Foam glass offers excellent thermal insulation and lightweight properties, making it suitable for energy-efficient security installations, while bulletproof glass provides high impact resistance and ballistic protection essential for secure environments. Choosing between foam glass and bulletproof glass depends on the required balance between insulation performance and physical security needs.
Table of Comparison
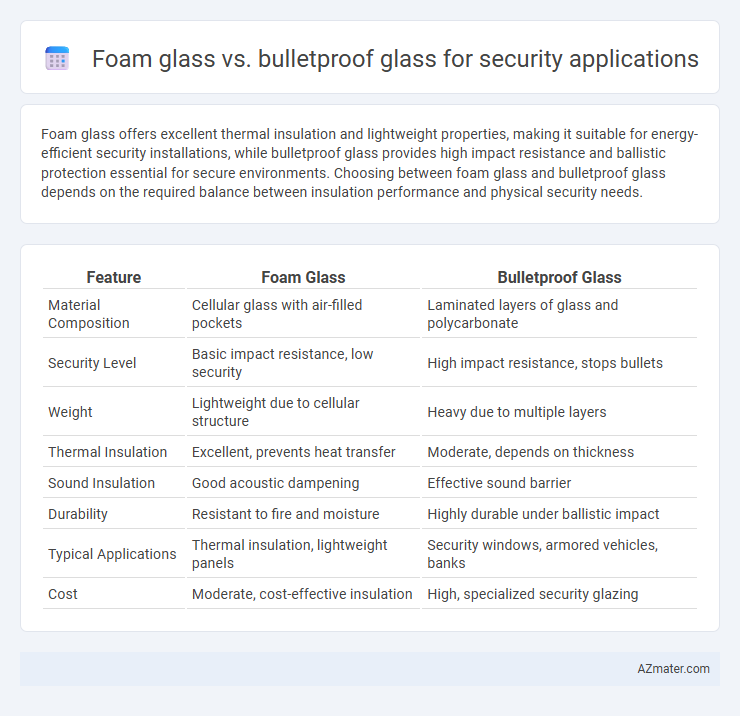
| Feature | Foam Glass | Bulletproof Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Cellular glass with air-filled pockets | Laminated layers of glass and polycarbonate |
| Security Level | Basic impact resistance, low security | High impact resistance, stops bullets |
| Weight | Lightweight due to cellular structure | Heavy due to multiple layers |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent, prevents heat transfer | Moderate, depends on thickness |
| Sound Insulation | Good acoustic dampening | Effective sound barrier |
| Durability | Resistant to fire and moisture | Highly durable under ballistic impact |
| Typical Applications | Thermal insulation, lightweight panels | Security windows, armored vehicles, banks |
| Cost | Moderate, cost-effective insulation | High, specialized security glazing |
Introduction to Security Glass Materials
Foam glass and bulletproof glass serve distinct roles in security applications, with foam glass offering lightweight thermal insulation and impact resistance due to its cellular structure, while bulletproof glass provides high-level protection through layered polycarbonate and laminated glass designed to absorb and disperse ballistic energy. Security glass materials are selected based on specific performance criteria such as impact resistance, weight, durability, and transparency. Advances in manufacturing techniques have enhanced the properties of both foam and bulletproof glass, enabling their use in environments demanding safety, energy efficiency, and structural strength.
Understanding Foam Glass: Composition and Properties
Foam glass is a lightweight, porous material composed of crushed glass fused at high temperatures to create a cellular structure, offering excellent thermal insulation and fire resistance. Unlike bulletproof glass, foam glass lacks impact resistance but provides superior energy absorption and soundproofing qualities due to its closed-cell architecture. Its chemical inertness and durability make foam glass a strategic choice for security applications requiring insulation and structural integrity rather than ballistic protection.
What is Bulletproof Glass? Structure and Features
Bulletproof glass is a composite material designed to resist penetration from bullets and other projectiles, typically composed of multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate or other plastics. Its structure includes alternating layers that absorb and disperse kinetic energy, preventing shattering and penetration by firearms. Key features include high impact resistance, transparency for visibility, and durability against repeated impacts, making it ideal for security applications in banks, military vehicles, and protective enclosures.
Comparative Strength: Foam Glass vs Bulletproof Glass
Foam glass offers excellent thermal insulation and lightweight properties but lacks the tensile and impact strength required for security applications. Bulletproof glass, typically made from layered polycarbonate and laminated glass, provides superior resistance against high-velocity projectiles and forced entry attempts. When comparing the materials for security, bulletproof glass consistently outperforms foam glass in terms of structural integrity and protection against ballistic threats.
Impact Resistance and Ballistic Protection
Foam glass offers excellent insulation and lightweight properties but has low impact resistance and is unsuitable for ballistic protection. Bulletproof glass, composed of multiple layers of laminated glass and polycarbonate, provides superior impact resistance and effective ballistic protection against various firearm calibers. For security applications requiring defense against gunfire and high-impact threats, bulletproof glass is the optimal choice due to its engineered multi-layer construction and certified ballistic ratings.
Insulation and Fire Resistance Capabilities
Foam glass offers superior thermal insulation and exceptional fire resistance due to its closed-cell structure and non-combustible composition, making it ideal for applications requiring energy efficiency and fire safety. Bulletproof glass, primarily designed for impact resistance, lacks significant insulating properties and has lower fire resistance compared to foam glass. For comprehensive security applications demanding both insulation and fire protection, foam glass provides enhanced performance.
Weight and Installation Considerations
Foam glass is significantly lighter than bulletproof glass, making it easier to handle and install in security applications where weight constraints are critical. Bulletproof glass, being denser and thicker, requires more robust framing and support structures, increasing both installation complexity and costs. The lightweight nature of foam glass allows for faster installation and reduced labor, while bulletproof glass demands precise fitting to maintain its ballistic resistance properties.
Cost Analysis: Foam Glass vs Bulletproof Glass
Foam glass offers a cost-effective solution for insulation and structural applications with prices significantly lower than bulletproof glass, which involves premium manufacturing processes due to its multi-layered polycarbonate and tempered glass composition. Bulletproof glass commands higher upfront investments, often ranging from $50 to $150 per square foot, reflecting its advanced ballistic protection capabilities essential for high-security environments. Foam glass's affordability and lightweight properties make it suitable for budget-sensitive projects, while bulletproof glass justifies its cost through superior impact resistance and enhanced security performance.
Typical Security Applications and Use Cases
Foam glass is predominantly used in security applications requiring lightweight, insulating, and fire-resistant materials, such as in building facades, secure storage facilities, and blast-resistant walls. Bulletproof glass, composed of laminated layers of glass and polycarbonate, is essential for high-threat environments like armored vehicles, banks, and government buildings, providing ballistic protection against firearms. Both materials serve distinct security roles: foam glass enhances structural integrity and thermal protection, while bulletproof glass ensures life safety by preventing penetration from bullets and shrapnel.
Choosing the Right Glass Material for Enhanced Security
Foam glass offers lightweight insulation and impact resistance, making it suitable for specific security applications requiring thermal efficiency and reduced structural load. Bulletproof glass provides superior ballistic protection through multi-layered materials engineered to absorb and disperse projectile energy, essential for high-security environments. Selecting the right glass material depends on the desired balance between impact resistance, weight, thermal insulation, and threat level to optimize security performance.
Infographic: Foam glass vs Bulletproof glass for Security application
 azmater.com
azmater.com