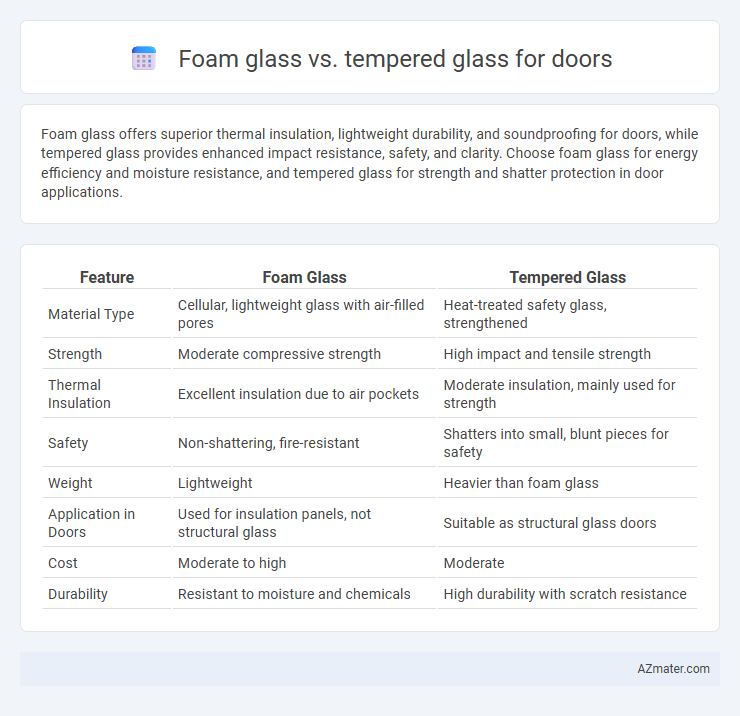
Foam glass offers superior thermal insulation, lightweight durability, and soundproofing for doors, while tempered glass provides enhanced impact resistance, safety, and clarity. Choose foam glass for energy efficiency and moisture resistance, and tempered glass for strength and shatter protection in door applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Foam Glass | Tempered Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Cellular, lightweight glass with air-filled pores | Heat-treated safety glass, strengthened |
| Strength | Moderate compressive strength | High impact and tensile strength |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent insulation due to air pockets | Moderate insulation, mainly used for strength |
| Safety | Non-shattering, fire-resistant | Shatters into small, blunt pieces for safety |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier than foam glass |
| Application in Doors | Used for insulation panels, not structural glass | Suitable as structural glass doors |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Moderate |
| Durability | Resistant to moisture and chemicals | High durability with scratch resistance |
Introduction to Foam Glass and Tempered Glass
Foam glass is a lightweight, porous material made from crushed glass combined with a foaming agent, providing excellent thermal insulation and fire resistance properties, ideal for energy-efficient door applications. Tempered glass, also known as toughened glass, undergoes controlled thermal or chemical treatments to increase its strength and safety, making it highly resistant to impact and thermal stress, commonly used for secure and durable doors. Both materials offer distinct advantages: foam glass excels in insulation and fireproofing, while tempered glass enhances structural integrity and safety.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Foam glass is composed of crushed recycled glass combined with a foaming agent, heated to create a cellular, lightweight structure through a sintering process, offering excellent insulation and moisture resistance. Tempered glass is made from annealed glass that is rapidly cooled in a controlled tempering oven, increasing its strength by introducing compressive stresses on the surface and tensile stresses inside. The manufacturing process of foam glass emphasizes energy-efficient recycling and shaping, while tempered glass relies on thermal treatment to enhance durability and safety for door applications.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Foam glass offers superior thermal insulation and lightweight durability due to its cellular structure, making it highly resistant to moisture and fire, ideal for energy-efficient doors. Tempered glass provides exceptional strength and impact resistance, shattering into small, blunt pieces to enhance safety, but lacks insulation properties compared to foam glass. Key physical properties such as density, thermal conductivity, and mechanical strength distinguish foam glass as an insulating material and tempered glass as a safety-focused option for door applications.
Insulation Performance: Foam Glass vs Tempered Glass
Foam glass offers superior insulation performance compared to tempered glass due to its closed-cell structure, which effectively reduces heat transfer and provides excellent thermal resistance. Tempered glass, while strong and impact-resistant, has limited insulating properties and allows more heat flow through its solid, transparent surface. For door applications requiring high thermal efficiency and energy savings, foam glass is the preferred material, as it enhances temperature control and reduces energy costs.
Strength and Durability Differences
Foam glass offers exceptional thermal insulation and is highly resistant to moisture and corrosion, making it durable in harsh environments but lacks the mechanical strength of tempered glass. Tempered glass, processed through controlled thermal or chemical treatments, provides superior impact resistance and can withstand significant force without shattering, ideal for door applications requiring enhanced safety and strength. While foam glass prioritizes insulation and longevity in damp conditions, tempered glass excels in structural integrity and durability against physical stress.
Safety Features and Impact Resistance
Foam glass offers excellent insulation and fire resistance but has lower impact resistance compared to tempered glass, which is specifically designed to withstand high impact and shatter into small, less harmful pieces for enhanced safety. Tempered glass meets stringent safety standards and is commonly used in doors where impact strength and injury prevention are critical. Foam glass doors prioritize thermal safety, while tempered glass doors provide superior protection against breakage and physical impact.
Aesthetic and Design Versatility
Foam glass doors offer a unique matte finish and lightweight structure, enhancing modern minimalist and eco-friendly design aesthetics. Tempered glass provides a sleek, glossy appearance with enhanced strength, allowing for intricate patterns, frosted designs, and vibrant color applications that elevate contemporary and luxury spaces. Both materials enable diverse customization, but tempered glass excels in allowing varied textures and transparency levels, expanding creative possibilities for door designs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Foam glass offers superior environmental benefits compared to tempered glass due to its composition from recycled glass and excellent insulation properties that reduce energy consumption in buildings. Its lightweight nature minimizes transportation emissions, while being fully recyclable enhances sustainability throughout its lifecycle. Tempered glass, though durable and safe, requires higher energy for production and lacks the insulating advantages of foam glass, making it less eco-friendly overall.
Cost Considerations for Door Applications
Foam glass generally costs more upfront than tempered glass due to its specialized manufacturing process and insulating properties, making it ideal for energy-efficient door applications. Tempered glass offers a more cost-effective choice for doors requiring high strength and safety, especially in commercial or high-traffic areas. Budget planning for door installations should weigh foam glass's durability and thermal benefits against tempered glass's affordability and impact resistance.
Choosing the Right Glass Type for Your Door
Foam glass offers excellent insulation, lightweight properties, and soundproofing, making it ideal for energy-efficient door applications. Tempered glass provides superior strength, safety, and shatter resistance, suitable for doors requiring high impact durability and security. Selecting the right glass type depends on prioritizing thermal insulation and weight versus safety and impact resistance for your specific door needs.
Infographic: Foam glass vs Tempered glass for Door
 azmater.com
azmater.com