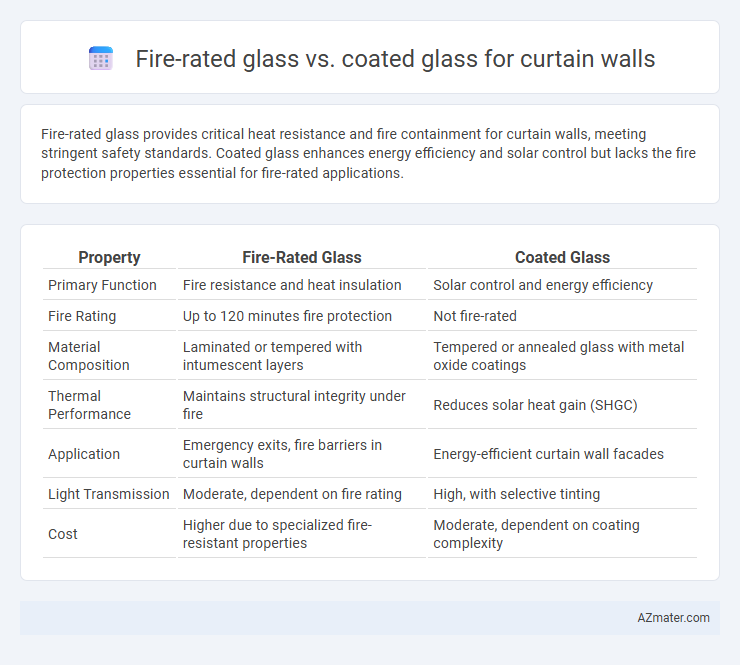
Fire-rated glass provides critical heat resistance and fire containment for curtain walls, meeting stringent safety standards. Coated glass enhances energy efficiency and solar control but lacks the fire protection properties essential for fire-rated applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fire-Rated Glass | Coated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Fire resistance and heat insulation | Solar control and energy efficiency |
| Fire Rating | Up to 120 minutes fire protection | Not fire-rated |
| Material Composition | Laminated or tempered with intumescent layers | Tempered or annealed glass with metal oxide coatings |
| Thermal Performance | Maintains structural integrity under fire | Reduces solar heat gain (SHGC) |
| Application | Emergency exits, fire barriers in curtain walls | Energy-efficient curtain wall facades |
| Light Transmission | Moderate, dependent on fire rating | High, with selective tinting |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized fire-resistant properties | Moderate, dependent on coating complexity |
Introduction to Curtain Wall Glazing Systems
Curtain wall glazing systems utilize both fire-rated glass and coated glass to enhance building safety and energy efficiency. Fire-rated glass provides critical fire resistance, preventing the spread of flames and smoke during emergencies, while coated glass improves thermal performance by reflecting solar radiation and reducing heat gain. Selecting the appropriate glazing type ensures compliance with building codes and optimizes the curtain wall's overall functionality.
Fire-Rated Glass: Key Features and Benefits
Fire-rated glass for curtain walls offers superior heat resistance and fire containment, maintaining structural integrity during fire emergencies up to specified time ratings such as 60, 90, or 120 minutes. Its key features include intumescent interlayers or ceramic glass technology that block flames and reduce heat transmission, ensuring occupant safety and minimizing fire spread. Benefits of using fire-rated glass in curtain walls include compliance with stringent building codes, enhanced fire protection without compromising natural light, and maintaining aesthetic transparency.
Coated Glass: Types and Primary Functions
Coated glass used in curtain walls offers various types such as low-emissivity (low-E), reflective, and anti-reflective coatings, each designed to enhance energy efficiency and occupant comfort. Low-E coatings minimize heat transfer by reflecting infrared radiation, improving thermal insulation and reducing HVAC loads, while reflective coatings reduce solar heat gain and glare. These functional coatings contribute to building sustainability by optimizing natural light penetration, controlling solar heat, and maintaining indoor temperature stability without compromising aesthetic appeal.
Safety Standards and Building Code Compliance
Fire-rated glass for curtain walls meets stringent safety standards such as ASTM E119 and UL 10B, providing critical fire resistance by preventing flame and heat transfer for specified durations. Coated glass, while offering enhanced thermal performance and solar control, typically does not satisfy fire-resistance requirements mandated by building codes like the International Building Code (IBC). Selecting fire-rated glass ensures compliance with fire safety regulations, whereas coated glass is primarily optimized for energy efficiency and may require additional fire protection measures to meet code standards.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Fire-rated glass for curtain walls provides superior thermal resistance by withstanding temperatures above 1,000degF (538degC) for extended periods, effectively preventing heat transfer and maintaining compartmentalization during fire events. Coated glass enhances thermal performance primarily through low-emissivity (low-E) coatings that reduce solar heat gain and improve energy efficiency but offer limited fire resistance compared to fire-rated glass. Selecting fire-rated glass ensures compliance with stringent fire safety standards, while coated glass is optimized for energy conservation and thermal comfort in building envelopes.
Fire Protection Capabilities: Glass Types Compared
Fire-rated glass in curtain walls is engineered to withstand extreme temperatures, preventing fire and smoke from spreading while maintaining structural integrity for specified timeframes such as 60 or 90 minutes. Coated glass offers improved heat resistance and solar control but does not provide certified fire resistance or containment during fire events. For comprehensive fire protection, fire-rated glass meets stringent building codes and safety standards essential in high-risk or commercial constructions.
Acoustic and UV Control Considerations
Fire-rated glass for curtain walls offers superior fire resistance and effective acoustic insulation, reducing sound transmission in high-risk environments, while coated glass primarily enhances UV control by blocking harmful ultraviolet rays and reducing solar heat gain. Acoustic performance in fire-rated glass is often achieved through laminated layers designed to absorb sound, whereas coated glass relies on specialized surface treatments that do not significantly affect sound insulation properties. For projects prioritizing fire safety and soundproofing, fire-rated glass is ideal, but for optimal UV protection and energy efficiency, coated glass provides targeted control without compromising natural light transmission.
Aesthetic and Design Flexibility
Fire-rated glass for curtain walls offers enhanced safety features with limited design options due to its thicker profiles and specialized coatings, often resulting in a slightly tinted or opaque appearance that can impact transparency. Coated glass provides greater aesthetic and design flexibility, featuring a variety of reflective, low-emissivity, and color-tinted finishes that enhance energy efficiency while preserving clear sightlines and sleek architectural appeal. Choosing between fire-rated and coated glass involves balancing stringent fire safety compliance against the desire for customized visual effects and facade transparency in curtain wall systems.
Cost Implications and Long-Term Value
Fire-rated glass for curtain walls typically incurs higher initial costs due to its specialized heat-resistant materials and certification requirements, while coated glass offers a more budget-friendly option focused on energy efficiency and aesthetics. In terms of long-term value, fire-rated glass enhances building safety and compliance with fire codes, potentially reducing insurance premiums and liability risks, whereas coated glass improves energy savings and occupant comfort but may incur replacement costs sooner. Choosing between the two depends on balancing upfront investment with prioritized performance benefits such as fire safety or energy conservation.
Choosing the Right Glass for Your Curtain Wall Project
Selecting fire-rated glass for curtain walls ensures enhanced safety by preventing fire spread and maintaining structural integrity during high temperatures, crucial for buildings with strict fire codes. Coated glass, offering superior energy efficiency and solar control, improves thermal performance and reduces glare, ideal for projects prioritizing sustainability and occupant comfort. Balancing fire safety requirements with energy performance goals is essential for choosing the right glass tailored to specific curtain wall project needs.
Infographic: Fire-rated glass vs Coated glass for Curtain wall
 azmater.com
azmater.com