composites and insulation applications requiring a balance between performance and affordability.
Chemical Composition Differences
Borosilicate glass contains approximately 70-80% silica (SiO2) and 7-13% boron oxide (B2O3), which enhances thermal resistance and chemical durability, making it ideal for high-temperature insulation applications. E-glass, or electrical glass, typically consists of 52-56% silica, 12-16% alumina (Al2O3), and significant amounts of calcium oxide (CaO) and magnesium oxide (MgO), providing superior electrical insulation and mechanical strength. The presence of boron oxide in borosilicate glass reduces thermal expansion, whereas the higher alumina and alkaline earth oxides in E-glass increase electrical performance and impact resistance in fiberglass insulation.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance with a melting point around 820degC, making it highly effective for high-temperature glass fiber insulation compared to E-glass, which melts near 1150degC but has lower thermal shock resistance. E-glass insulation typically provides excellent mechanical strength and is cost-effective but delivers lower thermal stability under extreme heat conditions, leading to faster degradation. For applications requiring enhanced thermal performance and durability under fluctuating temperatures, borosilicate glass fiber insulation is generally preferred due to its enhanced thermal shock resistance and lower thermal expansion coefficient.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Borosilicate glass exhibits higher mechanical strength and superior thermal stability compared to E-glass, making it more resistant to deformation and mechanical stress in glass fiber insulation applications. E-glass offers good tensile strength and is widely used due to its cost-effectiveness but has lower resistance to chemical corrosion and thermal degradation than borosilicate glass. The enhanced durability of borosilicate glass fibers ensures longer service life and better performance in harsh environments where insulation reliability is critical.
Moisture and Corrosion Resistance
Borosilicate glass exhibits superior moisture resistance and corrosion resistance compared to E-glass, making it highly effective for glass fiber insulation in humid or chemically aggressive environments. Its low alkali content and high silica percentage enhance durability by minimizing water absorption and chemical degradation. E-glass, while widely used for insulation, is more prone to moisture-induced weakening and corrosion due to its higher alkali content and lower chemical stability.
Cost Analysis: Borosilicate vs E-glass
Borosilicate glass fibers generally have a higher production cost due to their complex manufacturing process and superior thermal resistance properties, making them more expensive than E-glass fibers. E-glass, widely used in insulation applications, offers a lower cost alternative with adequate mechanical strength and electrical insulation, driving its preference in cost-sensitive projects. The cost difference significantly impacts large-scale insulation deployment, where E-glass provides a more economical option without compromising essential performance requirements.
Typical Applications and Use Cases
Borosilicate glass is preferred in high-temperature and chemical-resistant insulation applications such as laboratory equipment, aerospace components, and industrial furnaces due to its low thermal expansion and excellent durability. E-glass, composed primarily of alumino-borosilicate, is widely used in general-purpose insulation for electrical, marine, and automotive industries because of its superior electrical insulation properties and cost-effectiveness. The distinct performance features make borosilicate ideal for specialized, extreme conditions, while E-glass fits well in mass-produced, versatile insulation solutions.
Choosing the Right Glass for Insulation
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and chemical durability, making it ideal for high-temperature glass fiber insulation applications. E-glass, composed primarily of alumino-borosilicate, provides excellent electrical insulation, mechanical strength, and cost-effectiveness, widely used in standard insulation products. Selecting the right glass depends on operating temperature, environmental exposure, and budget constraints, with borosilicate preferred for extreme conditions and E-glass suitable for general-purpose insulation.
Infographic: Borosilicate glass vs E-glass for Glass fiber insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com