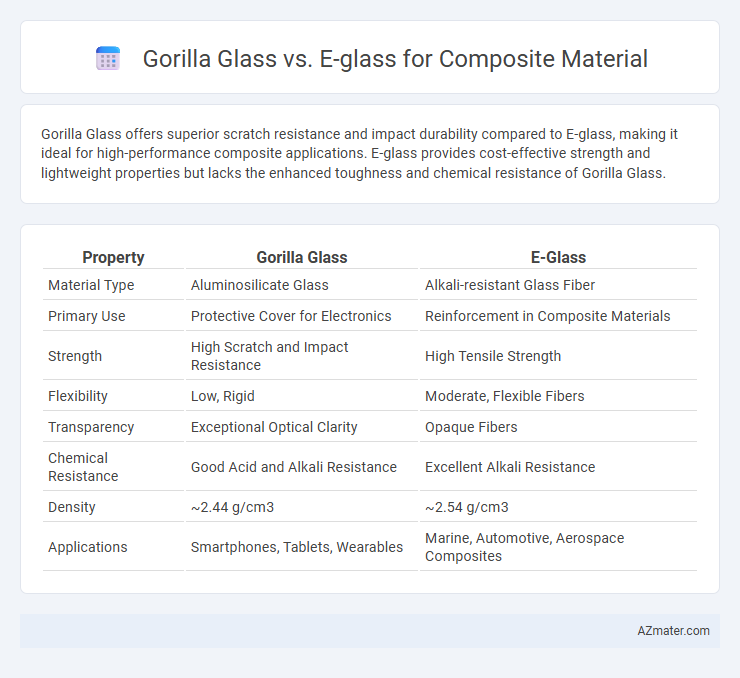
Gorilla Glass offers superior scratch resistance and impact durability compared to E-glass, making it ideal for high-performance composite applications. E-glass provides cost-effective strength and lightweight properties but lacks the enhanced toughness and chemical resistance of Gorilla Glass.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Gorilla Glass | E-Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Aluminosilicate Glass | Alkali-resistant Glass Fiber |
| Primary Use | Protective Cover for Electronics | Reinforcement in Composite Materials |
| Strength | High Scratch and Impact Resistance | High Tensile Strength |
| Flexibility | Low, Rigid | Moderate, Flexible Fibers |
| Transparency | Exceptional Optical Clarity | Opaque Fibers |
| Chemical Resistance | Good Acid and Alkali Resistance | Excellent Alkali Resistance |
| Density | ~2.44 g/cm3 | ~2.54 g/cm3 |
| Applications | Smartphones, Tablets, Wearables | Marine, Automotive, Aerospace Composites |
Introduction to Composite Materials
Composite materials combine two or more distinct substances to create a material with enhanced properties like increased strength, durability, and lightweight characteristics. Gorilla Glass, a chemically strengthened aluminosilicate glass, offers exceptional scratch resistance and toughness, making it ideal for high-performance display applications. E-glass, a standard fiberglass type, provides excellent mechanical strength, electrical insulation, and thermal stability, widely used in structural composites and insulation products.
Overview of Gorilla Glass
Gorilla Glass is an advanced chemically strengthened alkali-aluminosilicate glass known for its exceptional scratch resistance, toughness, and lightweight properties, making it ideal for high-performance composite applications. Engineered through an ion-exchange process, Gorilla Glass achieves a compressive surface layer that enhances durability and impact resistance, outperforming traditional glass variants like E-glass. Its superior optical clarity and flexibility under stress set it apart as a premium material in electronics, automotive, and aerospace composites.
Overview of E-Glass
E-Glass is a type of fiberglass reinforced composite known for its excellent electrical insulation and mechanical strength properties, making it widely used in aerospace, automotive, and marine industries. It offers superior corrosion resistance, high tensile strength, and good thermal stability, which distinguishes it from Gorilla Glass used primarily in consumer electronics. Unlike Gorilla Glass, E-Glass is more versatile in structural applications due to its layered fiber reinforcement and cost-effectiveness in large-scale manufacturing.
Key Mechanical Properties Comparison
Gorilla glass exhibits superior surface hardness and scratch resistance compared to E-glass, making it ideal for applications requiring enhanced durability and impact resistance. E-glass offers higher tensile strength and better flexibility, which benefits composites needing improved structural performance under dynamic loads. Both materials provide distinct advantages in mechanical properties, with Gorilla glass excelling in hardness and E-glass in tensile strength and toughness.
Chemical Resistance and Durability
Gorilla Glass exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to E-glass, effectively withstanding exposure to acids and alkaline environments without significant degradation. Its durability is enhanced by a chemically strengthened surface layer created through ion exchange, resulting in high scratch resistance and impact toughness. E-glass, while cost-effective and widely used in composites, tends to be more vulnerable to chemical attack and has lower resistance to mechanical wear and surface damage.
Weight and Density Analysis
Gorilla Glass exhibits a density of approximately 2.5 g/cm3, making it lighter and more suitable for lightweight composite applications compared to E-glass, which has a density around 2.54 g/cm3. The slightly lower density of Gorilla Glass contributes to improved weight reduction in composite structures, enhancing performance in aerospace, automotive, and consumer electronics. Weight analysis shows Gorilla Glass composites offer better strength-to-weight ratios, critical for high-performance, lightweight material design.
Cost-Effectiveness for Large-Scale Applications
Gorilla Glass offers superior strength and scratch resistance but comes at a higher production cost compared to E-glass, making it less cost-effective for large-scale composite applications. E-glass provides an optimal balance of affordability and mechanical performance, widely favored in industries requiring bulk material usage such as automotive and wind energy sectors. For large-scale projects, E-glass minimizes overall expenses while maintaining adequate durability, making it the preferred choice where budget constraints are critical.
Suitability for Aerospace and Automotive Industries
Gorilla Glass offers superior scratch resistance and lightweight properties, making it highly suitable for automotive applications where durability and weight reduction are critical. E-glass provides excellent impact resistance and cost-effectiveness, favoring its use in aerospace components that require strong structural integrity under variable stress conditions. Both materials serve key roles in composites, with Gorilla Glass focused on surface protection and E-glass enhancing mechanical strength in aerospace and automotive industries.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Gorilla Glass, made from alkali-aluminosilicate, offers limited recyclability due to its chemically strengthened structure, resulting in higher environmental impact during disposal compared to traditional composites. E-glass, a common fiberglass variant composed of alumina and silica, allows more straightforward recycling and reuse in composite applications, reducing landfill waste and promoting sustainable material cycles. The production of E-glass typically generates lower embodied energy and fewer greenhouse gas emissions than the specialized manufacturing process for Gorilla Glass, enhancing its eco-friendly profile.
Final Recommendations and Use-Case Scenarios
Gorilla Glass offers superior scratch resistance and high strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for applications requiring durable, lightweight protective surfaces such as smartphone screens and aerospace components. E-glass, known for excellent electrical insulation and cost-effectiveness, suits structural composites in wind turbine blades, automotive parts, and marine applications where impact resistance and affordability are prioritized. Selecting Gorilla Glass enhances performance in high-wear environments, while E-glass remains the preferred choice for large-scale, budget-sensitive composite manufacturing with moderate strength requirements.
Infographic: Gorilla glass vs E-glass for Composite material
 azmater.com
azmater.com